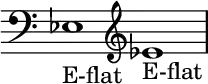
E♭ (E-flat) or mi bémol is the fourth semitone of the solfège.
It lies a diatonic semitone above D and a chromatic semitone below E, thus being enharmonic to D♯ (D-sharp) or re dièse. In equal temperament it is also enharmonic with F![]() (F-double flat). However, in some temperaments, D♯ is not the same as E♭. E♭ is a perfect fourth above B♭, whereas D♯ is a major third above B.
(F-double flat). However, in some temperaments, D♯ is not the same as E♭. E♭ is a perfect fourth above B♭, whereas D♯ is a major third above B.
When calculated in equal temperament with a reference of A above middle C as 440 Hz, the frequency of the E♭ above middle C (or E♭4) is approximately 311.127 Hz. See pitch (music) for a discussion of historical variations in frequency.
In German nomenclature, it is known as Es, sometimes (especially in the context of musical motifs, e.g. DSCH motif) abbreviated to S.
Designation by octave
| Scientific designation | Helmholtz designation | Octave name | Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| E♭−1 | E♭͵͵͵ or ͵͵͵E♭ or EEEE♭ | Subsubcontra | 9.723 |
| E♭0 | E♭͵͵ or ͵͵E♭ or EEE♭ | Subcontra | 19.445 |
| E♭1 | E♭͵ or ͵E♭ or EE♭ | Contra | 38.891 |
| E♭2 | E♭ | Great | 77.782 |
| E♭3 | e♭ | Small | 155.563 |
| E♭4 | e♭′ | One-lined | 311.127 |
| E♭5 | e♭′′ | Two-lined | 622.254 |
| E♭6 | e♭′′′ | Three-lined | 1244.508 |
| E♭7 | e♭′′′′ | Four-lined | 2489.016 |
| E♭8 | e♭′′′′′ | Five-lined | 4978.032 |
| E♭9 | e♭′′′′′′ | Six-lined | 9956.063 |
| E♭10 | e♭′′′′′′′ | Seven-lined | 19912.127 |
Scales
Common scales beginning on E♭
- E♭ major: E♭ F G A♭ B♭ C D E♭
- E♭ natural minor: E♭ F G♭ A♭ B♭ C♭ D♭ E♭
- E♭ harmonic minor: E♭ F G♭ A♭ B♭ C♭ D E♭
- E♭ melodic minor ascending: E♭ F G♭ A♭ B♭ C D E♭
- E♭ melodic minor descending: E♭ D♭ C♭ B♭ A♭ G♭ F E♭
Diatonic scales
Jazz melodic minor
- E♭ ascending melodic minor: E♭ F G♭ A♭ B♭ C D E♭
- E♭ Dorian ♭2: E♭ F♭ G♭ A♭ B♭ C D♭ E♭
- E♭ Lydian augmented: E♭ F G A B C D E♭
- E♭ Lydian dominant: E♭ F G A B♭ C D♭ E♭
- E♭ Mixolydian ♭6: E♭ F G A♭ B♭ C♭ D♭ E♭
- E♭ Locrian ♮2: E♭ F G♭ A♭ B
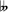 C♭ D♭ E♭
C♭ D♭ E♭ - E♭ altered: E♭ F♭ G♭ A
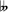 B
B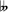 C♭ D♭ E♭
C♭ D♭ E♭
See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.