 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lorabid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601206 |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 25% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
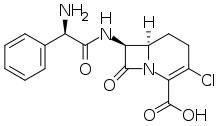
| Formula | C16H16ClN3O4 |
| Molar mass | 349.77 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Loracarbef is an antibiotic.[1] It is a carbacephem, but it is sometimes grouped together with the second-generation cephalosporin antibiotics. Loracarbef is a synthetic "carba" analog of cefaclor, and is more stable.
History
Loracarbef received FDA approval in 1991 and it was marketed under the trade name Lorabid. Its use was discontinued in 2006.
Usage & Indications
Loracarbef was used to treat infections of the lungs, maxillary sinuses, throat, skin, and urinary tract.[2]
Spectrum of Activity
Loracarbef had broad spectrum effectiveness against both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, including those precipitating infections of the respiratory tract, sinuses, tonsils, skin, urinary tract, and kidneys. It was of specific use in those infections caused by E. Coli, S. pyogenes, S. Aureus, S. saprphyticus, S. penumoniae, H. influenza, and M. catarrhalis. [3]
Side effects
Diarrhea is the most common adverse effect with loracarbef. Side effects are more frequently seen with children under the age of twelve.
References
- ↑ Biedenbach DJ, Jones RN (February 1994). "Predictive accuracy of disk diffusion test for Proteus vulgaris and Providencia species against five newer orally administered cephalosporins, cefdinir, cefetamet, cefprozil, cefuroxime, and loracarbef". Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 32 (2): 559–62. doi:10.1128/JCM.32.2.559-562.1994. PMC 263078. PMID 8150976.
- ↑ "Lorabid (Loracarbef): Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, Interactions, Warning". RxList. Retrieved 2020-06-15.
- ↑ "Loracarbef". www.drugbank.ca. Retrieved 2020-06-15.