 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
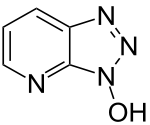
3H-[1,2,3]Triazolo[4,5-b]pyridin-3-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.122.938 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H4N4O | |
| Molar mass | 136.114 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.973 g/mL |
| Melting point | 213-216°C |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
    | |
| Danger | |
| H204, H301, H302, H315, H318, H319, H335 | |
| P210, P240, P250, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P310, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P380, P372, P373, P374, P401, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
1-Hydroxy-7-azabenzotriazole (HOAt) is a triazole used as a peptide coupling reagent.[2] It suppresses racemization that can otherwise occur during the reaction.[3]
HOAt has a melting point between 213 and 216 degrees Celsius.[4] As a liquid, it is transparent and without any color.
References
- ↑ GHS: Sigma Aldrich 445452
- ↑ Carpino, Louis A (1993). "1-Hydroxy-7-azabenzotriazole. An efficient peptide coupling additive". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 115 (10): 4397–4398. doi:10.1021/ja00063a082.
- ↑ Valeur, Eric; Bradley, Mark (2009). "Amide bond formation: beyond the myth of coupling reagents". Chemical Society Reviews. 38 (2): 606–631. doi:10.1039/b701677h. PMID 19169468.
- ↑ "HOAt". Chemical Book. Retrieved January 30, 2019.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.