| Regular hexagram | |
|---|---|
.svg.png.webp) A regular hexagram | |
| Type | Regular polygonal figure |
| Edges and vertices | 6 |
| Schläfli symbol | a{6}, {6/2}, 2{3} or {{3}} |
| Coxeter–Dynkin diagrams | |
| Symmetry group | Dihedral (D6) |
| Internal angle (degrees) | 60° |
| Properties | star, compound, cyclic, equilateral, isogonal, isotoxal |
| Dual polygon | self |
| Star polygons |
|---|
|
|

A hexagram (Greek) or sexagram (Latin) is a six-pointed geometric star figure with the Schläfli symbol {6/2}, 2{3}, or {{3}}. Since there are no true regular continuous hexagrams, the term is instead used to refer to a compound figure of two equilateral triangles. The intersection is a regular hexagon.
The hexagram is part of an infinite series of shapes which are compounds of two n-dimensional simplices. In three dimensions, the analogous compound is the stellated octahedron, and in four dimensions the compound of two 5-cells is obtained.
It has been historically used in various religious and cultural contexts and as decorative motifs. The symbol was used as a decorative motif in medieval Christian churches and Jewish synagogues.[1] The hexagram is thought to have originated in Buddhism and was also used by Hindus. It was used by Muslims as a mystic symbol in the medieval period, known as the Seal of Solomon, depicted as either a hexagram or pentagram. [2][3]
Group theory
In mathematics, the root system for the simple Lie group G2 is in the form of a hexagram, with six long roots and six short roots.

Construction by compass and a straight edge
A six-pointed star, like a regular hexagon, can be created using a compass and a straight edge:
- Make a circle of any size with the compass.
- Without changing the radius of the compass, set its pivot on the circle's circumference, and find one of the two points where a new circle would intersect the first circle.
- With the pivot on the last point found, similarly find a third point on the circumference, and repeat until six such points have been marked.
- With a straight edge, join alternate points on the circumference to form two overlapping equilateral triangles.
Construction by linear algebra
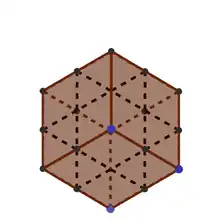
A regular hexagram can be constructed by orthographically projecting any cube onto a plane through three vertices that are all adjacent to the same vertex. The twelve midpoints to edges of the cube form a hexagram. For example, consider the projection of the unit cube with vertices at the eight possible binary vectors in three dimensions onto the plane . The midpoints are , and all points resulting from these by applying a permutation to their entries. These 12 points project to a hexagram: six vertices around the outer hexagon and six on the inner.
Origins and shape
As a derivative of two overlapping triangles, the hexagram may have developed from different peoples with no direct correlation to one another.
The mandala symbol called yantra, found on ancient South Indian Hindu temples, is a geometric toolset that incorporates hexagrams into its framework. It symbolizes the nara-narayana, or perfect meditative state of balance achieved between Man and God, and if maintained, results in "moksha," or "nirvana" (release from the bounds of the earthly world and its material trappings).
Some researchers have theorized that the hexagram represents the astrological chart at the time of David's birth or anointment as king. The hexagram is also known as the "King's Star" in astrological circles.
In antique papyri, pentagrams, together with stars and other signs, are frequently found on amulets bearing the Jewish names of God, and used to guard against fever and other diseases. Curiously the hexagram is not found among these signs. In the Greek Magical Papyri (Wessely, l.c. pp. 31, 112) at Paris and London there are 22 signs side by side, and a circle with twelve signs, but neither a pentagram nor a hexagram.
Religious usage
Indian religions
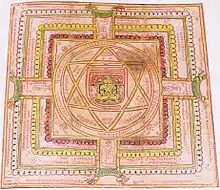
Six-pointed stars have also been found in cosmological diagrams in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. The reasons behind this symbol's common appearance in Indic religions and the West are unknown. One possibility is that they have a common origin. The other possibility is that artists and religious people from several cultures independently created the hexagram shape, which is a relatively simple geometric design.
Within Indic lore, the shape is generally understood to consist of two triangles—one pointed up and the other down—locked in harmonious embrace. The two components are called "Om" and the "Hrim" in Sanskrit, and symbolize man's position between earth and sky. The downward triangle symbolizes Shakti, the sacred embodiment of femininity, and the upward triangle symbolizes Shiva, or Agni Tattva, representing the focused aspects of masculinity. The mystical union of the two triangles represents Creation, occurring through the divine union of male and female. The two locked triangles are also known as 'Shanmukha'—the six-faced, representing the six faces of Shiva & Shakti's progeny Kartikeya. This symbol is also a part of several yantras and has deep significance in Hindu ritual worship and history.

In Buddhism, some old versions of the Bardo Thodol, also known as The "Tibetan Book of the Dead", contain a hexagram with a swastika inside. It was made up by the publishers for this particular publication. In Tibetan, it is called the "origin of phenomenon" (chos-kyi 'byung-gnas). It is especially connected with Vajrayogini, and forms the center part of her mandala. In reality, it is in three dimensions, not two, although it may be portrayed either way.
The Shatkona is a symbol used in Hindu yantra that represents the union of both the male and feminine form. More specifically it is supposed to represent Purusha (the supreme being), and Prakriti (mother nature, or causal matter). Often this is represented as Shiva - Shakti.[4]
Anahata or heart chakra is the fourth primary chakra, according to Hindu Yogic, Shakta and Buddhist Tantric traditions. In Sanskrit, anahata means "unhurt, unstruck, and unbeaten". Anahata Nad refers to the Vedic concept of unstruck sound (the sound of the celestial realm). Anahata is associated with balance, calmness, and serenity.
Judaism

The Magen David is a generally recognized symbol of Judaism and Jewish identity and is also known colloquially as the Jewish Star or "Star of David." Its usage as a sign of Jewish identity began in the Middle Ages, though its religious usage began earlier, with the current earliest archeological evidence being a stone bearing the shield from the arch of a 3–4th century synagogue in the Galilee.[5]
Christianity
The first and the most important Armenian Cathedral of Etchmiadzin (303 AD, built by the founder of Christianity in Armenia) is decorated with many types of ornamented hexagrams and so is the tomb of an Armenian prince of the Hasan-Jalalyan dynasty of Khachen (1214 AD) in the Gandzasar Church of Artsakh.
The hexagram may be found in some Churches and stained-glass windows. In Christianity, it is sometimes called the star of creation. A very early example, noted by Nikolaus Pevsner, can be found in Winchester Cathedral, England in one of the canopies of the choir stalls, circa 1308.[6]
Latter-day Saints (Mormons)

The Star of David is also used less prominently by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, in the temples and in architecture. It symbolizes God reaching down to man and man reaching up to God, the union of Heaven and earth. It may also symbolize the Tribes of Israel and friendship and their affinity towards the Jewish people. Additionally, it is sometimes used to symbolize the quorum of the twelve apostles, as in Revelation 12, wherein the Church of God is symbolized by a woman wearing a crown of twelve stars. It is also sometimes used to symbolize the Big Dipper, which points to the North Star, a symbol of Jesus Christ.
Islam
The symbol is known in Arabic as Khātem Sulaymān (Seal of Solomon; خاتم سليمان) or Najmat Dāwūd (Star of David; نجمة داوود). The "Seal of Solomon" may also be represented by a five-pointed star or pentagram.
In the Qur'an, it is written that David and King Solomon (Arabic, Suliman or Sulayman) were prophets and kings, and are figures revered by Muslims. The Medieval pre-Ottoman Hanafi Anatolian beyliks of the Karamanids and Jandarids used the star on their flag.[7] The symbol also used on Hayreddin Barbarossa flag. Today the six-pointed star can be found in mosques and on other Arabic and Islamic artifacts.
 Coin minted in the Emirate of Sicily during the reign of Al-Mustansir Billah (11th century CE)
Coin minted in the Emirate of Sicily during the reign of Al-Mustansir Billah (11th century CE) 1204 coin minted in Aleppo by Az-Zahir Ghazi
1204 coin minted in Aleppo by Az-Zahir Ghazi Hexagram at Humayun's Tomb, Delhi, India (late 16th century)
Hexagram at Humayun's Tomb, Delhi, India (late 16th century).jpg.webp) Hexagram on obverse of Moroccan 4 Falus coin (1873)
Hexagram on obverse of Moroccan 4 Falus coin (1873) Hexagram on the Minaret of Arasta Mosque, Prizren, Kosovo
Hexagram on the Minaret of Arasta Mosque, Prizren, Kosovo Morocco Fez Embroidery Horse Cover
Morocco Fez Embroidery Horse Cover Hexagram on the flag of Hayreddin Barbarossa
Hexagram on the flag of Hayreddin Barbarossa Hexagram on the flag of Karamanid beylik
Hexagram on the flag of Karamanid beylik The Gates from the tomb of Mahmud of Ghazni, taken to the Somnath temple
The Gates from the tomb of Mahmud of Ghazni, taken to the Somnath temple A Cirebonese cotton banner with a Chinese influenced lion with Arabic calligraphy with hexagrams; (dated to the late 18th or the 19th century)
A Cirebonese cotton banner with a Chinese influenced lion with Arabic calligraphy with hexagrams; (dated to the late 18th or the 19th century)
Usage in heraldry
In heraldry and vexillology, a hexagram is a fairly common charge employed, though it is rarely called by this name. In Germanic regions it is known simply as a "star." In English and French heraldry, however, the hexagram is known as a "mullet of six points," where mullet is a French term for a spur rowel which is shown with five pointed arms by default unless otherwise specified. In Albanian heraldry and vexillology, hexagram has been used since classical antiquity and it is commonly referred to as sixagram. The coat of arms of the House of Kastrioti depicts the hexagram on a pile argent over the double headed eagle.
Usage in Theosophy
The Star of David is used in the seal and the emblem of the Theosophical Society (founded in 1875). Although it is more pronounced, it is used along with other religious symbols. These include the Swastika, the Ankh, the Aum, and the Ouroboros. The star of David is also known as the Seal of Solomon, which was its original name, being in regular use until around 50 years ago.
Usage in occultism
The hexagram, like the pentagram, was and is used in practices of the occult and ceremonial magic and is attributed to the 7 "old" planets outlined in astrology.
The six-pointed star is commonly used both as a talisman[8] and for conjuring spirits and spiritual forces in diverse forms of occult magic. In the book The History and Practice of Magic, Vol. 2, the six-pointed star is called the talisman of Saturn and it is also referred to as the Seal of Solomon.[9] Details are given in this book on how to make these symbols and the materials to use.

Traditionally, the Hexagram can be seen as the combination of the four elements. Fire is symbolized as an upwards pointing triangle, while Air (its elemental opposite) is also an upwards pointing triangle, but with a horizontal line through its center. Water is symbolized as a downwards pointing triangle, while Earth (its elemental opposite) is also a downwards pointing triangle, but with a horizontal line through its center. When combined swith the symbols of fire and water, a hexagram (six-pointed star) is created. The same follows when combining the symbols of air and earth. Both hexagrams combined are called a double-hexagram. Thus, a combination of the elements is created.[10]
In Rosicrucian and Hermetic Magic, the seven Traditional planets correspond with the angles and the center of the Hexagram as follows, in the same patterns as they appear on the Sephiroth and on the Tree of Life. Saturn, although formally attributed to the Sephira of Binah, within this frame work nonetheless occupies the position of Daath.[11]
In alchemy, the two triangles represent the reconciliation of the opposites of fire and water.[12]
The hexagram is used as a sign for quintessence, the fifth element.
Usage in Freemasonry
"The interlacing triangles or deltas symbolize the union of the two principles or forces, the active and passive, male and female, pervading the universe ... The two triangles, one white and the other black, interlacing, typify the mingling of apparent opposites in nature, darkness and light, error and truth, ignorance and wisdom, evil and good, throughout human life." – Albert G. Mackey: Encyclopedia of Freemasonry
The hexagram is featured within and on the outside of many Masonic temples as a decoration. It may have been found within the structures of King Solomon's temple, from which Freemasons are inspired in their philosophies and studies. Like many other symbols in Freemasonry, the deciphering of the hexagram is non-dogmatic and left to the interpretation of the individual.
Other uses
.svg.png.webp)



Flags
- The flag of Australia had a six pointed star to represent the six federal states from 1901 to 1908.
- The Ulster Banner flag of Northern Ireland, used from 1953 to 1972. The six pointed star, representing the six counties that make up Northern Ireland. The star of the Ulster Banner is not the compound of two equilateral triangles. The intersection is not a regular hexagon.
- A flag used by rebels during the Whiskey Insurrection in South-Western Pennsylvania, 1794.
- A hexagram appears on the Dardania Flag, proposed for Kosovo by the Democratic League of Kosovo.
- The flag of Nigeria depicted a green hexagram surrounding a crown from with the white word "Nigeria" under it on a red disc from 1914 to 1960.
- The flag of Israel has a blue hexagram in the middle.
Other symbolic uses
- A six-point interlocking triangles has been used for thousands of years as an indication a sword was made, and "proved", in the Damascus area of the Middle East. Still today, it is a required "proved" mark on all official UK and United States military swords though the blades themselves no longer come from the Middle East.
- In southern Germany the hexagram can be found as part of tavern anchors. It is symbol for the tapping of beer and sign of the brewer's guild. In German this is called "Bierstern" (beer star) or "Brauerstern" (brewer's star).
- A six-point star is used as an identifying mark of the Folk Nation alliance of US street gangs.
- The Indian sage and seer Sri Aurobindo used it—e.g. on the cover of his books—as a symbol of the aspiration of humanity calling to the Divine to descend into life (the triangle with the point at the top), and the descent of the Divine into the Earth's atmosphere and all individuals in response to that calling (the triangle with the point at the bottom). (This was explained by the Mother, his spiritual partner in Her 14-volume Agenda and elsewhere by Sri Aurobindo in his writings.)
Man-made and natural occurrences
- The main runways and taxiways of Heathrow Airport were arranged roughly in the shape of a hexagram.[13]
- A hexagram in a circle is incorporated prominently in the supports of Worthing railway station's platform 2 canopy (UK).
- An extremely large, free-standing wood hexagram stands in the central park of the Municipality of El Tejar, Guatemala. Additionally, every year at Christmastime the residents of El Tejar erect a giant fake Christmas tree in front of their municipal building, with a hexagram sitting at its peak.
Unicode
- In Unicode, the "Star of David" symbol ✡ is encoded in U+2721.
Other hexagrams
The figure {6/3} can be shown as a compound of three digons.
Other hexagrams can be constructed as a continuous path.
| Regular compounds | D2 symmetry unicursal |
D3 symmetry isogonal |
D3 symmetry isotoxal | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.svg.png.webp) {6/2}=2{3} |
.svg.png.webp) {6/3}=3{2} |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
See also
Footnotes
- ↑ Scholem 1949, p. 244:"It is not to be found at all in medieval synagogues or on medieval ceremonial objects, although it has been found in quite a number of medieval Christian churches again, not as a Christian symbol but only as a decorative motif. The appearance of the symbol in Christian churches long before its appearance in our synagogues should warn the overzealous interpreters. "
- ↑ Scholem 1949, p. 246:"In the beginning these designs had no special names or terms, and it is only in the Middle Ages that definite names began to be given to some of those most widely used. There is very little doubt that terms like these first became popular among the Muslims, who showed a tremendous interest in all the occult sciences, arranging and ordering them systematically long before the Practical Cabalists thought of doing so.It is not to be wondered at, therefore, that for a long time both the five-pointed and the six-pointed stars were called by one name, the "Seal of Solomon," and that no distinction was made between them. This name is obviously related to the Jewish legend of Solomon's dominion over the spirits, and of his ring with the Ineffable Name engraved on it. These legends expanded and proliferated in a marked fashion during the Middle Ages, among Jews and Muslims alike, but the name, "Seal of Solomon," apparently originated with the Muslims."
- ↑ Leonora Leet, "The Hexagram and Hebraic Sacred Science" in :The Secret Doctrine of the Kabbalah, 1999, pp. 212-217.
- ↑ sivasakti.com: Introduction to Yantra
- ↑ "King Solomon's Seal", MFA, King Solomon-s Seal
- ↑ Buildings of England: Hampshire and the North (now second edition) ISBN 978 0 300 12084 4, p.604.
- ↑ The Muslim Empires of the Ottomans, Safavids, and Mughals, By Stephen F. Dale, 2009
- ↑ P299 (and throughout) of The Complete Goldendawn by Israel Regardie. ISBN 978-0875426631
- ↑ The History and Practice of Magic (Secaucus, NJ: University Books, published by arrangement with Lyle Stewart, 1979), Vol. II, p. 304
- ↑ P315-316 of The Wicca Bible by Ann-Marie Gallagher. ISBN 978-1-84181-250-2. Same information also found in many other books.
- ↑ P31 of The Ritual Magic Manual: A Complete Course in Practical Magic by David Griffin. ISBN 978-0965840897
- ↑ Allgemein (February 3, 2020). "Hexagram – The mystical symbol of the hexagram". Hermetic Academy. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ↑ bbc.co.uk and see File:Aerial photograph of Heathrow Airport, 1955.jpg
References
- Scholem, Gershom (September 1949). "The Curious History of the Six-Pointed Star: How the "Magen David" Became the Jewish Symbol". Commentary Magazine. Retrieved 2018-07-10.
- Graham, Dr. O.J. The Six-Pointed Star: Its Origin and Usage 4th ed. Toronto: The Free Press 777, 2001. ISBN 0-9689383-0-2
- Grünbaum, B. and G. C. Shephard; Tilings and Patterns, New York: W. H. Freeman & Co., (1987), ISBN 0-7167-1193-1.
- Grünbaum, B.; Polyhedra with Hollow Faces, Proc of NATO-ASI Conference on Polytopes ... etc. (Toronto 1993), ed T. Bisztriczky et al., Kluwer Academic (1994) pp. 43–70.
- Wessely, l.c. pp. 31, 112

