| Part of a series on |
| macOS |
|---|
The history of macOS, Apple's current Mac operating system formerly named Mac OS X until 2011 and then OS X until 2016, began with the company's project to replace its "classic" Mac OS. That system, up to and including its final release Mac OS 9, was a direct descendant of the operating system Apple had used in its Mac computers since their introduction in 1984. However, the current macOS is a UNIX operating system built on technology that had been developed at NeXT from the 1980s until Apple purchased the company in early 1997.[1]
Although it was originally marketed as simply "version 10" of Mac OS (indicated by the Roman numeral "X"), it has a completely different codebase from Mac OS 9, as well as substantial changes to its user interface. The transition was a technologically and strategically significant one. To ease the transition for users and developers, versions through 10.4 were able to run Mac OS 9 and its applications in the Classic Environment, a compatibility layer.
macOS was first released in 1999 as Mac OS X Server 1.0. It was built using the technologies Apple acquired from NeXT, but did not include the signature Aqua user interface (UI). The desktop version aimed at regular users—Mac OS X 10.0—shipped in March 2001. Since then, several more distinct desktop and server editions of macOS have been released. Starting with Mac OS X 10.7 Lion, macOS Server is no longer offered as a standalone operating system; instead, server management tools are available for purchase as an add-on. The macOS Server app was discontinued on April 21, 2022 and will stop working on macOS 13 Ventura or later. Starting with the Intel build of Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard, most releases have been certified as Unix systems conforming to the Single UNIX Specification.[2][3][4][5][6]
Lion was referred to by Apple as "Mac OS X Lion" and sometimes as "OS X Lion"; Mountain Lion was officially referred to as just "OS X Mountain Lion", with the "Mac" being completely dropped. The operating system was further renamed to "macOS" starting with macOS Sierra.
From the introduction of machines not supporting the classic Mac OS in 2003 until the introduction of iPhone OS in early 2007, Mac OS X was Apple's only software platform.
macOS retained the major version number 10 throughout its development history until the release of macOS 11 Big Sur in 2020.
Mac OS X 10.0 and 10.1 were given names of big cats as internal code names ("Cheetah" and "Puma"). Starting with Mac OS X 10.2 Jaguar, big cat names were used as marketing names; starting with OS X 10.9 Mavericks, names of locations in California were used as marketing names instead.
The current major version, macOS 14 Sonoma, was announced on June 5, 2023 at WWDC 2023 and released on September 26 of that year.
Development
Development outside Apple
After Apple removed Steve Jobs from management in 1985, he left the company and attempted to create the "next big thing", with funding from Ross Perot[7] and himself. The result was the NeXT Computer. As the first workstation to include a digital signal processor (DSP) and a high-capacity optical disc drive, NeXT hardware was advanced for its time, but was expensive relative to the rapidly commoditizing workstation market. The hardware was phased out in 1993; however, the company's object-oriented operating system NeXTSTEP had a more lasting legacy as it eventually became the basis for Mac OS X.
NeXTSTEP was based on the Mach kernel developed at CMU (Carnegie Mellon University)[8] and BSD, an implementation of Unix dating back to the 1970s. It featured an object-oriented programming framework based on the Objective-C language. This environment is known today in the Mac world as Cocoa. It also supported the innovative Enterprise Objects Framework database access layer and WebObjects application server development environment, among other notable features.
All but abandoning the idea of an operating system, NeXT managed to maintain a business selling WebObjects and consulting services, only ever making modest profits in its last few quarters as an independent company. NeXTSTEP underwent an evolution into OPENSTEP which separated the object layers from the operating system below, allowing it to run with less modification on other platforms. OPENSTEP was, for a short time, adopted by Sun and HP.
However, by this point, a number of other companies — notably Apple, IBM, Microsoft, and even Sun itself — were claiming they would soon be releasing similar object-oriented operating systems and development tools of their own. Some of these efforts, such as Taligent, did not fully come to fruition; others, like Java, gained widespread adoption.
On February 4, 1997, Apple Computer acquired NeXT for $427 million, and used OPENSTEP as the basis for Mac OS X, as it was called at the time.[9] Traces of the NeXT software heritage can still be seen in macOS. For example, in the Cocoa development environment, the Objective-C library classes have "NS" prefixes, and the HISTORY section of the manual page for the defaults command in macOS straightforwardly states that the command "First appeared in NeXTStep."
Internal development
Meanwhile, Apple was facing commercial difficulties of its own. The decade-old Macintosh System Software had reached the limits of its single-user, co-operative multitasking architecture, and its once-innovative user interface was looking increasingly outdated. A massive development effort to replace it, known as Copland, was started in 1994, but was generally perceived outside Apple to be a hopeless case due to political infighting and conflicting goals. By 1996, Copland was nowhere near ready for release, and the project was eventually cancelled. Some elements of Copland were incorporated into Mac OS 8, released on July 26, 1997.
After considering the purchase of BeOS — a multimedia-enabled, multi-tasking OS designed for hardware similar to Apple's, the company decided instead to acquire NeXT and use OPENSTEP as the basis for their new OS. Avie Tevanian took over OS development, and Steve Jobs was brought on as a consultant. At first, the plan was to develop a new operating system based almost entirely on an updated version of OPENSTEP, with the addition of a virtual machine subsystem — known as the Blue Box — for running "classic" Macintosh applications. The result was known by the code name Rhapsody, slated for release in late 1998.
Apple expected that developers would port their software to the considerably more powerful OPENSTEP libraries once they learned of its power and flexibility. Instead, several major developers such as Adobe told Apple that this would never occur, and that they would rather leave the platform entirely. This "rejection" of Apple's plan was largely the result of a string of previous broken promises from Apple; after watching one "next OS" after another disappear and Apple's market share dwindle, developers were not interested in doing much work on the platform at all, let alone a re-write.
Changed direction under Jobs
Apple's financial losses continued and the board of directors lost confidence in CEO Gil Amelio, asking him to resign. The board asked Steve Jobs to lead the company on an interim basis, essentially giving him carte blanche to make changes to return the company to profitability. When Jobs announced at the World Wide Developer's Conference that what developers really wanted was a modern version of the Mac OS, and Apple was going to deliver it, he was met with applause.
Over the next two years, a major effort was applied to porting the original Macintosh API to Unix libraries known as Carbon. Mac OS applications could be ported to Carbon without the need for a complete re-write, making them operate as native applications on the new operating system. Meanwhile, applications written using the older toolkits would be supported using the "Classic" Mac OS 9 environment. Support for C, C++, Objective-C, Java, and Python were added, furthering developer comfort with the new platform.
During this time, the lower layers of the operating system (the Mach kernel and the BSD layers on top of it[10]) were re-packaged and released under the Apple Public Source License. They became known as Darwin. The Darwin kernel provides a stable and flexible operating system, which takes advantage of the contributions of programmers and independent open-source projects outside Apple; however, it sees little use outside the Macintosh community.
During this period, the Java programming language had increased in popularity, and an effort was started to improve Mac Java support. This consisted of porting a high-speed Java virtual machine to the platform, and exposing macOS-specific "Cocoa" APIs to the Java language.
The first release of the new OS — Mac OS X Server 1.0 — used a modified version of the Mac OS GUI, but all client versions starting with Mac OS X Developer Preview 3 used a new theme known as Aqua. Aqua was a substantial departure from the Mac OS 9 interface, which had evolved with little change from that of the original Macintosh operating system: it incorporated full color scalable graphics, anti-aliasing of text and graphics, simulated shading and highlights, transparency and shadows, and animation. A new feature was the Dock, an application launcher which took advantage of these capabilities.
Despite this, Mac OS X maintained a substantial degree of consistency with the traditional Mac OS interface and Apple's own Apple Human Interface Guidelines, with its pull-down menu at the top of the screen, familiar keyboard shortcuts, and support for a single-button mouse. The development of Aqua was delayed somewhat by the switch from OpenStep's Display PostScript engine to one developed in-house that was free of any license restrictions, known as Quartz.
Releases
| Version | Release Name | Darwin version |
Processor support |
Application support |
Kernel | Date announced |
Release date |
Most recent version | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhapsody Developer Release | Grail1Z4/Titan1U (internal codename) |
Unknown | 32-bit PowerPC and Intel |
32-bit PowerPC and Intel |
32-bit | January 7, 1997[11] | August 31, 1997 | DR2 (May 14, 1998) | |
| Mac OS X Server 1.0 | Hera (internal codename) |
32-bit PowerPC | 32-bit PowerPC | Unknown | March 16, 1999 | 1.2v3 (October 27, 2000) | |||
| Mac OS X Developer Preview | Unknown | May 11, 1998[12] | March 16, 1999 | DP4 (April 5, 2000) | |||||
| Mac OS X Public Beta | Kodiak[13] (internal codename) |
May 15, 2000[14] | September 13, 2000 | — | |||||
| Mac OS X 10.0 | Cheetah (internal codename) |
1.3.1 | January 9, 2001[15] | March 24, 2001 | 10.0.4 (4Q12) (June 22, 2001) | ||||
| Mac OS X 10.1 | Puma (internal codename) |
1.4.1/5 | July 18, 2001[16] | September 25, 2001 | 10.1.5 (5S60) (June 6, 2002) | ||||
| Mac OS X 10.2 | Jaguar | 6 | 32/64-bit PowerPC[Note 1] | May 6, 2002[17] | August 24, 2002 | 10.2.8 (October 3, 2003) | |||
| Mac OS X 10.3 | Panther | 7 | June 23, 2003[18] | October 24, 2003 | 10.3.9 (7W98) (April 15, 2005) | ||||
| Mac OS X 10.4 | Tiger | 8 | 32/64-bit PowerPC and Intel |
32/64-bit PowerPC and Intel [Note 2] [Note 3] |
May 4, 2004[19] | April 29, 2005 | 10.4.11 (November 14, 2007) | ||
| Mac OS X 10.5 | Leopard | 9 | June 26, 2006[20] | October 26, 2007 | 10.5.8 (9L31a) (August 13, 2009) | ||||
| Mac OS X 10.6 | Snow Leopard | 10 | 32/64-bit Intel | 32/64-bit Intel 32-bit PowerPC[Note 3] |
32/64-bit[21] | June 9, 2008[22] | August 28, 2009 | 10.6.8 (10K549) (July 25, 2011) | |
| Mac OS X 10.7 | Lion | 11 | 64-bit Intel | 32/64-bit Intel | October 20, 2010[23] | July 20, 2011 | 10.7.5 (11G63) (October 4, 2012) | ||
| OS X 10.8 | Mountain Lion | 12 | 64-bit[24] | February 16, 2012[25] | July 25, 2012[26] | 10.8.5 (12F2560) (August 13, 2015) | |||
| OS X 10.9 | Mavericks | 13 | June 10, 2013[27] | October 22, 2013 | 10.9.5 (13F1911) (July 18, 2016) | ||||
| OS X 10.10 | Yosemite | 14 | June 2, 2014[28] | October 16, 2014 | 10.10.5 (14F2511) (July 19, 2017) | ||||
| OS X 10.11 | El Capitan | 15 | June 8, 2015[29] | September 30, 2015 | 10.11.6 (15G22010) (July 9, 2018) | ||||
| macOS 10.12 | Sierra | 16 | June 13, 2016[30] | September 20, 2016 | 10.12.6 (16G2136) (September 26, 2019) | ||||
| macOS 10.13 | High Sierra | 17 | June 5, 2017 | September 25, 2017 | 10.13.6 (17G14042) (November 12, 2020) | ||||
| macOS 10.14 | Mojave | 18 | June 4, 2018 | September 24, 2018 | 10.14.6 (18G9323) (July 21, 2021) | ||||
| macOS 10.15 | Catalina | 19 | 64-bit Intel | June 3, 2019 | October 7, 2019 | 10.15.7 (19H2026) (July 20, 2022) | |||
| macOS 11 | Big Sur | 20 | 64-bit Intel and ARM[Note 4] | June 22, 2020 | November 12, 2020 | 11.7.10 (20G1427) (September 11, 2023) | |||
| macOS 12 | Monterey | 21 | June 7, 2021 | October 25, 2021 | 12.7.2 (21G1974) (December 11, 2023) | ||||
| macOS 13 | Ventura | 22 | June 6, 2022 | October 24, 2022 | 13.6.3 (22G436) (December 11, 2023) | ||||
| macOS 14 | Sonoma | 23 | June 5, 2023 | September 26, 2023 | 14.2.1 (23C71) (December 19, 2023) | ||||
Legend: Old version Older version, still maintained Latest version | |||||||||
- 1.↑ The Power Mac G5 had special Jaguar builds.
- 2.↑ Tiger did not support 64-bit GUI applications, only 64-bit CLI applications.[31][32]
- 3.1 2 32-bit (but not 64-bit) PowerPC applications were supported on Intel processors with Rosetta.
- 4.↑ 64-bit Intel applications are supported on Apple silicon Macs with Rosetta 2. However, Intel-based Macs are unable to run ARM-based applications, such as iOS and iPadOS apps.
With the exception of Mac OS X Server 1.0 and the original public beta, the first several macOS versions were named after big cats. Prior to its release, version 10.0 was code named "Cheetah" internally at Apple, and version 10.1 was code named internally as "Puma".
After the code name "Jaguar" for version 10.2 received publicity in the media, Apple began openly using the names to promote the operating system: 10.3 was marketed as "Panther", 10.4 as "Tiger", 10.5 as "Leopard", 10.6 as "Snow Leopard", 10.7 as "Lion", and 10.8 as "Mountain Lion". "Panther", "Tiger", and "Leopard" were registered as trademarks.
Apple registered "Lynx" and "Cougar", but these were allowed to lapse.[33] Apple started using the name of locations in California for subsequent releases: 10.9 Mavericks was named after Mavericks, a popular surfing destination; 10.10 Yosemite was named after Yosemite National Park; 10.11 El Capitan was named for the El Capitan rock formation in Yosemite National Park; 10.12 Sierra was named for the Sierra Nevada mountain range; and 10.13 High Sierra was named for the area around the High Sierra Camps.[34]
In 2016, OS X was renamed to macOS. A few years later, in 2020, with the release of macOS Big Sur, the first component of the version number was incremented from 10 to 11, so Big Sur's initial release's version number was 11.0 instead of 10.16, making the version numbers of macOS behave the way the version numbers of Apple's other operating systems do.[35] All subsequent major releases also increased the first component of the version number.
Public Beta: "Kodiak"
On September 13, 2000, Apple released a $29.95[36] "preview" version of Mac OS X (internally codenamed Kodiak) in order to gain feedback from users.[37] It marked the first public availability of the Aqua interface, and Apple made many changes to the UI based on customer feedback. Mac OS X Public Beta expired and ceased to function in spring 2001.[38]
Version 10.0: "Cheetah"
On March 24, 2001, Apple released Mac OS X 10.0 (internally codenamed Cheetah).[39] The initial version was slow, incomplete, and had very few applications available at the time of its launch, mostly from independent developers. While many critics suggested that the operating system was not ready for mainstream adoption, they recognized the importance of its initial launch as a base on which to improve. Simply releasing Mac OS X was received by the Macintosh community as a great accomplishment, for attempts to completely overhaul the Mac OS had been underway since 1996, and delayed by countless setbacks. Following some bug fixes, kernel panics became much less frequent.
Version 10.1: "Puma"
Mac OS X 10.1 (internally codenamed Puma) was released on September 25, 2001.[40] It has better performance and provided missing features, such as DVD playback. Apple released 10.1 as a free upgrade CD for 10.0 users. Apple released a US$129 upgrade CD for Mac OS 9.
On January 7, 2002, Apple announced that Mac OS X was to be the default operating system for all Macintosh products by the end of that month.[41]
Version 10.2: "Jaguar"
On August 23, 2002,[42] Apple followed up with Mac OS X 10.2 Jaguar, the first release to use its code name as part of the branding.[43] It brought great raw performance improvements, a sleeker look, and many powerful user-interface enhancements (over 150, according to Apple[44] ), including Quartz Extreme for compositing graphics directly on an ATI Radeon or Nvidia GeForce2 MX AGP-based video card with at least 16 MB of VRAM, a system-wide repository for contact information in the new Address Book, and an instant messaging client named iChat.[45] The Happy Mac which had appeared during the Mac OS startup sequence for almost 18 years was replaced with a large grey Apple logo with the introduction of Mac OS X 10.2.
Version 10.3: "Panther"
Mac OS X Panther was released on October 24, 2003. In addition to providing much improved performance, it also incorporated the most extensive update yet to the user interface. Panther included as many or more new features as Jaguar had the year before, including an updated Finder, incorporating a brushed-metal interface, Fast user switching, Exposé (Window manager), FileVault, Safari, iChat AV (which added videoconferencing features to iChat), improved Portable Document Format (PDF) rendering and much greater Microsoft Windows interoperability.[46] Support for some early G3 computers such as the Power Macintosh and PowerBook was discontinued.
Version 10.4: "Tiger"
Mac OS X Tiger was released on April 29, 2005. Apple stated that Tiger contained more than 200 new features.[47] As with Panther, certain older machines were no longer supported; Tiger requires a Mac with a built-in FireWire port. Among the new features, Tiger introduced Spotlight, Dashboard, Smart Folders, updated Mail program with Smart Mailboxes, QuickTime 7, Safari 2, Automator, VoiceOver, Core Image and Core Video. The initial release of the Apple TV used a modified version of Tiger with a different graphical interface and fewer applications and services.[48]
On January 10, 2006, Apple released the first Intel x86-based Macs along with the 10.4.4 update to Tiger. This operating system functioned identically on the PowerPC-based Macs and the new Intel-based machines, with the exception of the Intel release dropping support for the Classic environment.[48] 10.4.4 introduced Rosetta, which translated 32-bit PowerPC machine code to 32-bit x86 code, allowing applications for PowerPC to run on Intel-based Macs without modification. Only PowerPC Macs can be booted from retail copies of the Tiger client DVD, but there is a Universal DVD of Tiger Server 10.4.7 (8K1079) that can boot both PowerPC and Intel Macs.
Version 10.5: "Leopard"
Mac OS X Leopard was released on October 26, 2007. Apple called it "the largest update of Mac OS X". Leopard supports both PowerPC- and Intel x86-based Macintosh computers; support for Macs with the G3 processor was dropped, and Macs with the G4 processor required a minimum clock rate of 867 MHz and at least 512 MB of RAM to be installed. The single DVD works for all supported Macs (including 64-bit machines). New features include a new look, an updated Finder, Time Machine, Spaces, Boot Camp pre-installed,[49] full support for 64-bit applications (including graphical applications), new features in Mail and iChat, and a number of new security features.
Leopard is an Open Brand UNIX 03 registered product on the Intel platform. It was also the first BSD-based OS to receive UNIX 03 certification.[2][50] Leopard dropped support for the Classic Environment and all Classic applications,[51] and was the final version of Mac OS X to support the PowerPC architecture.
Version 10.6: "Snow Leopard"
Mac OS X Snow Leopard was released on August 28, 2009, the last version to be available on disc. Rather than delivering big changes to the appearance and end user functionality like the previous releases of Mac OS X, the development of Snow Leopard was deliberately focused on "under the hood" changes, increasing the performance, efficiency, and stability of the operating system. For most users, the most noticeable changes are these: the disk space that the operating system frees up after a clean installation compared to Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard, a more responsive Finder rewritten in Cocoa, faster Time Machine backups, more reliable and user friendly disk ejects, a more powerful version of the Preview application, as well as a faster Safari web browser.[52]
An update introduced support for the Mac App Store, Apple's digital distribution platform for macOS applications and subsequent macOS upgrades.[52] Snow Leopard only supports Macs with Intel CPUs, requires at least 1 GB of RAM, and drops default support for applications built for the PowerPC architecture (Rosetta can be installed as an additional component to retain support for PowerPC-only applications).[53]
Version 10.7: "Lion"
Mac OS X Lion (also known as OS X Lion) was released on July 20, 2011. It brought developments made in Apple's iOS, such as an easily navigable display of installed applications (Launchpad) and (a greater use of) multi-touch gestures, to the Mac. This release removed Rosetta, making it incapable of running PowerPC applications. It dropped support for 32-bit Intel processors and requires 2GB of memory. Changes made to the GUI (Graphical User Interface) include the Launchpad (similar to the home screen of iOS and iPadOS devices), auto-hiding scrollbars that only appear when they are being used, and Mission Control, which unifies Exposé, Spaces, Dashboard, and full-screen applications within a single interface.[54] Apple also made changes to applications: they resume in the same state as they were before they were closed (similar to iOS). Documents auto-save by default.
Version 10.8: "Mountain Lion"
OS X Mountain Lion was released on July 25, 2012. It incorporates some features seen in iOS 5, which include Game Center, support for iMessage in the new Messages messaging application, and Reminders as a to-do list app separate from iCal (which is renamed as Calendar, like the iOS app). It also includes support for storing iWork documents in iCloud. 2GB of memory is required.[55] Notification Center, which makes its debut in Mountain Lion, is a desktop version similar to the one in iOS 5.0 and higher. Application pop-ups are now concentrated on the corner of the screen, and the Center itself is pulled from the right side of the screen. Mountain Lion also includes more Chinese features, including support for Baidu as an option for Safari search engine.[56] Notification Center is added, providing an overview of alerts from applications. Notes is added, as an application separate from Mail, synching with its iOS counterpart[57][58] through the iCloud service. Messages, an instant messaging software application,[59] replaces iChat.[60]
Version 10.9: "Mavericks"
OS X Mavericks was released on October 22, 2013, as a free update through the Mac App Store worldwide.[61] It placed emphasis on battery life, Finder enhancements, other enhancements for power users, and continued iCloud integration, as well as bringing more of Apple's iOS apps to the OS X platform. iBooks and Apple Maps applications were added. Mavericks requires 2GB of memory to operate. It is the first version named under Apple's then-new theme of places in California, dubbed Mavericks after the surfing location.[62][63] Unlike previous versions of OS X, which had progressively decreasing prices since 10.6, 10.9 was available at no charge to all users of compatible systems running Snow Leopard (10.6) or later,[64] beginning Apple's policy of free upgrades for life on its operating system and business software.[65]
Version 10.10: "Yosemite"
OS X Yosemite was released to the general public on October 16, 2014, as a free update through the Mac App Store worldwide. It featured a major overhaul of user interface, replaced skeuomorphism with flat graphic design and blurred translucency effects, following the aesthetic introduced with iOS 7. It introduced features called Continuity and Handoff, which allow for tighter integration between paired OS X and iOS devices: the user can handle phone calls or text messages on either their Mac or their iPhone, and edit the same Pages document on either their Mac or their iPad. A later update of the OS included Photos as a replacement for iPhoto and Aperture.
Version 10.11: "El Capitan"
OS X El Capitan was revealed on June 8, 2015, during the WWDC15 keynote speech.[66] It was made available as a public beta in July and was made available publicly on September 30, 2015. Apple described this release as containing "Refinements to the Mac Experience" and "Improvements to System Performance" rather than new features. Refinements include public transport built into the Maps application, GUI improvements to the Notes application, as well as adopting San Francisco as the system font. Metal API, an application enhancing software, had debuted in this operating system, being available to "all Macs since 2012".[67]
Version 10.12: "Sierra"
macOS Sierra was announced on June 13, 2016, during the WWDC16 keynote speech. The update brought the Siri assistant to macOS, featuring several Mac-specific features, like searching for files. It also allowed websites to support Apple Pay as a method of transferring payment, using either a nearby iOS device or Touch ID to authenticate. iCloud also received several improvements, such as the ability to store a user's Desktop and Documents folders on iCloud so they could be synced with other Macs on the same Apple ID. It was released publicly on September 20, 2016.[68]
Version 10.13: "High Sierra"
macOS High Sierra was announced on June 5, 2017, during the WWDC17 keynote speech. It was released on September 25, 2017. The release includes many under-the-hood improvements, including a switch to Apple File System (APFS), the introduction of Metal 2, support for HEVC video, and improvements to VR support. In addition, numerous changes were made to standard applications including Photos, Safari, Notes, and Spotlight.[69]
Version 10.14: "Mojave"
macOS Mojave was announced on June 4, 2018, during the WWDC18 keynote speech. It was released on September 24, 2018. Some of the key new features were Dark wallpaper in dark mode, Desktop stacks and Dynamic Desktop, which changes the desktop background image to correspond to the user's current time of day.[70]
Version 10.15: "Catalina"
macOS Catalina was announced on June 3, 2019, during the WWDC19 keynote speech. It was released on October 7, 2019. It primarily focuses on updates to built-in apps, such as replacing iTunes with separate Music, Podcasts, and TV apps, redesigned Reminders and Books apps, and a new Find My app. It also features Sidecar, which allows the user to use an iPad as a second screen for their computer, or even simulate a graphics tablet with an Apple Pencil. It is the first version of macOS not to support 32-bit applications. The Dashboard application was also removed in the update.[71][72] Since macOS Catalina, iOS apps can run on macOS with Project Catalyst but requires the app to be made compatible[73] unlike ARM-powered Apple silicon Macs that can run all iOS apps by default.[74]
Version 11: "Big Sur"
macOS Big Sur was announced on June 22, 2020, during the WWDC20 keynote speech.[75] It was released November 12, 2020.[76] The major version number is changed, for the first time since "Mac OS X" was released, making it macOS 11. It brings ARM support, new icons, GUI changes to the system,[77] and other bug fixes. Since macOS 11.2.3, it is no longer possible to install iOS apps by default from an IPA file instead of the Mac App Store on Apple silicon Macs, which now requires third-party software to unlock the functionality.[78][79] Big Sur introduced Rosetta 2 to allow 64-bit Intel applications to run on Apple silicon Macs. However, Intel-based Macs are unable to run ARM-based applications, including iOS and iPadOS apps.
Version 12: "Monterey"
macOS Monterey was announced on June 7, 2021, during the WWDC21 keynote speech.[80] It was released on October 25, 2021.[81] macOS Monterey introduces new features such as Universal Control, which allows users to use a single keyboard and mouse to move between devices; AirPlay, which now allows users to present and share almost anything; the Shortcuts app, also introduced to macOS, gives users access to galleries of pre-built shortcuts, designed for Macs, a service brought from iOS, and users can now also set up shortcuts, among other things.[82] macOS Monterey is the final version of macOS that officially supports macOS Server.
Version 13: "Ventura"
macOS Ventura was announced on June 6, 2022, during the WWDC22 keynote speech.[83] It was released on October 24, 2022.[84] macOS Ventura introduces Stage Manager, a new and optional window manager, a redesigned settings app, and Continuity Camera, which is a program that allows Mac users to use their iPhone as a camera, and several other new features.[83] It is also the first version of macOS without macOS Server support.
Version 14: "Sonoma"
macOS Sonoma was announced on June 5, 2023, during the WWDC23 keynote speech. Key changes include a revamp of Widgets, the user lock screen, and a video wallpaper/screensaver feature using Apple TV's screen saver videos.[85] It was released on September 26, 2023.[86]
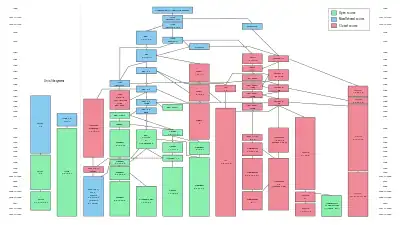
Timeline of Macintosh operating systems
| Timeline of Mac operating systems |
|---|
 |
See also
References
- ↑ sandaruwani, dilusha (2020-08-06). "Evolution of Mac OS". Medium. Retrieved 2023-07-05.
- 1 2 The Open Group. "Mac OS X version 10.5 Leopard on Intel-based Macintosh computers certification". Archived from the original on 2008-05-11. Retrieved 2007-06-12.
- ↑ The Open Group. "Mac OS X version 10.6 Leopard on Intel-based Macintosh computers certification". Archived from the original on 2014-11-16. Retrieved 2013-07-11.
- ↑ The Open Group. "Mac OS X version 10.8 Mountain Lion on Intel-based Macintosh computers certification". Archived from the original on 2014-11-16.
- ↑ The Open Group. "Mac OS X version 10.9 Mavericks on Intel-based Macintosh computers certification". Archived from the original on 2013-11-04. Retrieved 2013-09-18.
- ↑ The Open Group. "OS X version 10.10 Yosemite on Intel-based Macintosh computers certification". Archived from the original on 2014-11-10. Retrieved 2014-11-13.
- ↑ Isaacson, Walter (2011). Steve Jobs. Simon & Schuster. p. 227. ISBN 978-1-4087-0374-8.
- ↑ A Practical Guide to Linux Commands, Editors, and Shell Programming, 3rd edition, by Mark G. Sobell, page 2
- ↑ Linzmayer, Owen W. (1999). Apple Confidential: The Real Story of Apple Computer, Inc. ISBN 9781886411289.
- ↑ A Practical Guide to Linux Commands, Editors, and Shell Programming, 3rd edition by Mark G. Sobell, page 2
- ↑ "Apple Announces Future Macintosh Operating System (OS) Strategy and Road Map". Apple.com. Apple Computer, Inc. 7 January 1997. Archived from the original on 16 January 1999. Retrieved 18 September 2018.
- ↑ Davis, Jim (May 11, 1998). "OS X is the future for Apple". CNET. Archived from the original on September 13, 2014. Retrieved July 17, 2013.
- ↑ Steven Borden-Weill (April 15, 2011). "Kodiak to Lion: 10 years of Mac OS X". Network World. Archived from the original on June 17, 2016.
- ↑ "Apple Releases Mac OS X Developer Preview 4 with Final API Specs". Apple Newsroom. Retrieved 2018-09-18.
- ↑ "Apple's Mac OS X to Ship on March 24". Apple Newsroom. Retrieved 2018-09-17.
- ↑ "Apple Previews Next Version of Mac OS X" (Press release). Apple. July 18, 2001. Archived from the original on January 3, 2018. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple Previews "Jaguar", the Next Major Release of Mac OS X" (Press release). Apple. May 6, 2002. Archived from the original on January 3, 2018. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple Previews Mac OS X "Panther"" (Press release). Apple. June 23, 2003. Archived from the original on January 3, 2018. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Steve Jobs to Kick Off Apple's Worldwide Developers Conference 2004 with Preview of Mac OS X "Tiger"" (Press release). Apple. Archived from the original on January 3, 2018. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple Executives to Preview Mac OS X "Leopard" at WWDC 2006 Keynote" (Press release). Apple. Archived from the original on January 3, 2018. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Road to Mac OS X Snow Leopard: 64-bit to the Kernel". AppleInsider. October 28, 2008. Archived from the original on September 28, 2015. Retrieved September 28, 2015.
- ↑ "Apple Previews Mac OS X Snow Leopard to Developers" (Press release). Apple. June 9, 2008. Archived from the original on November 1, 2017. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple Gives Sneak Peek of Mac OS X Lion" (Press release). Apple. October 20, 2010. Archived from the original on January 3, 2018. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Older 64-bit Macs out of the picture for Mountain Lion". CNET. July 11, 2012. Archived from the original on October 1, 2015. Retrieved September 28, 2015.
- ↑ "Apple Releases OS X Mountain Lion Developer Preview with Over 100 New Features" (Press release). Apple. February 16, 2012. Archived from the original on November 23, 2017. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Mountain Lion Available Today From the Mac App Store" (Press release). Apple. July 25, 2012. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple Releases Developer Preview of OS X Mavericks With More Than 200 New Features" (Press release). Apple. June 10, 2013. Archived from the original on February 13, 2018. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple Announces OS X Yosemite" (Press release). Apple. June 2, 2014. Archived from the original on October 9, 2017. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple Announces OS X El Capitan with Refined Experience & Improved Performance" (Press release). Apple. June 8, 2015. Archived from the original on October 8, 2017. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple previews major update with macOS Sierra" (Press release). Apple. June 13, 2016. Archived from the original on January 3, 2018. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ↑ John Siracusa (April 28, 2005). "Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger". ArsTechnica.com. p. 4. Retrieved February 25, 2007.
- ↑ Apple (March 6, 2006). "Developing 64-bit applications". Apple Developer Connection. Archived from the original on September 25, 2007. Retrieved March 5, 2007.
- ↑ Trademark #78257226 for Panther, #78269988 for Tiger, #78270003 for Leopard, #78271630 for Cougar and #78271639 for Lynx, all registered in 2004 by Apple Computer, Inc. "United States Patent and Trademark Office". Archived from the original on December 20, 2006. Retrieved December 20, 2006.
- ↑ Ha, Anthony (2013-06-10). "Apple Has A New, California-Based Naming Scheme For OS X, Starting With OS X Mavericks". TechCrunch. Retrieved 2023-09-27.
- ↑ Mastroianni, Brian (June 13, 2016). "Apple unveils iOS 10, macOS, and more at WWDC 2016". CBS News.
Perhaps one of the announcements that stood out the most was a slight name change. The desktop operating system Mac OS X will now be called macOS to better match with the way the company's other operating systems are named.
- ↑ John Siracusa. "Mac OS X Beta – Page 1 – (10/2000)". Ars Technica. Condé Nast Digital. Archived from the original on October 30, 2009. Retrieved March 11, 2010.
- ↑
"Makefile". Apple. June 2005. Archived from the original on 2009-01-14. Retrieved December 15, 2008.
RC Release is Kodiak (Public Beta)
- ↑ "Mac OS X Public Beta Expires Today | News". The Mac Observer. Archived from the original on June 8, 2011. Retrieved March 11, 2010.
- ↑ Although the version is now called Cheetah by users, rare evidences can be found to prove that it was called so internally. For instance, a Q&A was created in 2005 which mentions it "Technical Q&A". Apple. October 4, 2005. Archived from the original on May 18, 2008. Retrieved December 20, 2006.
- ↑ "Cross-Development". Apple. November 11, 2006. Archived from the original on 2007-05-20. Retrieved December 20, 2006.
- ↑ "Apple Makes Mac OS X the Default Operating System on All Macs" (Press release). Apple. January 7, 2002. Retrieved December 3, 2006.
- ↑ "Jaguar "Unleashed" at 10:20 p.m. Tonight" (Press release). Apple. August 23, 2002. Retrieved January 10, 2018.
- ↑ The headline of the press release mention "Jaguar", while the codename was not mentioned for earlier versions. See Apple.com, "Jaguar" press release, compared to Mac OS X 10.0 press release and Mac OS X 10.1 press release
- ↑ "Apple – Mac OS X". Apple. August 29, 2002. Archived from the original on August 29, 2002. Retrieved June 12, 2008.
- ↑ "Apple Previews "Jaguar," the Next Major Release of Mac OS X" (Press release). Apple. May 6, 2002. Retrieved January 10, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple Announces Mac OS X "Panther"" (Press release). Apple. October 8, 2003. Retrieved January 10, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple Unleashes "Tiger Friday at 6:00 p.m." (Press release). Apple. April 28, 2005. Retrieved January 10, 2018.
- 1 2 "Apple unveils Intel iMacs". AppleInsider. January 2006. Retrieved January 10, 2018.
- ↑ "Apple – BootCamp". Apple. 2006. Archived from the original on June 2, 2006. Retrieved June 5, 2006.
- ↑
"Mac OS X Leopard – Technology – UNIX". Leopard Technology Overview. Apple. Archived from the original on June 9, 2011. Retrieved October 26, 2007.
Leopard is now an Open Brand UNIX 03 Registered Product, conforming to the SUSv3 and POSIX 1003.1 specifications for the C API, Shell Utilities, and Threads.
- ↑ "Do Classic applications work with Mac OS X 10.5 or Intel-based Macs?". Knowledge Base. Apple. January 13, 2006. Archived from the original on October 25, 2007. Retrieved October 25, 2007.
- 1 2 Reisinger, Don (January 6, 2011). "Mac App Store launches on Snow Leopard". CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on August 10, 2012.
- ↑ Lynch, Steven (June 12, 2008). "Mac OS X Snow Leopard Drops PowerPC Support". HardOCP. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved October 20, 2010.
- ↑ "Apple – OS X Lion – The world's most advanced desktop operating system". Apple. October 20, 2010. Archived from the original on October 22, 2010. Retrieved October 20, 2010.
- ↑ "Apple – OS X Mountain Lion – The world's most advanced desktop operating system". Apple. February 16, 2012. Archived from the original on February 16, 2012. Retrieved February 16, 2012.
- ↑ Panzarino, Matthew (February 16, 2012). "Apple courts China with Sina Weibo, Baidu, Youku and more integrated in Mountain Lion". The Next Web. Archived from the original on March 21, 2012. Retrieved March 15, 2012.
- ↑ "OS X Mountain Lion – See everything the new OS X can do". Apple. Section "Notes". Archived from the original on August 15, 2012. Retrieved February 22, 2012.
- ↑ Titlow, John Paul. "Apple's Convergence of Desktop and Mobile Continues With Mountain Lion". ReadWriteWeb. SAY Media. Archived from the original on 21 April 2012. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
- ↑ "OS X Mountain Lion – Inspired by iPad. Made for the Mac". Apple. Archived from the original on 2012-03-22. Retrieved 2012-03-23.
- ↑ Cheng, Jacqui (25 July 2012). "OS X Mountain Lion now available via Mac App Store". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on August 27, 2012. Retrieved September 1, 2012.
- ↑ "Apple Releases Developer Preview of OS X Mavericks With More Than 200 New Features" (Press release). Apple Inc. June 10, 2013.
- ↑ WWDC 2013 Keynote. Apple Inc. June 10, 2013. Archived from the original on February 18, 2014.
- ↑ Ha, Anthony (Jun 10, 2013). "Apple Has A New, California-Based Naming Scheme For OS X, Starting With OS X Mavericks". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on 2017-07-09.
- ↑ Souppouris, Aaron (October 22, 2013). "OS X Mavericks now available as a free download". The Verge. Archived from the original on October 22, 2013.
- ↑ Gupta, Poornima; Chan, Edwin (October 22, 2013). "Apple unveils iPad Air, new Macs for holidays". Reuters. Archived from the original on April 24, 2016.
- ↑ "Apple Announces OS X El Capitan with Refined Experience & Improved Performance". www.apple.com (Press release). Retrieved January 10, 2018.
- ↑ Dhiraj, Rav (June 2015). "What's New in Metal, Part 1" (PDF). Apple Developer. Apple. p. 84. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 17, 2015. Retrieved October 21, 2017.
- ↑ "macOS Sierra: Siri, Apple Pay for the Web, and More, Available Now". www.macrumors.com. July 19, 2017. Retrieved 2019-07-01.
- ↑ "macOS High Sierra". Apple. Retrieved September 26, 2017.
- ↑ "macOS – Mojave Preview". Apple. Retrieved June 5, 2018.
- ↑ "macOS Catalina: Just Announced, Coming This Fall". www.macrumors.com. June 27, 2019. Retrieved 2019-07-01.
- ↑ How to find 32-bit applications
- ↑ "iOS apps will run on macOS with Project Catalyst". 3 June 2019.
- ↑ "iOS apps will run natively on ARM-powered Macs".
- ↑ "Apple introduces macOS Big Sur with a beautiful new design" (Press release). Apple Inc. June 22, 2020.
- ↑ Haslam, Karen. "macOS Big Sur is here now... and so are the problems". Macworld UK. Retrieved 2020-11-20.
- ↑ "Apple unveils macOS 11.0 Big Sur, featuring a new aesthetic and redesigned apps". TechCrunch. 22 June 2020. Retrieved 2020-06-22.
- ↑ "How to run iOS apps on your M1 Mac". 28 January 2021.
- ↑ "How to launch an iOS app on macOS?". fr:Korben. 11 August 2021.
- ↑ Gallagher, William (June 7, 2021). "Apple unveils macOS Monterey at WWDC 2021". AppleInsider. Retrieved September 20, 2022.
- ↑ Fathi, Sami (October 18, 2021). "Apple Releasing macOS Monterey on October 25". MacRumors. Retrieved September 20, 2022.
- ↑ "macOS Monterey: All the New Features Detailed". MacRumors. Retrieved 2022-03-16.
- 1 2 Mauran, Cecily (June 6, 2022). "Apple WWDC introduces the world to macOS Ventura". Mashable. Retrieved September 20, 2022.
- ↑ Espósito, Filipe (2022-10-24). "macOS Ventura now available for Mac users with Camera Continuity and Stage Manager". 9to5mac.com. Retrieved 2022-10-24.
- ↑ "macOS Sonoma brings new capabilities for elevating productivity and creativity". Apple Newsroom. June 5, 2023. Retrieved September 27, 2023.
- ↑ "macOS Sonoma is available today". Apple Newsroom. September 26, 2023. Retrieved September 27, 2023.