| HAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | HAL, HIS, HSTD, histidine ammonia-lyase, Histidine ammonia-lyase | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 609457 MGI: 96010 HomoloGene: 68229 GeneCards: HAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| histidine ammonia-lyase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Histidine ammonia-lyase homotetramer, Pseudomonas putida | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 4.3.1.3 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9013-75-6 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Histidine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.3, histidase, histidinase) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HAL gene.[5][6] It converts histidine into ammonia and urocanic acid. Its systematic name is L-histidine ammonia-lyase (urocanate-forming).
Function
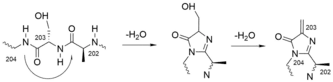
Histidine ammonia-lyase is a cytosolic enzyme catalyzing the first reaction in histidine catabolism, the nonoxidative deamination of L-histidine to trans-urocanic acid.[5] The reaction is catalyzed by 3,5-dihydro-5-methyldiene-4H-imidazol-4-one (MIO), an electrophilic cofactor which is formed autocatalytically by cyclization of the protein backbone of the enzyme.[7]
Pathology
Mutations in the gene for histidase are associated with histidinemia and urocanic aciduria.
See also
- Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, another enzyme that contains the MIO cofactor
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000084110 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020017 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: histidine ammonia-lyase".
- ↑ Suchi M, Sano H, Mizuno H, Wada Y (September 1995). "Molecular cloning and structural characterization of the human histidase gene (HAL)". Genomics. 29 (1): 98–104. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1219. PMID 8530107.
- ↑ Schwede TF, Rétey J, Schulz GE (Apr 27, 1999). "Crystal structure of histidine ammonia-lyase revealing a novel polypeptide modification as the catalytic electrophile". Biochemistry. 38 (17): 5355–5361. doi:10.1021/bi982929q. PMID 10220322.
Further reading
- Suchi M, Harada N, Wada Y, Takagi Y (1993). "Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding human histidase". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1216 (2): 293–5. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(93)90157-9. PMID 7916645.
- Davila S, Froeling FE, Tan A, et al. (2010). "New genetic associations detected in a host response study to hepatitis B vaccine". Genes Immun. 11 (3): 232–8. doi:10.1038/gene.2010.1. PMID 20237496. S2CID 11183658.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Eckhart L, Schmidt M, Mildner M, et al. (2008). "Histidase expression in human epidermal keratinocytes: regulation by differentiation status and all-trans retinoic acid". J. Dermatol. Sci. 50 (3): 209–15. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2007.12.009. PMID 18280705.
- Welsh MM, Karagas MR, Applebaum KM, et al. (2008). "A role for ultraviolet radiation immunosuppression in non-melanoma skin cancer as evidenced by gene-environment interactions". Carcinogenesis. 29 (10): 1950–4. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgn160. PMC 2556967. PMID 18641401.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2002). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. JSTOR 3074035. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Kawai Y, Moriyama A, Asai K, et al. (2005). "Molecular characterization of histidinemia: identification of four missense mutations in the histidase gene". Hum. Genet. 116 (5): 340–6. doi:10.1007/s00439-004-1232-5. PMID 15806399. S2CID 33960184.
- Taylor RG, García-Heras J, Sadler SJ, et al. (1991). "Localization of histidase to human chromosome region 12q22→q24.1 and mouse chromosome region 10C2→D1". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 56 (3–4): 178–81. doi:10.1159/000133082. PMID 2055114.
- Alemán G, Ortíz V, Langley E, et al. (2005). "Regulation by glucagon of the rat histidase gene promoter in cultured rat hepatocytes and human hepatoblastoma cells". Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 289 (1): E172–9. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00584.2004. PMID 15741241.
External links
- Histidine+Ammonia-Lyase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.