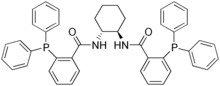 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1R,2R)-(+)-1,2-diaminocyclohexane-N,N'-bis(2-diphenylphosphinobenzoyl) | |
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N′-[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diyl]bis[2-(diphenylphosphanyl)benzamide] | |
| Other names
Trost's ligand | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C44H40N2O2P2 | |
| Molar mass | 690.75 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 136 to 142 °C (277 to 288 °F; 409 to 415 K) |
| Insoluble; soluble in organic solvents (e.g. acetonitrile, dichloromethane) 1,4-dioxane, methanol, tetrahydrofuran, toluene | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
The Trost ligand is a diphosphine used in the palladium-catalyzed Trost asymmetric allylic alkylation. Other C2-symmetric ligands derived from trans-1,2-diaminocyclohexane (DACH) have been developed, such as the (R,R)-DACH-naphthyl ligand derived from 2-diphenylphosphino-1-naphthalenecarboxylic acid. Related bidentate phosphine-containing ligands derived from other chiral diamines and 2-diphenylphosphinobenzoic acid have also been developed for applications in asymmetric synthesis.

(R,R)-DACH-naphthyl Trost ligand, (1R,2R)-(+)-1,2-diaminocyclohexane-N,N′-bis(2-diphenylphosphino-1-naphthoyl)
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.