 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
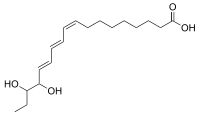
| Preferred IUPAC name
(9Z,11E,13E)-15,16-Dihydroxyoctadeca-9,11,13-trienoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H30O4 | |
| Molar mass | 310.434 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
15,16-Dihydroxy-α-eleostearic acid, or 15,16-Dihydroxy-(9Z,11E,13E)-9,11,13-octadecatrienoic acid, is an organic compound with formula C
18H
30O
4, or H3C-CH2-(-CH(OH)-)2(-CH=CH-)3-(-CH2-)7-(C=O)OH. It can be seen as derived from α-eleostearic acid by the replacement of two hydrogen atoms by two hydroxyl (OH) groups.
The compound is found in the pulp and seeds of bitter melons (the fruits of Momordica charantia). It has been found to induce apoptosis in HL60 leukemia cells in vitro at a concentration of 160 μM, although it is less potent in this regard than the unsubstituted α-eleostearic acid (also found in the seed oil). While α-eleostearic acid has been found to prevent carcinogenesis in rats, this derivative does not seem to have that effect.[1]
The compound can be extracted from the fruit with ethanol, and is soluble in ethyl acetate but not in water or acetone.
See also
References
- ↑ Masuko Kobori, Mayumi Ohnishi-Kameyama, Yukari Akimoto, Chizuko Yukizaki and Mitsuru Yoshida (2008) α-Eleostearic Acid and Its Dihydroxy Derivative Are MajorApoptosis-Inducing Components of Bitter Gourd. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, volume 56, issue 22, pages 10515–10520. doi:10.1021/jf8020877