| Hip bone | |
|---|---|
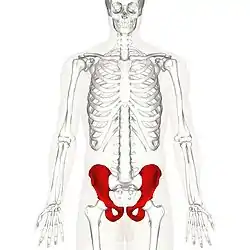 Position of the hip bones (shown in red) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | os coxae, os innominatum |
| MeSH | D010384 |
| TA98 | A02.5.01.001 |
| TA2 | 1307 |
| FMA | 16580 16585, 16580 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone[1] or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and the pubis.
The two hip bones join at the pubic symphysis and together with the sacrum and coccyx (the pelvic part of the spine) comprise the skeletal component of the pelvis – the pelvic girdle which surrounds the pelvic cavity. They are connected to the sacrum, which is part of the axial skeleton, at the sacroiliac joint. Each hip bone is connected to the corresponding femur (thigh bone) (forming the primary connection between the bones of the lower limb and the axial skeleton) through the large ball and socket joint of the hip.[2]
Structure
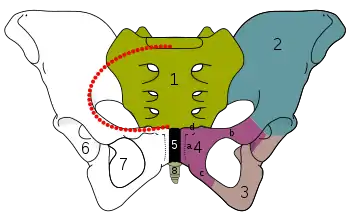
2–4. Hip bone (os coxae)
1. Sacrum (os sacrum), 2. Ilium (os ilium), 3. Ischium (os ischii)
4. Pubic bone (os pubis) (4a. corpus, 4b. ramus superior, 4c. ramus inferior, 4d. tuberculum pubicum)
5. Pubic symphysis, 6. Acetabulum (of the hip joint), 7. Obturator foramen, 8. Coccyx/tailbone (os coccygis)
Dotted. Linea terminalis of the pelvic brim.
The hip bone is formed by three parts: the ilium, ischium, and pubis. At birth, these three components are separated by hyaline cartilage. They join each other in a Y-shaped portion of cartilage in the acetabulum. By the end of puberty the three regions will have fused together, and by the age 25 they will have ossified. The two hip bones join each other at the pubic symphysis. Together with the sacrum and coccyx, the hip bones form the pelvis.[2]
Ilium
Ilium (plural ilia) is the uppermost and largest region. It makes up two fifths of the acetabulum. It is divisible into two parts: the body and the ala or wing of ilium; the separation is indicated on the top surface by a curved line, the arcuate line, and on the external surface by the margin of the acetabulum. The body of ilium forms the sacroiliac joint with the sacrum. The edge of the wing of ilium forms the S-shaped iliac crest which is easily located through the skin. The iliac crest shows clear marks of the attachment of the three abdominal wall muscles.[2]
Ischium
The ischium forms the lower and back part of the hip bone and is located below the ilium and behind the pubis. The ischium is the strongest of the three regions that form the hip bone. It is divisible into three portions: the body, the superior ramus, and the inferior ramus. The body forms approximately one-third of the acetabulum.
The ischium forms a large swelling, the tuberosity of the ischium, also referred to colloquially as the "sit bone". When sitting, the weight is frequently placed upon the ischial tuberosity. The gluteus maximus covers it in the upright posture, but leaves it free in the seated position.[2]
Pubis
The pubic region or pubis is the ventral and anterior of the three parts forming the hip bone. It is divisible into a body, a superior ramus, and an inferior ramus. The body forms one-fifth of the acetabulum. The body forms the wide, strong, medial and flat portion of the pubic bone which unites with the other pubic bone in the pubic symphysis.[2] The fibrocartilaginous pad which lies between the symphysial surfaces of the coxal bones, that secures the pubic symphysis, is called the interpubic disc.
Pelvic brim
The pelvic brim is a continuous oval ridge of bone that runs along the pubic symphysis, pubic crests, arcuate lines, sacral alae, and sacral promontory.[3]
False pelvis, pelvic inlet, and ramus
The false pelvis is that portion superior to the pelvic brim; it is bounded by the alae of the ilia laterally and the sacral promontory and lumbar vertebrae posteriorly.[3]
The true pelvis is the region inferior to the pelvic brim that is almost entirely surrounded by bone.[3]
The pelvic inlet is the opening delineated by the pelvic brim. The widest dimension of the pelvic inlet is from left to right, that is, along the frontal plane.[3] The pelvic outlet is the margin of the true pelvis. It is bounded anteriorly by the pubic arch, laterally by the ischia, and posteriorly by the sacrum and coccyx.[3]
The superior pubic ramus is a part of the pubic bone which forms a portion of the obturator foramen. It extends from the body to the median plane where it articulates with its fellow of the opposite side. It is conveniently described in two portions: a medial flattened part and a narrow lateral prismoid portion. The inferior pubic ramus is thin and flat. It passes laterally and downward from the medial end of the superior ramus. It becomes narrower as it descends and joins with the inferior ramus of the ischium below the obturator foramen.
Development and sexual dimorphism
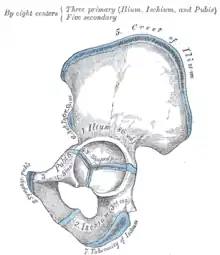
The hip bone is ossified from eight centers: three primary, one each for the ilium, ischium, and pubis, and five secondary, one each for the iliac crest, the anterior inferior spine (said to occur more frequently in the male than in the female), the tuberosity of the ischium, the pubic symphysis (more frequent in the female than in the male), and one or more for the Y-shaped piece at the bottom of the acetabulum.
The centers appear in the following order: in the lower part of the ilium, immediately above the greater sciatic notch, about the eighth or ninth week of fetal life; in the superior ramus of the ischium, about the third month; in the superior ramus of the pubis, between the fourth and fifth months. At birth, the three primary centers are quite separate, the crest, the bottom of the acetabulum, the ischial tuberosity, and the inferior rami of the ischium and pubis being still cartilaginous.
By the seventh or eighth year, the inferior rami of the pubis and ischium are almost completely united by bone. About the thirteenth or fourteenth year, the three primary centers have extended their growth into the bottom of the acetabulum, and are there separated from each other by a Y-shaped portion of cartilage, which now presents traces of ossification, often by two or more centers. One of these, the os acetabuli, appears about the age of twelve, between the ilium and pubis, and fuses with them about the age of eighteen; it forms the pubic part of the acetabulum. The ilium and ischium then become joined, and lastly the pubis and ischium, through the intervention of this Y-shaped portion.

At about the age of puberty, ossification takes place in each of the remaining portions, and they join with the rest of the bone between the twentieth and twenty-fifth years. Separate centers are frequently found for the pubic tubercle and the ischial spine, and for the crest and angle of the pubis. The proportions of the female hip bone may affect the ease of passage of the baby during childbirth.
Muscle attachments
Several muscles attach to the hip bone including the internal muscles of the pelvic, abdominal muscles, back muscles, all the gluteal muscles, muscles of the lateral rotator group, hamstring muscles, two muscles from the anterior compartment of the thigh.
Abdominal muscles
- The abdominal external oblique muscle attaches to the iliac crest.
- The abdominal internal oblique muscle attaches to pecten pubis.
- The transversus abdominis muscle attaches to the pubic crest and pecten pubis via a conjoint tendon
Back muscles
- The multifidus muscle in the sacral region attaches to the medial surface of posterior superior iliac spine, the posterior sacroiliac ligaments and several places to the sacrum.
Gluteal muscles
- The gluteus maximus muscle arises from the posterior gluteal line of the inner upper ilium, and the rough portion of bone including the iliac crest, the fascia covering the gluteus medius (gluteal aponeurosis), as well as the sacrum, coccyx, the erector spinae (lumbodorsal fascia), the sacrotuberous ligament.
- The gluteus medius muscle: originates on the outer surface of the ilium between the iliac crest and the posterior gluteal line above, and the anterior gluteal line below. The gluteus medius also originates from the gluteal aponeurosis that covers its outer surface.
- Gluteus minimus muscle originates between the anterior and inferior gluteal lines, and from the margin of the greater sciatic notch.
Lateral rotator group
- The piriformis muscle originates from the superior margin of the greater sciatic notch (as well as the sacroiliac joint capsule and the sacrotuberous ligament and part of the spine and sacrum.
- The superior gemellus muscle arises from the outer surface of the ischial spine
- The obturator internus muscle arises from the inner surface of the antero-lateral wall of the hip bone, where it surrounds the greater part of the obturator foramen, being attached to the inferior rami of the pubis and ischium, and at the side to the inner surface of the hip bone below and behind the pelvic brim, reaching from the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen above and behind to the obturator foramen below and in front. It also arises from the pelvic surface of the obturator membrane except in the posterior part, from the tendinous arch, and to a slight extent from the obturator fascia, which covers the muscle.
- The inferior gemellus muscle arises from the upper part of the tuberosity of the ischium, immediately below the groove for the obturator internus tendon.
- The obturator externus muscle arises from the margin of bone immediately around the medial side of the obturator foramen, from the rami of the pubis, and the inferior ramus of the ischium; it also arises from the medial two-thirds of the outer surface of the obturator membrane, and from the tendinous arch.
Hamstrings
- The long head biceps femoris arises from the lower and inner impression on the back part of the tuberosity of the ischium, by a tendon common to it and the semitendinosus, and from the lower part of the sacrotuberous ligament;[4]
- The semitendinosus arises from the lower and medial impression on the tuberosity of the ischium, by a tendon common to it and the long head of the biceps femoris; it also arises from an aponeurosis which connects the adjacent surfaces of the two muscles to the extent of about 7.5 cm. from their origin.
- The semimembranosus arises from the lower and medial impression on the tuberosity of the ischium
Anterior compartment of thigh
- The rectus femoris muscle arises by two tendons: one, the anterior or straight, from the anterior inferior iliac spine; the other, the posterior or reflected, from a groove above the rim of the acetabulum.
- The sartorius muscle arises by tendinous fibres from the anterior superior iliac spine,
Shoulder muscles
- The latissimus dorsi muscle attaches to the iliac crest and several places on the spine and ribs.
Clinical significance
Fractures
Fractures of the hip bone are termed pelvic fractures, and should not be confused with hip fractures, which are actually femoral fractures[5] that occur in the proximal end of the femur.
Preparation for childbirth
Pelvimetry is the assessment of the female pelvis[6] in relation to the birth of a baby in order to detect an increased risk for obstructed labor.
Evolution of the pelvis in animals
The hip bone first appears in fishes, where it consists of a simple, usually triangular bone, to which the pelvic fin articulates. The hip bones on each side usually connect with each other at the forward end, and are even solidly fused in lungfishes and sharks, but they never attach to the vertebral column.[7]
In the early tetrapods, this early hip bone evolved to become the ischium and pubis, while the ilium formed as a new structure, initially somewhat rod-like in form, but soon adding a larger bony blade. The acetabulum is already present at the point where the three bones meet. In these early forms, the connection with the vertebral column is not complete, with a small pair of ribs connecting the two structures; nonetheless the pelvis already forms the complete ring found in most subsequent forms.[7]
In practice, modern amphibians and reptiles have substantially modified this ancestral structure, based on their varied forms and lifestyles. The obturator foramen is generally very small in such animals, although most reptiles do possess a large gap between the pubis and ischium, referred to as the thyroid fenestra, which presents a similar appearance to the obturator foramen in mammals. In birds, the pubic symphysis is present only in the ostrich, and the two hip bones are usually widely separated, making it easier to lay large eggs.[7]
In therapsids, the hip bone came to rotate counter-clockwise, relative to its position in reptiles, so that the ilium moved forward, and the pubis and ischium moved to the rear. The same pattern is seen in all modern mammals, and the thyroid fenestra and obturator foramen have merged to form a single space. The ilium is typically narrow and triangular in mammals, but is much larger in ungulates and humans, in which it anchors powerful gluteal muscles. Monotremes and marsupials also possess a fourth pair of bones, the prepubes or "marsupial bones", which extend forward from the pubes, and help to support the abdominal muscles and, in marsupials, the pouch. In placental mammals, the pelvis as a whole is generally wider in females than in males, to allow for the birth of the young.[7]
The pelvic bones of cetaceans were formerly considered to be vestigial, but they are now known to play a role in sexual selection.[8]
Additional images
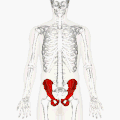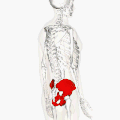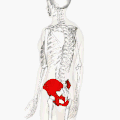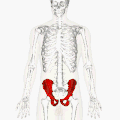 Position of the hip bones (shown in red). Animation.
Position of the hip bones (shown in red). Animation..gif) Right hip bone. Animation.
Right hip bone. Animation.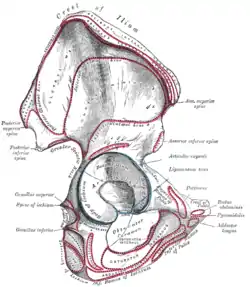 Right hip bone. External surface.
Right hip bone. External surface.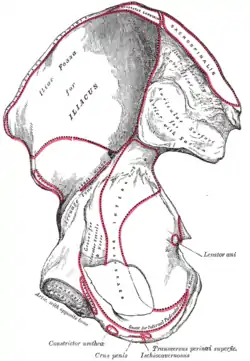 Right hip bone. Internal surface.
Right hip bone. Internal surface.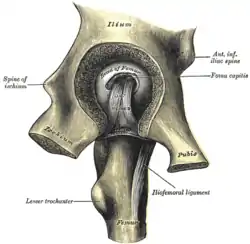 Left hip-joint, opened by removing the floor of the acetabulum from within the pelvis.
Left hip-joint, opened by removing the floor of the acetabulum from within the pelvis. Hip bone.Medial view.
Hip bone.Medial view. Hip bone. Lateral view.
Hip bone. Lateral view.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 231 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 231 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ "hip bone". Merriam Webster.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Bojsen-Møller, Finn; Simonsen, Erik B.; Tranum-Jensen, Jørgen (2001). Bevægeapparatets anatomi [Anatomy of the Locomotive Apparatus] (in Danish) (12th ed.). Munksgaard Danmark. pp. 237–239. ISBN 978-87-628-0307-7.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Multiple citations to "(J Bridges)" embedded in text.
- ↑ "Gray's Anatomy". 1918. Archived from the original on 22 December 2009.
- ↑ "hip fracture". McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine. 2002 – via TheFreeDictionary.
- ↑ "pelvimetry""at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- 1 2 3 4 Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 188–192. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
- ↑ Dines, James P., et al. "Sexual selection targets cetacean pelvic bones." Evolution 68.11 (2014): 3296-3306.
External links
- hip/hip%20bones/bones3 at the Dartmouth Medical School's Department of Anatomy
