| Lake zones |
|---|
| Lake stratification |
| Lake types |
| See also |
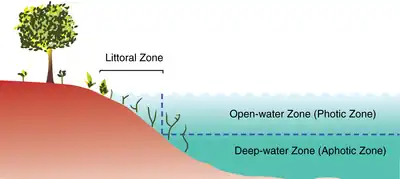
The limnetic zone is the open and well-lit area of a freestanding body of freshwater, such as a lake or pond. Not included in this area is the littoral zone, which is the shallow, near-shore area of the water body. The key difference between the littoral zone and the limnetic zone is the presence of rooted plant growth.[1] The floor under the limnetic zone cannot sustain plant growth due to a lack of sunlight for photosynthesis. In extremely shallow bodies of water, light may penetrate all the way to floor even in the deepest center parts of the lake. In this situation, there is an absence of a limnetic zone and the littoral zone spans the entire lake.[2] Together, these two zones comprise the photic zone.
There are two main sources of oxygen to the photic zone: atmospheric mixing and photosynthesis. Oxygen is dissolved when air interacts with water on the surface, and is increased with wave and wind action.[3] Unlike the profundal zone, the limnetic zone is the layer that receives sufficient sunlight, allowing for photosynthesis.[4] For this reason, it is often simply referred to as the photic zone. The limnetic zone is the most photosynthetically-active zone of a lake since it is the primary habitat for planktonic species.[5] Because phytoplankton populations are densest here, it is the zone most heavily responsible for oxygen production within the aquatic ecosystem.[5]
Limnetic communities are quite complex. Zooplankton populations often consist of copepods, cladocerans, and rotifers occurring in the open water of lakes. Most limnetic communities will consist of one dominant species of copepod, one dominant cladoceran, and one dominant rotifer.[6] Zooplanktons are able to move more freely through the limnetic zone than in the littoral zone, both vertically and horizontally. This is because the bottom of a lake's debris and substrates provide rich habitat niches.[6] A limnetic zooplankton population will usually consist of two to four species, each in a different genus.[6]
In addition to zooplankton, organisms in the limnetic zone include insects and fish. Many species of freshwater fish live in the limnetic zone because of the abundance of food, though these species often navigate into the littoral zone as well.
See also
References
- ↑ "Inland lake habitats critical to maintaining healthy lake ecosystems". MSU Extension.
- ↑ "limnetic zone". Oxford Reference. Oxford University Press.
- ↑ Rudolf, Rosen (2016). Texas Aquatic Science. Texas A&M University Press.
- ↑ Bhateria, Rachna; Jain, Disha (2016-06-01). "Water quality assessment of lake water: a review". Sustainable Water Resources Management. 2 (2): 161–173. doi:10.1007/s40899-015-0014-7. ISSN 2363-5045.
- 1 2 Havens, Karl E. (1991-06-01). "Summer zooplankton dynamics in the limnetic and littoral zones of a humic acid lake". Hydrobiologia. 215 (1): 21–29. doi:10.1007/BF00005897. ISSN 1573-5117. S2CID 39398719.
- 1 2 3 Pennak, Robert W. (July 1957). "Species Composition of Limnetic Zooplankton Communities1". Limnology and Oceanography. 2 (3): 222–232. Bibcode:1957LimOc...2..222P. doi:10.1002/lno.1957.2.3.0222.