| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methanimine | |||
| Other names
Formaldimine, azomethine, formaldehyde imine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 1900196 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| 163896 | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CNH3 | |||
| Molar mass | 29.042 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless gas | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
N-Methylmethanimine Ethanimine | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
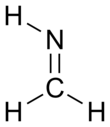
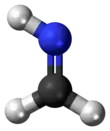
Methylene imine is an organic compound with the formula H2C=NH. The simplest imine, it is a stable, colorless gas that has been detected throughout the universe.[1] Structural parameters determined by microwave spectroscopy include a C=N bond length of 1.27 Å, an N–H bond length of 1.02 Å and an HNC bond angle of 110.5°.[2] Because unhindered imines polymerize or oligomerize when concentrated, methylene imine has not been isolated as a liquid or bulk solid. Attempted synthesis of methylene imine from the reaction of ammonia and formaldehyde produces hexamethylenetetramine.[3]

References
- ↑ Vuitton, V.; Yelle, R. V.; Anicich, V. G. (2006). "The nitrogen chemistry of Titan's upper atmosphere revealed". Astrophysical Journal. 647: L175–L178. doi:10.1086/507467.
- ↑ Richard Pearson Jr., Frank J. Lovas (1977). "Microwave spectrum and molecular structure of methylenimine (CH2NH)". J. Chem. Phys. 66: 4149. doi:10.1063/1.434490.
- ↑ Eller, K.; Henkes, E.; Rossbacher, R.; Höke, H. (2000). "Amines, Aliphatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001. ISBN 9783527306732.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.