| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 110 seats in the House of Representatives 56 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 74.68% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This lists parties that won seats. See the complete results below.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||




Parliamentary elections were held in Belarus on 11 September 2016.[1]
Electoral system
The 110 members of the House of Representatives were previously elected using the two-round system. However, a new electoral code was introduced in 2013, abolishing the requirement for candidates to receive an absolute majority, effectively changing the voting system to first-past-the-post. All candidates are elected in single-member constituencies.[2] However, if there is only one candidate, they are required to receive at least 50% of the votes cast (voters may also vote against all).[2][3] Voter turnout in a constituency must be at least 50% for the election to be deemed valid.[3]
In cases where the turnout have not been met or no candidate has been elected, repeat elections will be held.[3]
| Region | Seats |
|---|---|
| City of Minsk | 20 |
| Brest Region | 16 |
| Gomel Region | 17 |
| Grodno Region | 13 |
| Mogilev Region | 13 |
| Minsk Region | 17 |
| Vitebsk Region | 14 |
| Total seats | 110 |

Participating parties
The pro-government Communist Party of Belarus, the Liberal Democratic Party, the Republican Party of Labour and Justice and the Belarusian Patriotic Party all participated in the elections, whilst many pro-government candidates ran as independents.
In contrast to the previous elections in 2012, the opposition did not boycott the elections, instead forming an alliance under the name Prava Vybaru (Belarusian: Права Выбару, Russian: Право выбора, 'The Right to Choose') consisting of the BPF Party, the Belarusian Christian Democracy, the Belarusian Social Democratic Party (Assembly), the Za svabodu movement, the United Civic Party of Belarus, the Belarusian Party "The Greens", the Belarusian Liberal Party of Freedom and Progress and the Trade Union of Electric Industry.[4] The Belarusian Left Party "A Just World" also contested the elections.[5]
| Party | Leader | Ideology | Position | Number of participating constituencies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liberal Democratic Party | Sergei Gaidukevich | Pan-Slavism | Constructive opposition (declarative) Pro-government (in fact) | 73 |
| United Civic Party of Belarus | Anatoly Lebedko | Liberal conservatism | Part of the opposition alliance "The Right to Choose" | 53 |
| BPF Party | Alaksiej Janukievich | Belarusian nationalism | Part of the opposition alliance "The Right to Choose" | 45 |
| Belarusian Left Party "A Just World" | Sergey Kalyakin | Democratic socialism | Opposition | 37 |
| Communist Party of Belarus | Igor Karpenko | Communism, Marxism–Leninism | Pro-government | 36 |
| Belarusian Social Democratic Party (Assembly) | Irina Veshtard | Social democracy | Part of the opposition alliance "The Right to Choose" | 27 |
| Republican Party of Labour and Justice | Vasil Zadnyaprany | Social democracy | Pro-government | 16 |
| Belarusian Patriotic Party | Nikolai Ulakhovich | Social justice | Pro-government | 16 |
| Belarusian Party "The Greens" | Aleh Novikaŭ | Green Politics | Part of the opposition alliance "The Right to Choose" | 5 |
Results
The Central Election Commission stated that elections had been deemed valid in all constituencies. At the same time, independent observers declared that turnout data had been falsified in many constituencies, particularly in Minsk, and the real turnout was less than 50% required for the results in a constituency to be deemed valid.
_Ergebnisse.svg.png.webp)
The elections saw two opposition candidates win seats, the first since 2004. Hanna Kanapatskaya, a member of the United Civic Party won in one of the Minsk constituencies, whilst independent candidate Alena Anisim won in a constituency in the Minsk Region. The other 93 independent candidates were considered to be pro-government. The Communist Party of Belarus, the Republican Party of Labour and Justice and the Belarusian Patriotic Party all support President Alexander Lukashenko, and although the Liberal Democratic Party declares to be "constructive democratic opposition", it is de facto pro-government.
.svg.png.webp) |
|---|
|
|
|
|
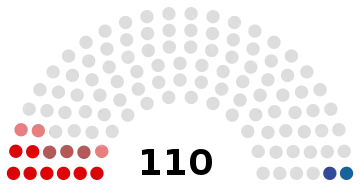 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
| Communist Party of Belarus | 380,770 | 7.40 | 8 | +5 | |
| Liberal Democratic Party | 218,081 | 4.24 | 1 | +1 | |
| Republican Party of Labour and Justice | 147,378 | 2.87 | 3 | +2 | |
| United Civic Party | 111,227 | 2.16 | 1 | New | |
| Belarusian Patriotic Party | 111,045 | 2.16 | 3 | New | |
| BPF Party | 88,511 | 1.72 | 0 | 0 | |
| Belarusian Left Party "A Just World" | 72,185 | 1.40 | 0 | 0 | |
| Belarusian Social Democratic Party (Assembly) | 66,381 | 1.29 | 0 | 0 | |
| Belarusian Green Party | 9,038 | 0.18 | 0 | New | |
| Independents | 3,445,562 | 67.01 | 94 | –11 | |
| Against all | 491,986 | 9.57 | – | – | |
| Total | 5,142,164 | 100.00 | 110 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 5,142,164 | 98.66 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 69,707 | 1.34 | |||
| Total votes | 5,211,871 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 6,978,490 | 74.68 | |||
| Source: CEC (results), CEC (candidate information) | |||||
References
- ↑ Global electoral calendar NDI
- 1 2 Electoral System Design data for Belarus IDEA
- 1 2 3 Article 87. Repeated elections Electoral Code of the Republic of Belarus
- ↑ About Archived 2016-09-03 at the Wayback Machine Prava Vybaru
- ↑ Оппозиционные коммунисты рассказали, с чем пойдут на выборы Archived 2016-08-24 at the Wayback Machine Tut, 20 June 2016 (in Russian)
External links
- Elections In Belarus: The Continuation Of A New Model? Belarus Digest
- Belarusian Opposition Prepares For The 2016 Parliamentary Elections Belarus Digest
- Formation Of Precinct Election Commissions - Digest Of The 2016 Parliamentary Elections Belarus Digest
- Nomination And Registration Of Candidates - Digest Of The 2016 Parliament Elections Belarus Digest