| Rosy-faced lovebird | |
|---|---|
_2.jpg.webp) | |
| in Erongo, Namibia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Psittaciformes |
| Family: | Psittaculidae |
| Genus: | Agapornis |
| Species: | A. roseicollis |
| Binomial name | |
| Agapornis roseicollis (Vieillot, 1818) | |
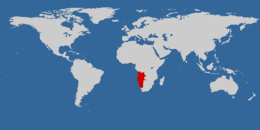 | |
| Native ranges in the Namib Desert and arid areas of Namibia and Angola | |
_composite.jpg.webp)
The rosy-faced lovebird (Agapornis roseicollis), also known as the rosy-collared or peach-faced lovebird, is a species of lovebird native to arid regions in southwestern Africa such as the Namib Desert. Loud and constant chirpers, these birds are very social animals and often congregate in small groups in the wild. They eat throughout the day and take frequent baths. Coloration can vary widely among populations. Plumage is identical in males and females. Lovebirds are renowned for their sleep position in which they sit side-by-side and turn their faces in towards each other. Also, females are well noted to tear raw materials into long strips, "twisty-tie" them onto their backs, and fly substantial distances back to make a nest. These birds are common in the pet industry.
Taxonomy
It was described by the French ornithologist Louis Pierre Vieillot in 1818. It was originally named Psittacus roseicollis but later moved to the genus Agapornis with the other lovebirds.
Two subspecies are recognised:[2]
- Agapornis roseicollis, (Vieillot, 1818)
Description
The rosy-faced lovebird is a fairly small bird, 17–18 cm (6.7–7.1 in) long, with an average wing length of 106 mm (4.2 in) and tail length of 44–52 mm (1.7–2.0 in).[4] Wild birds are mostly green with a blue rump. The face and throat are pink, darkest on the forehead and above the eye. The bill is horn-coloured, the iris is brown, and the legs and feet are grey. The pink of the A. r. roseicollis is lighter than that of the A. r. catumbella.[3] Juvenile birds have a pale pink face and throat, a greenish fore crown and crown, and the beak has a brownish base.[3]
Distribution and habitat
The rosy-faced lovebird inhabits dry, open country in southwest Africa. Its range extends from southwest Angola across most of Namibia to the lower Orange River valley in northwest South Africa. It lives up to 1,600 metres (5,200 ft) above sea level in broad-leaved woodland, semi-desert, and mountainous areas. It is dependent on the presence of water sources and gathers around pools to drink.
Escapes from captivity are frequent in many parts of the world and feral birds dwell in metropolitan Phoenix, Arizona, where they live in a variety of habitats, both urban and rural. Some dwell in cacti and others have been known to frequent feeders in decent-sized flocks.[5] Temperatures in Arizona regularly exceed 40 °C (104 °F) and feral lovebirds have been observed perching in large numbers on air-conditioner vents in order to remain cool.[6] Feral rosy-faced lovebird colonies can also be found on Maui and the Big Island in Hawaii.[7] Although they have been observed in the wild in Puerto Rico, they are probably the result of escaped pets, and no reproduction has been recorded.[8]
Status and conservation
Populations have been reduced in some areas by trapping for the pet trade. However, numbers may have increased in other areas due to human creation of new water sources and the building of artificial structures which provide new nesting sites. Because of this, the species is classed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).[1]
Behaviour in the wild
_flock.jpg.webp)
The rosy-faced lovebird has various harsh, shrieking calls.
Feeding
The diet consists mainly of seeds and berries. When food is plentiful, the birds may gather in flocks containing hundreds of individuals. They can sometimes be pests in agricultural areas, feeding on crops such as millet.
Breeding

Lovebirds are monomorphic, meaning the male and female of the species look alike. The nest is built in a rock crevice or within a compartment of the large communal nests built by sociable weavers. Man-made structures such as the roofs of houses may also be used. A total of 4-6 eggs are laid between February and April. They are dull white and measure 23.5 by 17.3 mm (0.93 by 0.68 in). They are incubated for about 23 days. The young birds fledge after 43 days.[4]
Aviculture
Rosy-faced lovebirds are one of the more common parrots kept in captivity, because of their small size and ease of care and breeding. The birds are kept alone or in pairs, although due to their social requirements, they are best kept in pairs.[9] They can be aggressive, and tend to bond towards an individual, either human or avian, and may not get on well with other people or pets. Two lovebirds may not always get along, and may have to be separated, and lovebirds should not be kept with smaller species of birds. Lovebirds require daily exercise.
- Captive bred birds
-2.JPG.webp) Pair at nestbox
Pair at nestbox A pet chick
A pet chick An adult lutino in nestbox with eggs and chicks
An adult lutino in nestbox with eggs and chicks Pet playing
Pet playing Feral lovebirds eating seeds from a garden feeder in Arizona, USA
Feral lovebirds eating seeds from a garden feeder in Arizona, USA Lovebird playing with toy
Lovebird playing with toy Pair in captivity
Pair in captivity
Mutations
Rosy-faced lovebirds have the widest range of colour mutations of all the Agapornis genus. Generally speaking, these mutations fall into the genetic categories of dominant, codominant, recessive, and sex-linked recessive. While this seems fairly straightforward, it can quickly become confusing when a single specimen has multiple examples of these mutational traits.
- Colour varieties in aviculture
 Wild type
Wild type Left: Wild type
Left: Wild type
Right: Lutino mutation Left: Wild type
Left: Wild type
Right: Pied Green mutation Aqua Turquoise mutation
Aqua Turquoise mutation Left: Pied mutation
Left: Pied mutation
Center: Hybrid of peach-face and a fischeri
Right: Orange-face mutation Turquoise mutation
Turquoise mutation Green Single Violet factor Opaline mutation
Green Single Violet factor Opaline mutation They can be tamed
They can be tamed Opaline Double Dark factor mutation
Opaline Double Dark factor mutation Lutino lovebirds with mutation where facial coloration covers entire head
Lutino lovebirds with mutation where facial coloration covers entire head Aqua harlequin
Aqua harlequin Whiteface violet
Whiteface violet
References
Citations
- 1 2 BirdLife International (2018). "Agapornis roseicollis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22685342A131916302. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22685342A131916302.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ↑ "Zoological Nomenclature Resource: Psittaciformes (Version 9.004)". www.zoonomen.net. 5 July 2008.
- 1 2 3 4 Forshaw (2006). plate 45.
- 1 2 McLachlan G. R. & Liversidge, R. (1981) Roberts Birds of South Africa, John Voelcker Bird Book Fund, Cape Town. ISBN 0-620-03118-2
- ↑ Clark, Greg. "Peach-faced Lovebird Range Expansion Data in Greater Phoenix, Arizona Area". Retrieved 27 February 2011.
- ↑ GrrlScientist. "How Lovebirds Keep Their Cool When It's Really Hot". Forbes. Retrieved 29 March 2021.
- ↑ "Rosy-faced Lovebird". birdfinding.info. Retrieved 29 November 2023.
- ↑ Falcón, Wilfredo; Tremblay, Raymond L. (2018). "From the cage to the wild: introductions of Psittaciformes to Puerto Rico". PeerJ. 6:e5669: e5669. doi:10.7717/peerj.5669. PMC 6214232. PMID 30397538.
- ↑ "Bird Care Guide: Lovebirds". MSPCA–Angell. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
Cited texts
- Forshaw, Joseph M. (2006). Parrots of the World; an Identification Guide. Illustrated by Frank Knight. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-09251-6.
General references
- "Species factsheet: Agapornis roseicollis". BirdLife International (2008). Retrieved 9 July 2008.
- Burt, D.W.; White, S.J. (July 2007). "Avian Genomics in the 21st Century". Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 117 (1–4: Avian Genomics in Evolution, Agriculture and Health): 6–13. doi:10.1159/000103159. ISBN 978-3-8055-8338-1. PMID 17675839. S2CID 23593471.
- Rosy-faced Lovebird Bird Observations, Jan–Dec, 2003–2011, eBird.org
- Luft, Stefan (2007). Parrots of Africa (1st ed.). Norderstedt, Germany: Books On Demand. ISBN 978-3-8334-8445-2. OCLC 176931136.
External links
- Peach Faced Lovebird mutation information Information on PFLB mutations
- Peach-faced Lovebird Range Expansion Data in Greater Phoenix, Arizona
- African Love Bird Society An international organization dedicated to the keeping, breeding, and showing of Love Birds.
- Rosy-faced lovebird - Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds.
