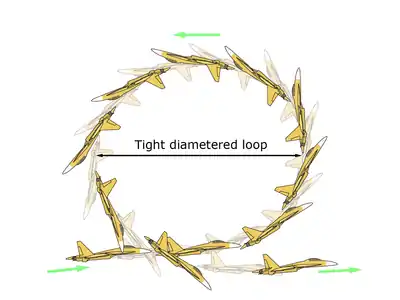
The "Kulbit" (also known as the "Frolov chakra") is an aerial maneuver developed by Russian pilots in which the aircraft performs an extremely tight loop, often not much wider than the length of the aircraft itself. It differs from the traditional inside loop as it uses post-stall maneuvering capabilities,[1] a type of supermaneuverability.[1] Like most post-stall maneuvers, it demonstrates pitch control outside the normal flight envelope wherein pitch control is made possible by having aerodynamic flow over the aircraft's elevators or stabilators.
The name "Kulbit" is derived from the Russian Кульбит, meaning "somersault". The alternate name, "Frolov's Chakra", refers to Russian test pilot Yevgeni Frolov, the pilot who first carried out the maneuver, while "chakra" is a yogic term, meaning "vortex" or "whirlpool".
The Kulbit drastically decreases the aircraft's speed and could theoretically be used to cause a pursuing aircraft to overshoot its target. The maneuver is closely related to the famous "Pugachev's Cobra" maneuver, but the Kulbit completes the loop that the Cobra almost immediately cuts off.
Aircraft known to be able to execute the "Kulbit"
The following aircraft are currently known to be able to execute the "Kulbit":
- F-22 Raptor[2][3]
- MiG-29OVT[4]
- Sukhoi Su-30
- Sukhoi Su-35[5]
- Sukhoi Su-37[6]
- Sukhoi Su-47 Berkut
- Sukhoi Su-57
All have performed the Kulbit in airshow displays in the past.
References
- 1 2 "Fighter Technology of the Future". Archived from the original on 2012-02-07. Retrieved 2007-08-22.
- ↑ Archived at Ghostarchive and the Wayback Machine: "F-22 Raptor Performs Somersault (Kulbit)". YouTube.
- ↑ F-22 Raptor Kulbit video
- ↑ Double Kulbit by MiG-29OVT
- ↑ "Летчики ВВО проверили новейшие истребители Су-35 на сверхманевренность". 4 March 2015.
- ↑ Kulbit by SU-37