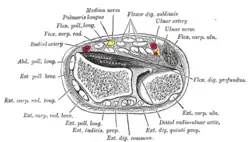
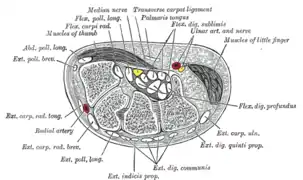
| Anterior compartment of the forearm | |
|---|---|
 Cross-section through the middle of the forearm. (Anterior compartment is at top; posterior compartment is at bottom.) | |
| Details | |
| Artery | ulnar artery |
| Nerve | median nerve (anterior interosseous nerve), ulnar nerve (muscular branches of ulnar nerve) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | compartimentum antebrachii anterius |
| TA98 | A04.6.01.004 |
| TA2 | 2476 |
| FMA | 12255 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The anterior compartment of the forearm (or flexor compartment)[1] contains the following muscles:[2]
| Level | Muscle | Extrinsic/Intrinsic | Nerve |
| superficial | flexor carpi radialis | extrinsic | median |
| superficial | palmaris longus | extrinsic | median |
| superficial | flexor carpi ulnaris | extrinsic | ulnar |
| superficial | pronator teres | intrinsic | median |
| superficial (or intermediate) | flexor digitorum superficialis | extrinsic | median |
| deep | flexor digitorum profundus | extrinsic | ulnar + median (as anterior interosseous nerve) |
| deep | flexor pollicis longus | extrinsic | median (as anterior interosseous nerve) |
| deep | pronator quadratus | intrinsic | median (as anterior interosseous nerve) |
The muscles are largely involved with flexion and supination.[2] The superficial muscles have their origin on the common flexor tendon.[2] The ulnar nerve and artery are also contained within this compartment.[2] The flexor digitorum superficialis lies in between the other four muscles of the superficial group and the three muscles of the deep group. This is why it is also classified as the intermediate group.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "Topographical Anatomy of the Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically". University of Arkansas. Archived from the original on 2008-01-19. Retrieved 2011-10-02.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Moore, Keith L.; Dalley, Arthur F.; Agur, Anne M. R. (2010). "Upper Limb". Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 6th Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 746–749. ISBN 978-0-7817-7525-0.
External links
- MedicalMnemonics.com: 273 1117
- Topographical Anatomy of the Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically Archived 2008-01-19 at the Wayback Machine University of Arkansas
Additional images
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.