| L-23/U-8 Seminole | |
|---|---|
 | |
| US Army U-8D Seminole liaison version | |
| Role | Utility aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Beech Aircraft Corporation |
| First flight | 1949 |
| Introduction | 1952 |
| Retired | 1992 |
| Primary users | United States Army Pakistan Army |
| Produced | 1952-1961 (L-23A/E) 1958-1963 (L-23F/U-8F) |
| Number built | 288 (including 71 L-23F/U-8F) |
| Developed from | Beechcraft Twin Bonanza |
| Variants | Beechcraft Queen Air |
The Beechcraft L-23 Seminole (later designated U-8) was the United States Armed Forces designation for the Beechcraft Twin Bonanza and Queen Air aircraft in its inventory.
Design and development
In 1951 the United States Army evaluated a Model 50 Twin Bonanza at Fort Bragg, North Carolina and subsequently ordered four off-the-shelf Model 50s as YL-23s, these being delivered in early 1952.[1] Further examples of the Model 50 were ordered under the designation L-23A and Model B50s were also ordered under the designation L-23B.[1] These accounted for the majority of Twin Bonanza production during 1952 and 1953, the first L-23A being delivered in February 1953 and the last L-23B being delivered in April the following year.,[1] shortly before cessation of the Korean War.
In 1955 the United States Air Force ordered a single Model C50 Twin Bonanza under the designation XL-23C for evaluation; this was the only L-23 variant not delivered to the US Army as no further orders were placed by the Air Force.[1][2][3] In 1956 deliveries of L-23s to the Army recommenced when Beechcraft delivered six Model D50s under the designation L-23E. In January 1957 the first example of the L-23D was delivered, based on the Model E50 Twin Bonanza.[1]
During 1958 the remaining L-23A and L-23B aircraft in service (a few had crashed) were returned to the Beechcraft factory, where they were remanufactured to a similar standard as new-build L-23Ds and then re-designated as such with new constructor's numbers and military serial numbers.[1][4][5] In 1958 the Army also ordered 11 RL-23Ds with further examples being converted from L-23Ds. These aircraft featured belly-mounted radar, either AN/APS-85 in a large pod or AN/APQ-86 in a long narrow pod mounted on brackets with a modified nose as well.[1]
Also in 1958 Beechcraft began to develop a variant with a larger cabin at the request of the US Army. The L-23F that emerged had the same wings and tail but up to ten people could now fit in the longer, wider and higher cabin compared to only five in earlier L-23s.[1] Beechcraft gave the type the in-house designation of Model 65 and developed it as a civilian aircraft as well, christening it the "Queen Air". The first two Model 65s built were retained by Beechcraft as prototypes and the third was delivered to the Army in 1960, with a further 23 being delivered that year and in 1961.[1][5][6][7]
Operational history

The first L-23As entered service in 1953 and the type served the US Army for almost forty years, the last U-8Fs being retired in 1992. When US military aircraft designations were revised in 1962, the remaining L-23D, RL-23D, L-23E and L-23F aircraft became U-8Ds, RU-8Ds, U-8Es and U-8Fs.[1] A further 47 Model 65s were ordered in 1962 and 1963 as U-8Fs; one of these was delivered to the Pakistan Army, formally the only L-23 or U-8 delivery to a foreign user[1][8] (although other nations bought Queen Airs off-the-shelf as military aircraft). These were the final new-build aircraft in the series, however the unique Beechcraft Model 87 turboprop proof-of-concept aircraft used in developing the King Air was delivered to the Army as the NU-8F in 1964 (this was later re-designated the YU-21) and a few used Queen Airs were also taken by the Army.
Many U-8Fs were modified during their service lives to a similar standard as civilian Excalibur Queen Airs. The most obvious modifications are more powerful Lycoming IO-720 eight-cylinder engines in place of the factory-fitted six-cylinder engines; and bulged main landing gear doors that fully enclose the wheels when the gear is retracted instead of the wheels partially protruding through the doors. Many L-23Ds/U-8Ds and U-8Fs have been registered as civilian aircraft since retirement from military service.
Variants
- YL-23
- Four Model 50 Twin Bonanzas evaluated by the US Army subsequently converted to L-23A standard.[9]
- L-23A
- 55 delivered to the US Army, many subsequently converted to L-23D standard.[9]
- L-23B
- Based on B50. 40 delivered to the US Army from 1954, with many subsequently converted to L-23D standard.[10][11]
- L-23D
- 100 delivered new to the US Army plus 93 L-23As and Bs rebuilt to L-23D standard.[4][5][12][13]
- RL-23D
- variant with belly-mounted radar. Eleven new-build aircraft delivered to the US Army, plus 29 converted from L-23Ds.[5][13]
- L-23E
- Six delivered to the United States Army.[12]
- U-8D
- L-23D redesignated in 1962.
- U-8E
- L-23E redesignated in 1962.

- U-8F
- L-23F redesignated in 1962 and 46 new-build aircraft delivered to the US Army, plus single Beechcraft Model 87 delivered used as NU-8F in 1964[8][14] and one Queen Air purchased second-hand in 1966.[15] In addition, one U-8F was delivered to the Pakistan Army instead of the US Army[8] and two Queen Airs confiscated from drug runners were added to the US Army inventory in 1981 as U-8Fs.[16]
- NU-8F
- US military designation assigned to a modified commercial Queen Air converted as the prototype Model 65-90 King Air, and fitted with two 500 shp Pratt & Whitney PT6A-6 turboprop engines.[17] The aircraft was evaluated by the US Army in 1964.
Military operators
Aircraft on display
- 56-3701 – U-8D on static display at the Pima Air & Space Museum in Tucson, Arizona.[19]
- 58-1358 – RU-8D on static display at the Combat Air Museum in Topeka, Kansas.[20]
- 58-3051 – U-8D on static display at the U.S. Army Transportation Museum at Joint Base Langley–Eustis near Newport News, Virginia.[21]
- 59-4991 – RU-8D on static display at the National Vigilance Park at Fort Meade, Maryland.[22] This airframe was previously on display at the U.S. Army Transportation Museum.[23]
- 62-3838 – U-8F on static display at the Kansas Aviation Museum in Wichita, Kansas.[24][25]
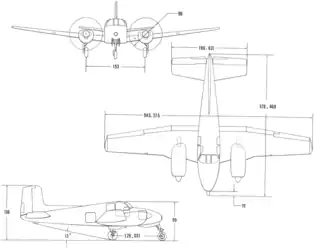
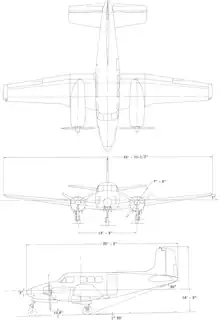
Specifications (L-23D)
Data from U.S. Army Aircraft Since 1947[26]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Capacity: 6 passengers
- Length: 31 ft 6 in (9.60 m)
- Wingspan: 45 ft 3 in (13.79 m)
- Height: 11 ft 6 in (3.51 m)
- Wing area: 277 sq ft (25.7 m2)
- Empty weight: 4,970 lb (2,254 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 7,300 lb (3,311 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 180 US gal (150 imp gal; 680 L)[27]
- Powerplant: 2 × Lycoming GSO-480-A1A6 (Military designation O-480-1) , 340 hp (250 kW) each [28]
Performance
- Maximum speed: 233 mph (375 km/h, 202 kn)
- Cruise speed: 180 mph (290 km/h, 160 kn)
- Range: 1,350–1,470 mi (2,170–2,370 km, 1,170–1,280 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 27,000 ft (8,200 m)
See also
Related development
Related lists
References
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Phillips, Edward H. Beechcraft - Pursuit of Perfection, A History of Beechcraft Airplanes. Flying Books, Eagan, Minnesota 1992. ISBN 0-911139-11-7.
- 1 2 Swanborough and Bowers 1963, pp. 42–43
- 1 2 Pelletier 1995, p. 106.
- 1 2 3 4 Baugher, Joe. "USAF/US Army 1957 Serials list." USAF Aircraft.Retrieved: 11 June 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Baugher, Joe. "USAF/US Army 1958 Serials list." USAF Aircraft. Retrieved: 11 June 2011
- 1 2 Baugher, Joe. "USAF/US Army 1960 Serials list." USAF Aircraft. Retrieved: 11 June 2011.
- 1 2 Baugher, Joe. "USAF/US Army 1961 Serials list." USAF Aircraft. Retrieved: 11 June 2011.
- 1 2 3 Baugher, Joe (13 November 2021). "1963 USAF Serial Numbers". joebaugher.com. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- 1 2 Harding 1990, p. 12.
- ↑ Harding 1990, p. 13.
- ↑ Pelletier 1995, pp. 105–106.
- 1 2 3 4 Baugher, Joe. "USAF/US Army 1956 Serials list." USAF Aircraft. Retrieved: 11 June 2011.
- 1 2 3 Baugher, Joe. "USAF/US Army 1959 Serials list." USAF Aircraft. Retrieved: 11 June 2011.
- ↑ Baugher, Joe. "USAF/US Army 1962 Serials list." USAF Aircraft. Retrieved: 11 June 2011.
- ↑ Baugher, Joe. "USAF/US Army 1966 Serials list." USAF Aircraft. Retrieved: 11 June 2011.
- ↑ Baugher, Joe. "USAF/US Army 1981 Serials list." USAF Aircraft. Retrieved: 11 June 2011.
- ↑ Harding 1997, p. 22.
- ↑ Baugher, Joe. "USAF/US Army 1955 Serials list." USAF Aircraft. Retrieved: 11 June 2011.
- ↑ "SEMINOLE". Pima Air & Space Museum. Pimaair.org. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
- ↑ "Beech RU-8D Twin Bonanza". Combat Air Museum. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier - Beech U-8D Seminole, s/n 58-3051 US, c/n RLH-52". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ "RU-8D Comes to National Vigilance Park". NSA | CSS. 3 May 2016. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier - Beech RU-8D Seminole, s/n 59-4991 US, c/n LH-197". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ "Beech U-8 Queen Air". Kansas Aviation Museum. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ "Airframe Dossier - Beech U-8F Seminole, s/n 62-3838 US, c/n LF.36". Aerial Visuals. AerialVisuals.ca. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ Harding 1990, p. 16.
- ↑ "Beechcraft Model 50 Type Certificate." FAA. Retrieved: 11 June 2011.
- ↑ Pelletier 1995, p. 107.
Bibliography
- Harding, Stephen. U.S. Army Aircraft Since 1947: An Illustrated Directory. Shrewsbury, UK: Airlife Publishing, 1990. ISBN 1-85310-102-8.
- Harding, Stephen. U.S. Army Aircraft Since 1947: An Illustrated Reference. Atglen, PA: Schiffer Publishing Ltd., 1997. ISBN 978-0-7643-0190-2.
- Pelletier, A. J. Beech Aircraft and their Predecessors. Annapolis, Maryland, USA: Naval Institute Press, 1995. ISBN 1-55750062-2.
- Swanborough, F. G. and Bowers, Peter M. United States Military Aircraft since 1909. London: Putnam, 1963.