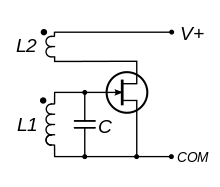
The Armstrong oscillator[1] (also known as the Meissner oscillator[2]) is an electronic oscillator circuit which uses an inductor and capacitor to generate an oscillation. It is the earliest oscillator circuit, invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong in 1912 and independently by Austrian engineer Alexander Meissner in 1913, and was used in the first vacuum tube radio transmitters. It is sometimes called a tickler oscillator because its distinguishing feature is that the feedback signal needed to produce oscillations is magnetically coupled into the tank inductor in the input circuit by a "tickler coil" (L2, right) in the output circuit. Assuming the coupling is weak but sufficient to sustain oscillation, the oscillation frequency f is determined primarily by the LC circuit (tank circuit L1 and C in the figure on the right) and is approximately given by
This circuit was widely used in the regenerative radio receiver, popular until the 1940s. In that application, the input radio frequency signal from the antenna is magnetically coupled into the LC circuit by an additional winding, and the feedback is reduced with adjustable gain control in the feedback loop, so the circuit is just short of oscillation. The result is a narrow-band radio-frequency filter and amplifier. The non-linear characteristic of the transistor or tube also demodulated the RF signal to produce the audio signal.
The circuit diagram shown is a modern implementation, using a field-effect transistor as the amplifying element. Armstrong's original design used a triode vacuum tube.
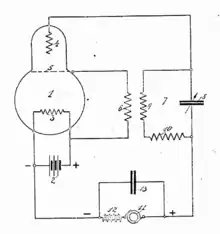
In the Meissner variant, the LC resonant circuit is exchanged with the feedback coil, i.e., in the output path (vacuum tube plate, field-effect transistor drain, or bipolar transistor collector) of the amplifier (e.g., Grebennikov, Fig. 2.8).[3] Many publications, however, embrace both variants with either name. English speakers call it the "Armstrong oscillator", whereas German speakers call it the "Meißner oscillator".
See also
Footnotes
- ↑ US 1113149, Armstrong, Edwin H., "Wireless receiving system", published 19 October 1913, issued 6 October 1914. In Figure 1, a tapped inductor ("auto-transformer") provides the feedback; in Figure 6, a transformer provides the feedback.
- ↑ DE 291604, Meissner, Alexander, "Einrichtung zur Erzeugung elektrischer Schwingungen", published April 10, 1913, issued June 23, 1919, [Equipment for production of electrical oscillations] in German. The patent does not mention Meissner; the patent was issued to Gesellschaft für Drahtlose Telegraphie mbH [Corporation for Wireless Telegraphy].
- See also: Meissner, Alexander. "Production of waves by cathode-ray tubes" U.S. Patent No. 1,924,796. (filed: 16 March 1914; issued: 29 August 1933).
- ↑ Grebennikov, A. (2007), RF and Microwave Transistor Oscillator Design, Wiley, ISBN 978-0-470-02535-2
External links
 Media related to Armstrong oscillators at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Armstrong oscillators at Wikimedia Commons