Bartholomew County | |
|---|---|
 Bartholomew County courthouse in Columbus, Indiana | |
 Seal | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Indiana | |
 Indiana's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 39°13′N 85°54′W / 39.21°N 85.9°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 12 February 1821 |
| Named for | Joseph Bartholomew |
| Seat | Columbus |
| Largest city | Columbus |
| Area | |
| • Total | 409.52 sq mi (1,060.7 km2) |
| • Land | 406.91 sq mi (1,053.9 km2) |
| • Water | 2.62 sq mi (6.8 km2) 0.64% |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 82,208 |
| • Density | 189/sq mi (72.88/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 6th |
| Website | www |
| Indiana county number 3 | |
Bartholomew County is a county located in the U.S. state of Indiana. The population was 82,208 at the 2020 census. The county seat is Columbus.[1] The county was determined by the U.S. Census Bureau to be home to the mean center of U.S. population in 1900.[2]
Bartholomew County makes up the Columbus, Indiana Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is part of the Indianapolis-Carmel-Muncie Combined Statistical Area.
History
Bartholomew County was formed on February 12, 1821, and was named for Lt. Col. Joseph Bartholomew, wounded at the Battle of Tippecanoe.[3] The site of the county seat was chosen on February 15, 1821, by a team of commissioners, who suggested the name Tiptona, in honor of John Tipton.
Courthouse
The current Bartholomew County courthouse was built from 1870 to 1874 by McCormack and Sweeney of Columbus at a cost of $225,000.
It was designed by architect Isaac Hodgson, who was born in Belfast, Ireland in 1826 and immigrated to the United States in 1848; he designed six Indiana courthouses, including the one in Henry County.
The courthouse is built largely of brick and has mansard roofs typical of the Second Empire French style. Its asymmetrical "L" shape allows it to face two major streets in Columbus. The inscription indicating the commissioners, architect and date is high up on the east facade.[4]
Today the Bartholomew County Veterans Memorial designed by American architect Charles Rose sits adjacent to the Courthouse.
Geography
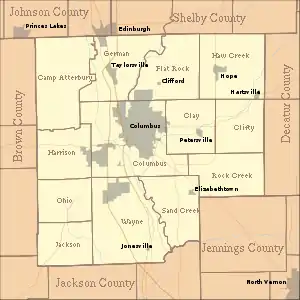
According to the 2010 census, the county has a total area of 409.52 square miles (1,060.7 km2), of which 406.91 square miles (1,053.9 km2) (or 99.36%) is land and 2.62 square miles (6.8 km2) (or 0.64%) is water.[5] Camp Atterbury occupies the northwestern corner of the county.
Adjacent counties
- Johnson County (northwest)
- Shelby County (northeast)
- Decatur County (east)
- Jennings County (southeast)
- Jackson County (south)
- Brown County (west)
City
Towns
Census-designated place
Other unincorporated places
- Azalia
- Bethany
- Burnsville
- Corn Brook
- Everroad Park
- Flat Rock Park
- Garden City
- Grammer
- Grandview Lake
- Jewell Village
- Lowell
- Mount Healthy
- Newbern
- North Columbus
- North Gate
- North Ogilville
- Northcliff
- Nortonburg
- Ogilville
- Old Saint Louis
- Parkside
- Petersville
- Pleasant View Village
- Rosstown
- Rugby
- Saint Louis Crossing
- Stony Lonesome
- Walesboro
- Waymansville
- Waynesville
Extinct towns
Townships
Transit
Major highways
Airport
- KBAK - Columbus Municipal Airport
Railroads
Climate and weather
| Columbus, Indiana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In recent years, average temperatures in Columbus have ranged from a low of 19 °F (−7 °C) in January to a high of 86 °F (30 °C) in July, although a record low of −27 °F (−33 °C) was recorded in January 1912 and a record high of 111 °F (44 °C) was recorded in July 1934. Average monthly precipitation ranged from 2.63 inches (67 mm) in February to 4.63 inches (118 mm) in May.[6]
Government
| Bartholomew County Sheriff's Department | |
|---|---|
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| Operations jurisdiction | Bartholomew, Indiana, United States |
| Legal jurisdiction | As per operations jurisdiction |
| General nature | |
| Operational structure | |
| Agency executive |
|
Politics
The county government is a constitutional body, and is granted specific powers by the Constitution of Indiana, and by the Indiana Code.
County Council: The county council is the legislative branch of the county government and controls all the spending and revenue collection in the county. Representatives are elected from county districts. The council members serve four-year terms. They are responsible for setting salaries, the annual budget, and special spending. The council also has limited authority to impose local taxes, in the form of an income and property tax that is subject to state level approval, excise taxes, and service taxes.[7][8]
Board of Commissioners: The executive body of the county is made of a board of commissioners. The commissioners are elected county-wide, in staggered terms, and each serves a four-year term. One of the commissioners, typically the most senior, serves as president. The commissioners are charged with executing the acts legislated by the council, collecting revenue, and managing the day-to-day functions of the county government.[7][8]
Court: The county maintains a small claims court that can handle some civil cases. The judge on the court is elected to a term of four years and must be a member of the Indiana Bar Association. The judge is assisted by a constable who is also elected to a four-year term. In some cases, court decisions can be appealed to the state level circuit court.[8]
County Officials: The county has several other elected offices, including sheriff, coroner, auditor, treasurer, recorder, surveyor, and circuit court clerk. Each of these elected officers serves a term of four years and oversees a different part of county government. Members elected to county government positions are required to declare a party affiliation and to be residents of the county.[8]
Bartholomew County is part of Indiana's 6th congressional district and Indiana's 9th congressional district; Indiana Senate district 41;[9] and Indiana House of Representatives districts 57, 59 and 65.[10]
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2020 | 22,410 | 61.74% | 12,934 | 35.63% | 956 | 2.63% |
| 2016 | 20,640 | 63.09% | 9,841 | 30.08% | 2,236 | 6.83% |
| 2012 | 18,083 | 61.52% | 10,625 | 36.15% | 684 | 2.33% |
| 2008 | 17,067 | 54.90% | 13,567 | 43.64% | 455 | 1.46% |
| 2004 | 19,093 | 66.96% | 9,191 | 32.23% | 231 | 0.81% |
| 2000 | 16,200 | 62.87% | 9,015 | 34.98% | 554 | 2.15% |
| 1996 | 13,188 | 51.60% | 9,301 | 36.39% | 3,069 | 12.01% |
| 1992 | 13,146 | 47.91% | 8,284 | 30.19% | 6,010 | 21.90% |
| 1988 | 17,364 | 66.05% | 8,804 | 33.49% | 123 | 0.47% |
| 1984 | 18,704 | 69.35% | 8,075 | 29.94% | 191 | 0.71% |
| 1980 | 15,801 | 58.58% | 9,260 | 34.33% | 1,913 | 7.09% |
| 1976 | 14,771 | 56.41% | 11,203 | 42.78% | 213 | 0.81% |
| 1972 | 17,365 | 70.87% | 6,974 | 28.46% | 163 | 0.67% |
| 1968 | 13,628 | 55.80% | 8,268 | 33.85% | 2,528 | 10.35% |
| 1964 | 11,026 | 45.77% | 12,940 | 53.72% | 124 | 0.51% |
| 1960 | 13,606 | 59.09% | 9,290 | 40.35% | 130 | 0.56% |
| 1956 | 12,227 | 59.78% | 8,134 | 39.77% | 92 | 0.45% |
| 1952 | 11,462 | 58.77% | 7,844 | 40.22% | 196 | 1.01% |
| 1948 | 7,804 | 48.74% | 7,960 | 49.71% | 248 | 1.55% |
| 1944 | 7,689 | 50.99% | 7,139 | 47.34% | 252 | 1.67% |
| 1940 | 7,890 | 48.84% | 8,180 | 50.63% | 86 | 0.53% |
| 1936 | 6,484 | 42.92% | 8,536 | 56.50% | 87 | 0.58% |
| 1932 | 6,015 | 43.16% | 7,533 | 54.05% | 390 | 2.80% |
| 1928 | 6,788 | 57.76% | 4,881 | 41.53% | 83 | 0.71% |
| 1924 | 6,606 | 56.62% | 4,760 | 40.80% | 302 | 2.59% |
| 1920 | 6,585 | 53.93% | 5,420 | 44.39% | 205 | 1.68% |
| 1916 | 3,287 | 47.08% | 3,441 | 49.29% | 253 | 3.62% |
| 1912 | 1,321 | 20.26% | 3,147 | 48.26% | 2,053 | 31.48% |
| 1908 | 3,306 | 46.13% | 3,637 | 50.75% | 224 | 3.13% |
| 1904 | 3,510 | 51.60% | 3,038 | 44.66% | 254 | 3.73% |
| 1900 | 2,375 | 41.08% | 3,300 | 57.07% | 107 | 1.85% |
| 1896 | 3,264 | 50.03% | 3,198 | 49.02% | 62 | 0.95% |
| 1892 | 2,297 | 40.38% | 3,217 | 56.56% | 174 | 3.06% |
| 1888 | 2,742 | 46.27% | 3,109 | 52.46% | 75 | 1.27% |
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1830 | 5,476 | — | |
| 1840 | 10,042 | 83.4% | |
| 1850 | 12,428 | 23.8% | |
| 1860 | 17,865 | 43.7% | |
| 1870 | 21,133 | 18.3% | |
| 1880 | 22,777 | 7.8% | |
| 1890 | 23,867 | 4.8% | |
| 1900 | 24,594 | 3.0% | |
| 1910 | 24,813 | 0.9% | |
| 1920 | 23,887 | −3.7% | |
| 1930 | 24,864 | 4.1% | |
| 1940 | 28,276 | 13.7% | |
| 1950 | 36,108 | 27.7% | |
| 1960 | 48,198 | 33.5% | |
| 1970 | 57,022 | 18.3% | |
| 1980 | 65,088 | 14.1% | |
| 1990 | 63,657 | −2.2% | |
| 2000 | 71,435 | 12.2% | |
| 2010 | 76,794 | 7.5% | |
| 2020 | 82,208 | 7.1% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[12][13] 1790-1960[14] 1900-1990[15] 1990-2000[16] 2010-2013[17] | |||
As of the 2020 United States Census, there were 82,208 people and 31,452 households residing in the county.[18] The population density was 188.7 inhabitants per square mile (72.9/km2). There were 33,098 housing units at an average density of 81.3 per square mile (31.4/km2).[5] Per the 2020 census, the racial makeup of the county was 80.0% white, 6.6% Asian, 2.2% black or African American, 0.4% American Indian, 0.1% Pacific islander, 4.7% from other races, and 6.1% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 8.8% of the population.[18] In terms of ancestry, according the 2010 census, 28.5% were German, 12.4% were English, 12.2% were Irish, and 10.7% were American.[19]
Of the 29,860 households in 2010, 34.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 54.1% were married couples living together, 10.7% had a female householder with no husband present, 30.4% were non-families, and 25.3% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.53 and the average family size was 3.02. The median age was 38.2 years.[18]
In 2010, the median income for a household in the county was $47,697 and the median income for a family was $64,024. Males had a median income of $50,358 versus $32,334 for females; the per capita income for the county was $26,860; and approximately 7.7% of families and 10.4% of the population were below the poverty line, including 15.8% of those under age 18 and 5.3% of those age 65 or over.[20]
Education
Public schools in Bartholomew County are administered by the Bartholomew Consolidated School Corporation and the Flat Rock-Hawcreek School Corporation. The county's first tuition-free public charter school, the International School of Columbus, a middle school/high school, opened in 2009–10. The ISC was an International Baccalaureate World School offering the Diploma Program. The ISC closed due to financial difficulties in the fall of 2013.
Ivy Tech Community College Columbus is located in Bartholomew County.[21]
See also
- The Republic, daily newspaper covering Bartholomew County
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Bartholomew County, Indiana
References
- ↑ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on July 12, 2012. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- ↑ "Mean Center of Population for the United States: 1790 to 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 3, 2001. Retrieved September 17, 2011.
- ↑ Baker, Ronald L.; Carmony, Marvin (1975). Indiana Place Names. Bloomington, Indiana: Indiana University Press. p. 9.
- ↑ Counts, Will; Jon Dilts (1991). The 92 Magnificent Indiana Courthouses. Bloomington, Indiana: Indiana University Press. pp. 12–13. ISBN 978-0-253-33638-5.
- 1 2 "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- 1 2 "Monthly Averages for Columbus, Indiana". The Weather Channel. Retrieved January 27, 2011.
- 1 2 Indiana Code. "Title 36, Article 2, Section 3". IN.gov. Archived from the original on October 5, 2008. Retrieved September 16, 2008.
- 1 2 3 4 Indiana Code. "Title 2, Article 10, Section 2" (PDF). IN.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 29, 2008. Retrieved September 16, 2008.
- ↑ "Indiana Senate Districts". State of Indiana. Archived from the original on January 15, 2011. Retrieved January 23, 2011.
- ↑ "Indiana House Districts". State of Indiana. Archived from the original on January 15, 2011. Retrieved January 23, 2011.
- ↑ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved May 14, 2018.
- ↑ "Indiana's Census 2020 Redistricting Data Dashboard". Census.gov. Retrieved October 3, 2021.
- ↑ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- ↑ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- ↑ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- ↑ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- ↑ "American FactFinder". US Census Bureau. United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 14, 2020. Retrieved April 22, 2019.
- 1 2 3 "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- ↑ "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 14, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- ↑ "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 14, 2020. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- ↑ "Columbus - Ivy Tech Community College of Indiana". www.ivytech.edu. Retrieved November 19, 2019.