 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
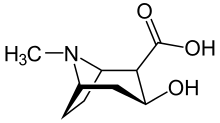
| IUPAC name
3β-Hydroxytropane-2β-carboxylic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,2R,3S,5S)-3-Hydroxy-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.879 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H15NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 185.223 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.293±0.06 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 198 to 199 °C (388 to 390 °F; 471 to 472 K) (hydrate) |
| Pharmacology | |
| Legal status |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Ecgonine (tropane derivative) is a tropane alkaloid found naturally in coca leaves. It has a close structural relation to cocaine: it is both a metabolite and a precursor, and as such, it is a controlled substance in many jurisdictions, as are some substances which can be used as precursors to ecgonine itself.
Structurally, ecgonine is a cycloheptane derivative with a nitrogen bridge. It is obtained by hydrolysis of cocaine with acids or alkalis, and crystallizes with one molecule of water, the crystals melting at 198–199 °C. It is levorotary, and on warming with alkalis gives iso-ecgonine, which is dextrorotary.[1]
It is a tertiary base, and has the properties of an acid and an alcohol. It is the carboxylic acid corresponding to tropine, for it yields the same products on oxidation, and by treatment with phosphorus pentachloride is converted into anhydroecgonine, C9H13NO2, which, when heated to 280 °C with hydrochloric acid, eliminates carbon dioxide and yields tropidine, C8H13N.[1]
See also
References
- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Ecgonine". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 8 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 870.