| Cheat River | |
|---|---|
 The Cheat River Gorge, as viewed from Cooper's Rock Overlook | |
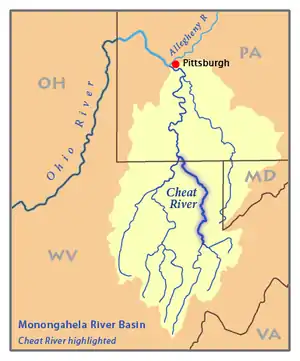 Map of the Monongahela River basin, with the Cheat River highlighted. | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Pennsylvania, West Virginia |
| County | Fayette PA, Monongalia WV, Preston WV, Tucker WV |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Shavers Fork |
| • location | West Virginia |
| • coordinates | 38°23′50″N 79°59′09″W / 38.39722°N 79.98583°W |
| • elevation | 4,620 ft (1,410 m) |
| 2nd source | Black Fork |
| • location | Hendricks, West Virginia |
| • coordinates | 39°04′20″N 79°37′45″W / 39.07222°N 79.62917°W |
| • elevation | 1,700 ft (520 m) |
| Source confluence | |
| • location | Parsons, WV |
| • coordinates | 39°07′01″N 79°40′51″W / 39.11694°N 79.68083°W |
| • elevation | 1,621 ft (494 m) |
| Mouth | Monongahela River[1] |
• location | Point Marion, PA |
• coordinates | 39°44′34″N 79°54′08″W / 39.74278°N 79.90222°W |
• elevation | 760 ft (230 m) |
| Length | 78 mi (126 km)[2] |
| Basin size | 1,423 sq mi (3,690 km2)[2] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Rowlesburg, WV[3] |
| • average | 3,880 cu ft/s (110 m3/s) |
| • minimum | 908 cu ft/s (25.7 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 53,400 cu ft/s (1,510 m3/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Parsons, WV[4] |
| • average | 3,700 cu ft/s (100 m3/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | generally north |
| River system | Monongahela River |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Brannons Run, Clover Run, Upper Jonathan Run, Jonathan Run, Bull Run, Bearwallow Run, Licking Creek, Louse Camp Run, Ford Run, Muddy Run, Big Run, Keyser Run, Scott Run, Little Buffalo Creek, Buffalo Creek, Tray Run, Buckhorn Run, Pringle Run, Lick Run, Heather Run, Greens Run, Laurel Run, Hackelberry Run, Gum Run, Bull Run, Bee Run, Buzzard Run, Maple Run, Crammeys Run |
| • right | Devils Dump Run, Wolf Run, Mill Run, Dry Run, Horseshoe Run, Dry Run, Minear Run, Clay Lick, Laurel Run, Tobes Run, Stave Run, Panther Run, Glades Run, Wolf Creek, Madison Run, Saltlick Creek, Hickory Bearpen Run, Bearwallow Run, Stamping Ground Run, Joes Run, Buffalo Run, Ashpole Run, Elsey Run, Daugherty Run, Roaring Creek, Muddy Creek, Beech Run, Conner Run, Gibson Run, Big Sandy Creek, Big Run, Christopher Run, Scott Run, Quarry Run, Kelley Run, Coles Run, Morgan Run, Rubles Run, Grassy Run |
The Cheat River is a 78.3-mile-long (126.0 km)[5] tributary of the Monongahela River in eastern West Virginia and southwestern Pennsylvania in the United States. Via the Ohio River, the Cheat and Monongahela are part of the Mississippi River watershed. Owing to the ruggedness of the surrounding Allegheny Mountains, the Cheat remains largely remote with few settlements or developments along its banks. Its headwaters are in the Cheat-Potomac Ranger District of the Monongahela National Forest.
Geography
The Cheat is formed at Parsons, West Virginia, by the confluence of Shavers Fork and Black Fork. Black Fork is fed by the Blackwater River and by the Dry, Glady, and Laurel Forks — these are traditionally referred to as the five Forks of Cheat. (The "High Falls of Cheat" [15 feet/4.6 m high] is a few miles upstream of Bemis on Shavers Fork.) From Parsons the Cheat River flows generally northward through Tucker and Preston counties, past the towns of Rowlesburg and Albright. It then flows through an impressive gorge — Cheat Canyon — northeastwardly from Albright, collecting Big Sandy Creek before entering Monongalia County, where a hydro-electric dam just south of the Pennsylvania border causes it to widen as the Cheat Lake reservoir. It then flows for a short distance through southwestern Fayette County, Pennsylvania, before joining the Monongahela River at Point Marion, Pennsylvania. Upstream of its dam, the Cheat is one of the largest undammed watersheds in the eastern United States.
Cheat Mountain, a high and rugged ridge, runs about 50 miles (80 km) southward from its northernmost tip, just a few miles west of the confluence at Parsons.
Name
The Delaware (Lenape) Indian name for Cheat was reportedly Ach-sin-ha-nac, meaning "stony river". "Cheat River" is variously reported to have been named for (1) a French explorer (or an Indian) named Cheat or Chaet, (2) an abundance of cheat grass along its banks (possibly a misidentification of frost-killed wheat), or (3) deceptively deep sections containing whirlpools that presumably "cheated" men of their lives by drowning them.[6] None of these theories have strong documentary support, but the latter is the most often cited.
Historical names
According to the Geographic Names Information System,[1] the Cheat River has formerly been known as:
- Ach-sin-ha-nac
- Achsinhanac
- Cheal River
- Chealt River
- Eleat River
- Wilmoths River
History
18th century
In 1756, the Eckarly family became the first white settlers to move into the Cheat River Valley when they lodged at Dunkard's Bottom in what is now Preston County, West Virginia. They, and a few in the surrounding region, were soon forced to abandon their homesteads by hostile Indians and no further attempts at settlement were made until after the conclusion of the French and Indian War (1754-1763).[7] In October 1767, Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon completed their famous survey of the Maryland–Pennsylvania border shortly after extending it to a crossing of the Cheat River just above its confluence with the Monongahela. (The party was forced to stop a few miles west at Dunkard Creek near present-day Mount Morris, Pennsylvania. Their Iroquois guides had refused to go any further, having reached the border of their lands with the Lenape, with whom they were engaged in hostilities.[8]) According to George W. Atkinson (1876), "From 1765 to 1774 there were comparatively few attacks made upon the white colonists by the Indians. The Treaty of Paris [1763] resulted in general peace along the frontiers, had been pretty generally adhered to by all the savage tribes. The peace, however, which had for nine years blessed and fostered the frontier settlements, was suddenly broken by the murder of several friendly Indians, in 1774, on the Monongahela and Cheat rivers. This unfortunate aggression on the part of these white men gave rise to a general raid by the Indians upon all the settlements of the frontier."[9]
The Cheat River Valley was part of a much larger area disputed in the 1770s by the Colonies of Pennsylvania and Virginia. (This was before the parties agreed to extend the Mason–Dixon line westward from Maryland.) Virginia attempted to administer this vast region as the District of West Augusta between 1774 and 1776, after which it subdivided the District into three counties, the Cheat River becoming part of Monongalia County. Meanwhile, Pennsylvania tried to oversee it as part of the overlapping Westmoreland County. After additional surveys, and the resolution of the Virginia-Pennsylvania border dispute in the 1780s, it became established that all but the lowermost 3 miles of the Cheat were within the state of Virginia. The Cheat River country remained part of Monongalia County until 1791 when that county was divided into a smaller Monongalia County and Randolph County.[10]
19th century
The Virginia General Assembly authorized the first two ferries on the Cheat in 1806. On January 2, a ferry in Monongalia County was approved on Charles Stuart property to James Stafford property. On January 18, the Assembly authorized the second ferry in Monongalia County from the forge location of Samuel Jackson to Charles Magill property. Another act in 1806 authorized to conduct a lottery to fund the construction of a toll bridge across Cheat River near Dunkard's Bottom. Concerned included Michael Kern, John Steally, Augustus Werninger, Ralph Barkshire, and William N. Jarrett. The Assembly also authorized in 1806 the construction of mill dams across the Monongahela River, Cheat River, Tygart Valley River, or the West Fork of the Monongahela River.[11]
Along with the rest of western Virginia, the Cheat River Valley became part of the new state of West Virginia in 1863.
20th century
A state militia facility, Camp Dawson, was established on the banks of the Cheat in Preston County in 1909 and continues in operation today.
1985 flood
In November 1985, heavy rains caused a massive flood on the Cheat, essentially wiping out the small town of Albright. The river flow was estimated at 190,000 cubic feet per second, much larger than normal flows ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 cubic feet per second. The massive flood also caused the Cheat River to leave its banks and flood the small town of Rowlesburg. The town lost many businesses, and many families left their homes or the land that they owned. The flood also wiped out the school in Rowlesburg, which caused the consolidation of a high school for the county. The devastation was caused not so much by the steady-state flow of water, but rather by the repeated damming of the river by debris under the various road and railroad bridges that crossed the Cheat. Thus as the flood proceeded down the river, the water would rise behind the obstructed bridge, break through the inadvertent dam, and pick up more debris that would block the river at the next bridge site, repeating the process.
Pollution

In the vicinity of Albright, the Cheat has been plagued by pollution, notably acid mine drainage. Although the rocks downstream of Albright have been stained a rust brown, and the river has a very low fish population below Albright, water quality has been making slow improvements since the 1990s. Friends of the Cheat, the local river advocacy organization, has been instrumental in promoting remediation, cleanup, river stewardship, and education.

Whitewater recreation
The Cheat Canyon section of the Cheat River (from Albright to Jenkinsburg, West Virginia), which features Class IV rapids (and Class V rapids at upper levels), has become a favorite destination for whitewater kayaking and rafting. On the first weekend in May of every year, paddlers gather from many states to attend the Cheat Festival. A very popular whitewater race—the Cheat River Race—takes place in the 10-mile (16 km) Cheat Canyon on the Friday of that weekend. Unlike the overwhelming majority of whitewater races, which employ a staggered start, this race uses a mass start (in which all participants start at the same time). For the first few miles, paddlers must avoid one another, in addition to the whitewater hazards that the river presents. The race, which usually attracts 150 people, is often cited as the largest whitewater race in existence.[12]
The Cheat Narrows section of the Cheat River (upstream of Albright) is also utilized by whitewater paddlers, and features Class II and III rapids.
See also
References
- 1 2 U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Cheat River
- 1 2 Kosky, James P.E.; Lessons Learned: Cheat River and Tygart River Flood Warning Systems; retrieved from stormwatch.com March 13, 2007.
- ↑ United States Geological Survey; USGS 03069870 CHEAT RIVER AT HWY 50 NEAR ROWLESBURG, WV; retrieved March 13, 2007.
- ↑ United States Geological Survey; USGS 03069500 CHEAT RIVER NEAR PARSONS, WV; retrieved March 13, 2007.
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline data. The National Map Archived 2012-03-29 at the Wayback Machine, accessed August 15, 2011
- ↑ Kenny, Hamill (1945). West Virginia Place Names: Their Origin and Meaning, Including the Nomenclature of the Streams and Mountains. Piedmont, WV: The Place Name Press. p. 167.
- ↑ Writers Program, Works Project Administration (1941), West Virginia: A Guide to the Mountain State; New York, Oxford University Press, pg 36.
- ↑ Danson, Edwin (2001). Drawing the Line: How Mason and Dixon Surveyed the Most Famous Border in America. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 178–79.
- ↑ Atkinson, George W. (1876). History of Kanawha County. Charleston, WV: West Virginia Journal.
- ↑ Preston County was created from Monongalia in 1818 and Tucker County from Randolph in 1856. Since then, the Cheat has flowed through these three (West) Virginia counties and one Pennsylvania county.
- ↑ West Virginia Division of Culture and History. Charleston, WV. "West Virginia Archives and History."
- ↑ "Cheat River Race". Retrieved October 26, 2011.