| Itbayat | |
|---|---|
| Ibatan | |
| Itbayaten | |
| Native to | Philippines |
| Region | Itbayat Island |
| Ethnicity | Ivatan people Yami people |
Native speakers | (3,500 cited 1996 census)[1] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | itba1237 |
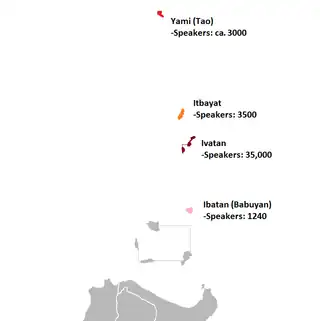 Itbayat and the other Batanic languages | |
The Itbayat language or Itbayaten (also known generically as Ibatan) is an Austronesian language, in the Batanic group, spoken on Itbayat Island in the Batanes Islands, Philippines.
Phonology
Vowels
/a, ɜ, i, o/
Vowels are contrasted between long and short vowels, for example as seen in the words tokod ('support') and tookod ('a kind of yam').[2]
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | |||
| Plosive/ Affricate |
voiceless | p | t | t͡ʃ | k | ʔ | |
| voiced | b | d | d͡ʒ | ɡ | |||
| Fricative | voiceless | (f) | s | h | |||
| voiced | v | ɣ | ʁ | ||||
| Approximant | l | j | w | ||||
| Trill | r | ||||||
- /f/ is only used in loanwords but tends to become /p/.[2]
Grammar
Pronouns
The following set of pronouns is found in the Itbayat language.[2]
| Nominative | Genitive | Locative | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| free | bound | free | bound | ||||
| 1st person |
singular | yaken | ako | ñaken | ko | jaken | |
| dual | – | ta | – | – | – | ||
| plural | inclusive | yaten | ta | ñaten | ta | jaten | |
| exclusive | yamen | kami | ñamen | namen | jamen | ||
| 2nd person |
singular | imo | ka | nimo | mo | dimo | |
| plural | imiyo | kamo | nimiyo | miyo | dimiyo | ||
| 3rd person |
singular | – | – | niya/ña | na | dira | |
| plural | sira | sira | nira | da | dira | ||
References
- ↑ Ivatan at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- 1 2 3 Yamada, Yukihiro (2002). Itbayat–English Dictionary (PDF). ELPR Publications Series A3-006. hdl:10108/75457.
Further reading
- Yamada, Yukihiro (2014). A Grammar of the Itbayat Language of the Philippines. Himeji, Japan.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
| Batanic (Bashiic) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Luzon |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Central Luzon |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Northern Mindoro | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greater Central Philippine |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalamian | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sangiric | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minahasan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other branches |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reconstructed | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Official languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regional languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indigenous languages (by region) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immigrant languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sign languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical languages | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.