| Red-necked falcon | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Falco chicquera chicquera (India) | |
.jpg.webp) | |
| Falco chicquera ruficollis (Etosha, Namibia) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Falconiformes |
| Family: | Falconidae |
| Genus: | Falco |
| Species: | F. chicquera |
| Binomial name | |
| Falco chicquera Daudin, 1800 | |
| Subspecies | |
|
See text | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
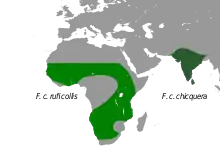
The red-necked falcon (Falco chicquera) is a bird of prey in the falcon family with two disjunct populations, one in India and the other in Africa. This medium-sized falcon has bluish grey wings and upper body, a chestnut red cap with short chin straps passing through the eye. The primary feathers of the wing are black and a single black band at the tip of the tail are distinctive. The Indian subspecies Falco chicquera chicquera also known as the red-headed merlin or red-headed falcon is found mainly in the open plains of the India Subcontinent although it is thought to have occurred further west in southeastern Iran. The subspecies Falco chicquera ruficollis found in sub-Saharan Africa is sometimes treated as a full species, the rufous-necked falcon (Falco ruficollis), on the basis of its well-separated geographic range and distinctive pattern. It appears very similar to the Indian form but has dark barring on the upperparts, a rufous breast band, and black moustachial and eye stripes. As in most falcons, the females are larger and falconers in India called the female turumti and the male as chatwa. They hunt in pairs mostly at dawn and dusk, capturing small birds, bats and squirrels.
Description

| Measurements | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominate[3] | |||
| Culmen | 19–24 mm (0.7–0.9 in) | ||
| 25 mm (0.98 in) | |||
| Wing | 190–207 mm (7.5–8.1 in) | ||
| 220–232 mm (8.7–9.1 in) | |||
| Tail | 124–137 mm (4.9–5.4 in) | ||
| 148–156 mm (5.8–6.1 in) | |||
| Tarsus | 35–40 mm (1.4–1.6 in) | ||
| 38–41 mm (1.5–1.6 in) | |||
| ruficollis[4] | |||
| Wing | 227–240 mm (8.9–9.4 in) | ||
| Weight | 193–239.4 g (6.8–8.4 oz) | ||
The red-necked falcon is a medium-sized, long-winged species with a bright rufous crown and nape. It is on average 30–36 cm (12–14 in) in length with a wingspan of 85 cm (33 in). The wings and upper parts are bluish grey and the tail has narrow bars, a broad subterminal black band tipped with white. The wingtip does not reach the tip of the tail at rest.[5] The second and third primaries are the longest and almost equal in length while the first is a fourth the length. The first two primaries are notched.[6] The legs, ceres and eyering are yellow. The tip of the bill is black while the basal portion is greenish yellow. The voice of this species is a shrill ki-ki-ki-ki. The sexes are similar except in size, males are smaller than females as is usual in falcons. Young birds are buff below with less extensive barring and duller upper plumage.[7]
Subspecies
The adult of the African subspecies Falco chicquera ruficollis (a full species, F. ruficollis, in many treatments) first described by William Swainson[8] in 1837 has a white face apart from black on the moustachial stripe. The upperparts are pale grey, with black primary wing feathers and the broad tail band. The underparts are white with dark barring on the underwings, lower breast, belly and undertail. There is a rufous foreneck band (not present in the Indian form). West African males are known to weigh between 139 and 178 grams, while females are found between 190 and 305 grams. The particularly large African birds from south of the Zambezi River are often separated as subspecies Falco chicquera horsbrughi, which was described by J. W. B. Gunning & Austin Roberts in 1911 on the basis of a single specimen,[9] but the size variation may be clinal and the subspecies may not be valid.
The Asian nominate subspecies Falco chicquera chicquera has rufous moustachial stripes, lacks the buff breast band, and is less extensively barred than the African form.
Taxonomy

The species was described on the basis of a specimen obtained by François Levaillant from Chandernagore in Bengal where he was told it went by the name of Chicquera.[10] This local name was probably attributed to this species by mistake as the name probably referred to a shikra.[11] Levaillant did not use binomials but called it Le Chicquera and François Marie Daudin gave it the binomial Falco chicquera in 1800.[12] Early authors placed it in the genus Aesalon along with the merlin and later in the genus Lithofalco. Others have placed it in the genus Chicquera or Hypotriorchis.[6]
Studies of molecular sequence divergence in the cytochrome b gene suggest that the African and Indian forms are distinctive due to separation for as long as 0.9 million years. With non-overlapping ranges they are often treated as full species.[9][13]
Habitat and distribution
In Africa, the red-necked falcon is found in semi-desert, savannah and other dry open country with some trees, but also riverine forest. It often perches and makes use of the crowns of Borassus palms (Borassus aethiopum) for breeding. They are mostly resident but may make nomadic movements in response to weather. In India, they are found in open habitats and is not found in dense forests or high hills. The nominate subspecies is believed to have occurred west until Iran although no records exist from there since 1970.[14] They were recorded breeding in 1911 by Nikolai Zarudny.[15] It is a winter vagrant in northern Sri Lanka[5] where it was first recorded by E.L. Layard.[16]
Behaviour
The red-necked falcon usually hunts in pairs, often at dawn and dusk, sometimes utilizing a technique in which one of the pair flies low and flushes up small birds while the other follows higher up and seizes the prey as it flushes from cover. They fly with a fast and dashing flight.[3][17][18]
It prefers to prey on birds found in open areas and some of the species it has been recorded to hunt are Eurasian tree sparrow (Passer montanus), house sparrow (Passer domesticus), white-browed wagtail (Motacilla madaraspatensis), rosy starling (Sturnus roseus), chestnut-tailed starling (Sturnus malabaricus), Indian cuckoo (Cuculus micropterus), Kentish plover (Charadrius alexandrinus), little ringed plover (Charadrius dubius), ashy-crowned finch-lark (Eremoptrix griseus), besides robins, quails, babblers, swifts, bulbuls, pipits, larks (mainly Calandrella, Alauda, Galerida sp.), pied cuckoo (Clamator jacobinus), rock pigeon (Columba livia), collared dove (Streptopelia decaocto), laughing dove (Streptopelia senegelensis), brown crake (Lanius cristatus), tailor bird (Orthotomus sutorius), brown shrike (Lanius cristatus), white-breasted kingfisher (Halcyon smyrnensis), little stint (Calidris minuta), plain martin (Riparia paludicola) and pied bushchat (Saxicola caprata). In addition mice, lizards, large insects are also taken.[19] In one study in Bangladesh, adults fed mainly on small sparrow sized birds (72%) and Pipistrellus bats (28%).[20] They may sometimes pirate prey obtained by other medium-sized raptors.[21] Prey may sometimes be cached and eaten subsequently.[22]

The red-necked falcon drinks water where available during the afternoons. This has been observed both in India and in Africa, where it sometimes visits waterholes.[23]
The breeding season in India is January to March. In Zambia, the breeding season begins in August. Pairs may indulge in courtship feeding in which the female feeds the male, an unusual behaviour that has also been noted in captivity.[18][24] This falcon usually reuses the old tree nest platforms, particularly of corvids, or lays its 3-5 eggs in a nest that it builds on the fork of a tall tree or in the crown of a palm tree. In Africa, they have been known to reuse the nests of pied crows (Corvus albus), African fish eagles (Halieaetus vocifer) on Acacia apart from building their own nest in Borassus palms. In India, the nest is often placed in a large mango tree (Mangifera indica) and concealed inside foliage. The nest territory is well-guarded and crows and kites driven away.[7] This falcon has been documented to nests in trees amidst dense human population.[23] The clutch consists of two to four eggs which are incubated only by the female which begins after the last egg of the clutch is laid. The eggs hatch after about 32 to 34 days and the newly hatched young are covered in white down and are brooded by the female for a week. The male brings food which is torn by the female and fed to the chicks. The young fledge in about 35 to 37 days in Africa and up to 48 days in India.[23][25][26]
In falconry
The turumti was a favourite among Indian falconers who would fly it especially at the Indian roller which would make evasive aerial manoeuvres that entertained the onlookers.[27] These falcons were caught using a bal-chatri, as they not only captured prey in the air like other falcons, but will also pursue on the ground and thereby could get entangled in the horsehair nooses.[11] Turumta was a name used in Iran for the merlin.[28]
Parasites and diseases
Captive birds can be affected by Newcastle disease virus,[29] as well as many parasites including Trichomonas (in subsp. ruficollis)[30] and nematodes such as Cyrnea eurycerca.[31]
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Falco chicquera". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22727778A94961899. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22727778A94961899.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ "Catalogue of the Birds of India, with remarks on their geographical description". Ibis. 5 (17): 1–31. 1863. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919x.1863.tb06042.x.
- 1 2 Ali, Salim, Ripley S.D (1978). Handbook of the Birds of India and Pakistan. Volume 1. New Delhi: Oxford University Press. pp. 359–360.
- ↑ Mendelsohn, J. M.; A. C. Kemp; H. C. Biggs; R. Biggs; C. J. Brown (1989). "Wing areas, wing loading and wing spans of 66 species of African raptors". Ostrich: Journal of African Ornithology. 60 (1): 35–42. doi:10.1080/00306525.1989.9634503.
- 1 2 Rasmussen, P.C. & J.C. Anderton (2005). Birds of South Asia. The Ripley Guide. Volume 2. Washington DC and Barcelona: Smithsonian Institution and Lynx Edicions. p. 113.
- 1 2 Blanford, W.T. (1895). The Fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Birds. Volume 3. London: Taylor and Francis. pp. 426–428.
- 1 2 Baker, E.C. Stuart (1928). The Fauna of British India including Ceylon and Burma. Birds. Volume 5 (2nd ed.). London: Taylor and Francis. pp. 47–49.
- ↑ Swainson, William (1837). The Natural History of the Birds of Western Africa. Volume 1. Edinburgh: W.H. Lizars. pp. 107–108.
- 1 2 Wink, Michael; Sauer-Gürth, Hedi (2000). "Advances in the molecular systematics of African raptors" (PDF). In Chancellor, R.D.; B.-U. Meyburg (eds.). Raptors at Risk. pp. 135–147.
- ↑ Levaillant, F. (1799). Histoire naturelle des oiseaux d'Afrique. Volume 1. Paris: J.H.Fuchs. pp. 128–129.
- 1 2 Phillott, D.C. (1907). "Note on the Red-headed Merlin (Aesalon chicquera)". Journal and Proceedings of the Asiatic Society of Bengal. New Series. 3 (6): 395–399.
- ↑ Daudin, F.M. (1800). Traité élémentaire et complet d'ornithologie, ou, Histoire naturelle des oiseaux. Volume 2. pp. 121–122.
- ↑ Wink, M.; Seibold, I.; Lofikhah, F.; Bednarek, W. (1998). "Molecular systematics of Holarctic Raptors (Order Falconiformes)" (PDF). In Chancellor, R.D.; B.-U. Meyburg; J.J. Ferrero (eds.). Holarctic Birds of Prey. pp. 29–48.
- ↑ Scott, Derek A. (2008). "Rare Birds in Iran in the Late 1960s and 1970s" (PDF). Podoces. 3 (1/2): 1–30.
- ↑ Zarudny, N.A. (1911). "Verzeichnis der Vögel Persiens". Journal für Ornithologie (in German). 59 (2): 185–241. doi:10.1007/bf02091053. S2CID 26703364.
- ↑ Wait, W.E. (1921). "The owls and diurnal birds of prey found in Ceylon". Spolia Zeylanica. 11: 317–380.
- ↑ Radcliffe, E. Delme (1871). Notes on falconidae used in falconry. Southsea: Mills and Son. pp. 13–14.
- 1 2 Subramanya, S. (1985). "Hunting and feeding habits of the Redheaded Merlin Falco chicquera". Newsletter for Birdwatchers. 25 (1&2): 4–8.
- ↑ Naoroji, Rishad (2007). Birds of Prey of the Indian Subcontinent. Om Books International. pp. 564–571.
- ↑ Foysal, Mohammod (2015). "Observations of Red-headed Falcon Falco chicquera (Aves: Falconiformes: Falconidae) nest at Keraniganj, Dhaka, Bangladesh, with a focus on post-fledging behaviour" (PDF). Journal of Threatened Taxa. 7 (5): 7138–7145. doi:10.11609/jott.o3895.7138-45.
- ↑ Clark, William S.; Schmitt, N. John (1993). "Red-headed falcon pirates prey from Montagu's harrier" (PDF). Journal of Field Ornithology. 64 (2): 244–245.
- ↑ Subramanya, S (1980). "Redheaded Merlin Falco chicquera". Newsletter for Birdwatchers. 20 (2): 3–5.
- 1 2 3 Naoroji, Rishad (2011). "Breeding of the Red-headed Falcon Falco chicquera in Saurashtra, Gujarat, India" (PDF). Forktail. 27: 1–6.
- ↑ Olwagen, C.D.; Olwagen, K. (1984). "Propagation of captive red-necked falcons Falco chicquera". Koedoe. 27: 45–59. doi:10.4102/koedoe.v27i1.550.
- ↑ Osborne, Timothy O. (1981). "Ecology of the red-necked falcon Falco chicquera in Zambia". Ibis. 123 (3): 289–297. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919X.1981.tb04031.x.
- ↑ Subramanya, S (1982). "Nesting of Redheaded Merlin (Falco chicquera Daudin) in Bangalore, Karnataka". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 79 (2): 412–413.
- ↑ Jerdon, T.C. (1862). The Birds of India. Volume 1. Calcutta: Military Orphan Press. pp. 36–38.
- ↑ Phillott, D.C. (1908). The Qawanin u's-Sayyad of Khuda Yar Khan Abbasi. Calcutta: Asiatic Society of Bengal. p. ix.
- ↑ Chu, H.P.; E.W. Trow; A.G. Greenwood; A.R. Jennings & I.F. Keymer (1976). "Isolation of Newcastle disease virus from birds of prey". Avian Pathology. 5 (3): 227–233. doi:10.1080/03079457608418189. PMID 18777349.
- ↑ Redig, Patrick (1993). Raptor Biomedicine Hardcover. University of Minnesota Press. p. 24. ISBN 978-0816622191.
- ↑ Kumar, P.; Gupta, S. P. (1980). "Hadjelia tringae sp.n. (Spirurata) from gizzard of Tringa hypoleucos (L.)". Helminthologia. 17 (2): 109–116.
External links
- Red-necked falcon - Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds.
