| Great complex icosidodecahedron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Uniform star polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 32, E = 60 (30x2) V = 12 (χ = -16) |
| Faces by sides | 20{3}+12{5/2} |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Wythoff symbol | 5 | 3 5/3 |
| Symmetry group | Ih, [5,3], *532 |
| Index references | U-, C-, W- |
| Dual polyhedron | Great complex icosidodecacron |
| Vertex figure | 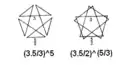 (3.5/3)5 (3.5/2)5/3 |
| Bowers acronym | Gacid |
In geometry, the great complex icosidodecahedron is a degenerate uniform star polyhedron. It has 12 vertices, and 60 (doubled) edges, and 32 faces, 12 pentagrams and 20 triangles. All edges are doubled (making it degenerate), sharing 4 faces, but are considered as two overlapping edges as topological polyhedron.
It can be constructed from a number of different vertex figures.
As a compound
The great complex icosidodecahedron can be considered a compound of the small stellated dodecahedron, {5/2,5}, and great icosahedron, {3,5/2}, sharing the same vertices and edges, while the second is hidden, being completely contained inside the first.
See also
References
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.

