 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
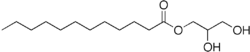
| IUPAC name
2,3-Dihydroxypropyl dodecanoate | |
| Other names
Glyceryl laurate; Monolauroylglycerin; Glycerol monolaurate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.024 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H30O4 | |
| Molar mass | 274.401 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 63 °C |
| Boiling point | 186 °C / 1mmHg |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Monolaurin (abbreviated GML; also called glycerol monolaurate, glyceryl laurate, and 1-lauroyl-glycerol) is a monoglyceride. It is the mono-ester formed from glycerol and lauric acid. Its chemical formula is C15H30O4.
Occurrence
Monolaurin is found in coconut oil and may be similar to other monoglycerides found in human breast milk.[1]
Lauric acid can be ingested in coconut oil and the human body converts it into monolaurin. Furthermore, coconut oil, coconut cream, grated coconut and others products are sources of lauric acid and, consequently, monolaurin.[2]
Uses
Monolaurin is most commonly used as a surfactant in cosmetics, such as deodorants. As a food additive it is also used as an emulsifier or preservative. Monolaurin is also marketed as a dietary supplement.

Monolaurin is sold as a dietary supplement and as an ingredient in certain foods. The United States Food and Drug Administration categorizes it as generally recognized as safe.[3]
References
- ↑ Hegde, BM (2006). "View Point: Coconut Oil – Ideal Fat next only to Mother's Milk (Scanning Coconut's Horoscope)" (PDF). Journal of the Indian Academy of Clinical Medicine. 7: 16–19.
- ↑ Lieberman, S.; Enig, M. G.; Preuss, H. G. (2006). "A Review of Monolaurin and Lauric Acid: Natural Virucidal and Bactericidal Agents". Alternative and Complementary Therapies. 12 (6): 310–314. doi:10.1089/act.2006.12.310.
- ↑ "Code of Federal Regulations title 21". www.accessdata.fda.gov.