Kaarst | |
|---|---|
 Saint Martin Church | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Kaarst within Rhein-Kreis Neuss district 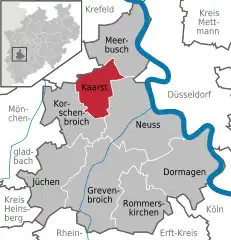 | |
 Kaarst  Kaarst | |
| Coordinates: 51°13′N 06°37′E / 51.217°N 6.617°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia |
| Admin. region | Düsseldorf |
| District | Rhein-Kreis Neuss |
| Subdivisions | 5 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–25) | Ursula Baum[1] (FDP) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 37.48 km2 (14.47 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 45 m (148 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 35 m (115 ft) |
| Population (2021-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 43,661 |
| • Density | 1,200/km2 (3,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 41564 |
| Dialling codes | 02131 |
| Vehicle registration | NE |
| Website | www |
Kaarst (German pronunciation: [ˈkaːɐ̯st]; Limburgish: Kaasj) is a town in Germany. It lies in the district of Rhein-Kreis Neuss in North Rhine-Westphalia. It is 5 km west of Neuss and 12 km east of Mönchengladbach.
Division of the town
Kaarst consists of 5 subdivisions
- Kaarst (23,495 inhabitants)
- Büttgen (6,415 inhabitants)
- Driesch (645 inhabitants)
- Holzbüttgen (5,967 inhabitants)
- Vorst (5,671 inhabitants)
History
Before 100 BC Celts lived in the area. Later the Franks came into this area as graves from the 7th century prove. The first written document is the Life of the first bishop of Münster. It describes how bishop Ludger walked from Budica, now Büttgen, through the forest of Hamrithi. The earliest known written mention of Kaarst refers to it as 'Karlesforst' and dates back to 1218. Karl was a very common name for frankish nobles including king Charlemagne ('Karl der Große'), but a link between Charlemagne and Kaarst has not been proven.
Kaarst and Büttgen both have churches built in the 12th century. Both villages were destroyed by Charles the Bold duke of Burgundy (Karl der Kühne, 1474–1475), in the Cologne War (1585 to 1586) and in the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). Jan von Werth, a celebrated general during the Thirty Years' War, was born near Büttgen in 1591.
During the Thirty Years' War, Kaarst was attacked several times by hostile armies, e.g. the one of Northern-Hesse (Northern-Hesse collaborated with Sweden and France, whereas the southern part of Hesse did not). Some time in 1642, a Hessian troop entered the city murdering the local preacher and destroying the vicarage. From 1794 till 1814 Kaarst was in the area occupied by France under Napoleon I. The French redrew district boundaries in 1798 and assigned Kaarst to Kanton Neuss. A relic of Napoleon I is the Nordkanal, a canal to connect the rivers Maas and Rhine.
In 1936 Büttgen had 4,400 inhabitants and Kaarst 2,000.
In 1975 Büttgen and villages around Kaarst were formally amalgamated into Kaarst to form administrative area with 33,500 inhabitants.
Politics
In the 2015 communal elections, Dr. Ulrike Nienhaus (CDU) was elected mayor of Kaarst with 55.8 percent of the valid votes. She was the first female mayor of Kaarst. In the 2020 communal elections, Ursula Baum (FDP) was elected mayor of Kaarst. She won the runoff election in September 2020 with 59.35 percent of the valid votes against Lars Christoph (CDU).[3]
Transport
Kaarster See station is the western terminus of the Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn line S 28. The town is also served by Kaarster Bahnhof, Kaarst Mitte/Holzbüttgen and Kaarst IKEA stations. Kaarst-Büttgen is served by the S-Bahn line S 8. Both lines connect Kaarst with the capital city Düsseldorf.
Kaarst is connected to the motorway system via the Bundesautobahn 52 and Bundesautobahn 57, which intersect here.
Twin towns – sister cities
 La Madeleine, France
La Madeleine, France Perleberg, Germany
Perleberg, Germany
Notable people
- Johann von Werth (1591–1652), General in the Thirty Years' War
- Berti Vogts (born 1946), football player and manager
- Sebastian Vollmer (born 1984), NFL player
Gallery
.JPG.webp) Alte Mühle, windmill in Kaarst
Alte Mühle, windmill in Kaarst.JPG.webp) Braunsmühle in Kaarst-Büttgen
Braunsmühle in Kaarst-Büttgen
References
- ↑ Wahlergebnisse in NRW Kommunalwahlen 2020, Land Nordrhein-Westfalen, accessed 29 June 2021.
- ↑ "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden Nordrhein-Westfalens am 31. Dezember 2021" (in German). Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- ↑ "Bürgermeisterstichwahl - Kommunalwahlen 2020 in Kaarst - Gesamtergebnis" (in German). ITK Rheinland. Retrieved 2 November 2020.
- ↑ "Partnerstädte". kaarst.de (in German). Kaarst. Retrieved 2021-02-15.
External links
- Official website (in German)