| NGC 6087 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Right ascension | 16h 18m 48s[1] |
| Declination | −57° 56′[1] |
| Distance | ~3500LY (~1000pc) |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.4 |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 12′ |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Other designations | S Normae Cluster, Caldwell 89, Cr 300 |
| Associations | |
| Constellation | Norma |
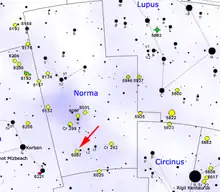
Map showing the location of NGC 6087
NGC 6087 (also known as Caldwell 89 or the S Normae Cluster) is an open cluster of 40 or more[2][3] stars centered on the Cepheid variable S Normae in the constellation Norma. At a distance of about 3500 ly and covering a field of almost one quarter of a degree, the stars range from seventh- to eleventh-magnitude, the brightest being 6.5 magnitude S Normae. The aggregate visual magnitude of the cluster is about 5.4.
Spectral analysis of the radial motion of the stars confirm that S Normae is a member of the cluster,[3] and the period/luminosity relationship of Cepheid variables allows the distance to be determined with confidence.
References
- 1 2 "NGC 6087". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2007-04-18.
- ↑ Burnham's Celestial Handbook gives the number 40, though other studies go as high as 349; see Stephen James O'Meara, The Caldwell Objects, Cambridge University Press, 2002, p. 351.
- 1 2 A. U. Landolt (1964). "The Galactic Cluster NGC 6087". Astrophysical Journal Supplement. 8: 329–351. Bibcode:1964ApJS....8..329L. doi:10.1086/190092. Retrieved 4 April 2013.
External links
 Media related to NGC 6087 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to NGC 6087 at Wikimedia Commons- NGC 6087 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.