| Coronoid process of the mandible | |
|---|---|
 Position of coronoid process in skull (shown in red) | |
 Position of coronoid process in mandible (shown in red) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | mandible |
| System | skeletal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | processus coronoideus mandibulae |
| TA98 | A02.1.15.032 |
| TA2 | 869 |
| FMA | 52833 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
In human anatomy, the mandible's coronoid process (from Greek korōnē, denoting something hooked) is a thin, triangular eminence, which is flattened from side to side and varies in shape and size. Its anterior border is convex and is continuous below with the anterior border of the ramus. Its posterior border is concave and forms the anterior boundary of the mandibular notch. The lateral surface is smooth, and affords insertion to the temporalis and masseter muscles. Its medial surface gives insertion to the temporalis, and presents a ridge which begins near the apex of the process and runs downward and forward to the inner side of the last molar tooth.
Between this ridge and the anterior border is a grooved triangular area, the upper part of which gives attachment to the temporalis, the lower part to some fibers of the buccinator.
Clinical significance
Fractures of the mandible are common. However, coronoid process fractures are very rare.[1] Isolated fractures of the coronoid process caused by direct trauma are rare, as it is anatomically protected by the complex zygomatic arch/ temporo-zygomatic bone and their associated muscles. Most fractures here are caused by strokes (contusion or penetrating injuries).[2] Conservative management of minor fractures can lead to trismus (lockjaw) that can later only be corrected by removing the coronoid process.[1] For serious fractures, a surgery involving open reduction and internal fixation can have good outcomes.[1]
Additional images
 Position of coronoid process in skull (shown in red)
Position of coronoid process in skull (shown in red) Position of coronoid process in mandible (shown in red)
Position of coronoid process in mandible (shown in red)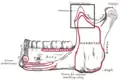 Mandible outer surface (side view; coronoid process labeled at top center)
Mandible outer surface (side view; coronoid process labeled at top center)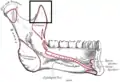 Medial surface
Medial surface The temporalis, with the zygomatic arch and masseter removed
The temporalis, with the zygomatic arch and masseter removed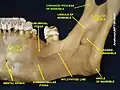 Coronoid process of mandible
Coronoid process of mandible Deep dissection of the mandibular nerve and bone (anterior view)
Deep dissection of the mandibular nerve and bone (anterior view) Deep dissection of the infratemporal fossa, showing the lingual and inferior alveolar nerve (anterolateral view)
Deep dissection of the infratemporal fossa, showing the lingual and inferior alveolar nerve (anterolateral view)
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 174 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 174 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- 1 2 3 Shen, L.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Long, J.; Tian, W.; Tang, W. (June 2013). "Mandibular coronoid fractures: treatment options". International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 42 (6): 721–726. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2013.03.009. ISSN 1399-0020. PMID 23602277.
- ↑ Pricop, Marius; Urechescu, Horațiu; Sîrbu, Adrian (March 2012). "Fracture of the mandibular coronoid process — case report and review of the literature". Revista de chirurgie oro-maxilo-facială și implantologie|Rev. Chir. Oro-maxilo-fac. Implantol. (in Romanian). 3 (1): 1–4. ISSN 2069-3850. 58. Retrieved 2012-08-19.
External links
- lesson1 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Anatomy photo:22:os-1006 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Osteology of the Skull: Mandible of Intact Skull"
- "Anatomy diagram: 34256.000-2". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2013-06-11.