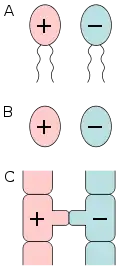
Isogamy is a form of sexual reproduction that involves gametes of the same morphology (indistinguishable in shape and size), and is found in most unicellular eukaryotes.[1] Because both gametes look alike, they generally cannot be classified as male or female.[2] Instead, organisms undergoing isogamy are said to have different mating types, most commonly noted as "+" and "−" strains.[3]
Etymology
The literal meaning of isogamy is "equal marriage" which refers to equal contribution of resources by both gametes to a zygote.[4] The term isogamous was first used in the year 1887.[5]
Characteristics of isogamous species
Isogamous species often have two mating types. Some isogamous species have more than two mating types, but the number is usually lower than ten. In some extremely rare cases a species can have thousands of mating types. In all cases, fertilization occurs when gametes of two different mating types fuse to form a zygote.[6]
Evolution
It is generally accepted that isogamy is an ancestral state for anisogamy[1][7] and that isogamy was the first stage in the evolution of sexual reproduction. Isogamous reproduction evolved independently in several lineages of plants and animals to anisogamous species with gametes of male and female types and subsequently to oogamous species in which the female gamete is much larger than the male and has no ability to move. This pattern may have been driven by the physical constraints on the mechanisms by which two gametes get together as required for sexual reproduction.[8]
Isogamy is the norm in unicellular eukaryote species, although it is possible that isogamy is evolutionarily stable in multicellular species.[1]
Occurrence
Almost all unicellular eukaryotes are isogamous.[9] Among multicellular organisms, isogamy is restricted to fungi such as baker's yeast[1] and algae.[10] Many species of green algae are isogamous. It is typical in the genera Ulva, Hydrodictyon, Tetraspora, Zygnema, Spirogyra, Ulothrix, and Chlamydomonas.[1][11] Many fungi are isogamous.[12]
See also
Biology
Social anthropology
Notes and references
- 1 2 3 4 5 Lehtonen, Jussi; Kokko, Hanna; Parker, Geoff A. (2016-10-19). "What do isogamous organisms teach us about sex and the two sexes?". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 371 (1706). doi:10.1098/rstb.2015.0532. ISSN 0962-8436. PMC 5031617. PMID 27619696.
- ↑ Sawada, Hitoshi; Inoue, Naokazu; Iwano, Megumi (2014). Sexual Reproduction in Animals and Plants. Springer. p. 216. ISBN 978-4-431-54589-7.
- ↑ Kumar R, Meena M, Swapnil P (2019). "Anisogamy". In Vonk J, Shackelford T (eds.). Anisogamy. Encyclopedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior. Cham: Springer International Publishing. pp. 1–5. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-47829-6_340-1. ISBN 978-3-319-47829-6.
Anisogamy can be defined as a mode of sexual reproduction in which fusing gametes, formed by participating parents, are dissimilar in size.
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Evolutionary Biology. Vol. 2. Academic Press. 2016-04-14. p. 212. ISBN 978-0-12-800426-5.
- ↑ "Definition of ISOGAMOUS". www.merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 2021-09-14.
- ↑ Krumbeck, Yvonne; Constable, George W. A.; Rogers, Tim (2020-02-26). "Fitness differences suppress the number of mating types in evolving isogamous species". Royal Society Open Science. 7 (2): 192126. arXiv:1906.07117. Bibcode:2020RSOS....792126K. doi:10.1098/rsos.192126. ISSN 2054-5703. PMC 7062084. PMID 32257356.
- ↑ Pitnick, Scott S.; Hosken, Dave J.; Birkhead, Tim R. (2008-11-21). Sperm Biology: An Evolutionary Perspective. Academic Press. pp. 43–45. ISBN 978-0-08-091987-4.
- ↑ Dusenbery, David B. (2009). Living at Micro Scale, Chapter 20. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts ISBN 978-0-674-03116-6.
- ↑ Bell, Graham (2008). Selection: The Mechanism of Evolution. OUP Oxford. p. 439. ISBN 978-0-19-856972-5.
- ↑ Togashi, Tatsuya; Cox, Paul Alan (2011-04-14). The Evolution of Anisogamy: A Fundamental Phenomenon Underlying Sexual Selection. Cambridge University Press. p. 96. ISBN 978-1-139-50082-1.
- ↑ Sharma, O. P. (1986-01-01). Textbook of Algae. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. p. 130. ISBN 978-0-07-451928-8.
- ↑ Heitman, Joseph; Howlett, Barbara J.; Crous, Pedro W.; Stukenbrock, Eva H.; James, Timothy Yong; Gow, Neil A. R. (2020-07-10). The Fungal Kingdom. John Wiley & Sons. p. 149. ISBN 978-1-55581-958-3.
- Sa Geng; Peter De Hoff; James G. Umen (July 8, 2014). "Evolution of Sexes from an Ancestral Mating-Type Specification Parthway". PLOS Biology. 12 (7): e1001904. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001904. PMC 4086717. PMID 25003332.