| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
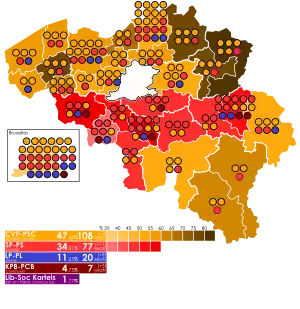 Chamber seat distribution by constituency | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|---|
|
|
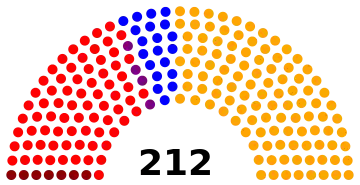
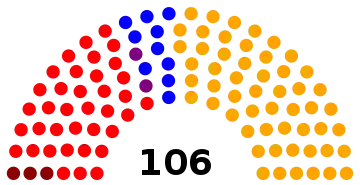
General elections were held in Belgium on 4 June 1950.[1] The result was a victory for the Christian Social Party, which won 108 of the 212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 54 of the 106 seats in the Senate.[2] Voter turnout was 92.6%.[3] This election was the last one in Belgian history where a single party achieved an absolute majority. Elections for the nine provincial councils were also held.
The elections took place a few months after the divisive referendum on returning King Leopold III from exile and restoring his monarchial duties (the Royal Question). Following the election, a single-party Catholic government was formed with Jean Duvieusart as Prime Minister, who oversaw the return of King Leopold III, but who was quickly succeeded by Joseph Pholien as Prime Minister, following strikes and protests due to Leopold's return, which ultimately led to his abdication.
Results
Chamber of Deputies
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
| Christian Social Party | 2,356,608 | 47.68 | 108 | +3 | |
| Belgian Socialist Party | 1,705,781 | 34.51 | 73 | +7 | |
| Liberal Party | 556,102 | 11.25 | 20 | –9 | |
| Communist Party of Belgium | 234,541 | 4.75 | 7 | –5 | |
| Liberal–Socialist Kartels | 87,252 | 1.77 | 4 | +4 | |
| Cosmocraten | 1,535 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | |
| Belgian Patriotic Party | 656 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | |
| Independents | 332 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 4,942,807 | 100.00 | 212 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 4,942,807 | 94.70 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 276,471 | 5.30 | |||
| Total votes | 5,219,278 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 5,635,452 | 92.62 | |||
| Source: Belgian Elections | |||||
Senate
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
| Christian Social Party | 2,210,712 | 47.19 | 54 | 0 | |
| Belgian Socialist Party | 1,631,368 | 34.82 | 37 | +4 | |
| Liberal Party | 526,575 | 11.24 | 10 | –4 | |
| Communist Party of Belgium | 229,093 | 4.89 | 3 | –2 | |
| Liberal–Socialist Kartels | 86,801 | 1.85 | 2 | +2 | |
| Independents | 262 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 4,684,811 | 100.00 | 106 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 4,684,811 | 94.34 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 280,854 | 5.66 | |||
| Total votes | 4,965,665 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 5,635,452 | 88.11 | |||
| Source: Belgian Elections | |||||
References
- ↑ Dieter Nohlen & Philip Stöver (2010) Elections in Europe: A data handbook, p289 ISBN 978-3-8329-5609-7
- ↑ Nohlen & Stöver, pp 309–311
- ↑ Nohlen & Stöver, p291

