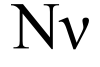 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greek alphabet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Use in other languages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related topics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nu /ˈnjuː/ (Greek: vι ni [ni] nee) is the thirteenth letter of the Greek alphabet (uppercase Ν, lowercase v), representing the voiced alveolar nasal IPA: [n]. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 50. It is derived from the ancient Phoenician language nun ![]() . Its Latin equivalent is N, though the lowercase () resembles the Roman lowercase v.
. Its Latin equivalent is N, though the lowercase () resembles the Roman lowercase v.
The name of the letter is written νῦ in Ancient Greek and traditional Modern Greek polytonic orthography, while in Modern Greek it is written νι [ni].
Symbology
Like Mu, the uppercase Nu is normally identical to Latin N and is therefore not used internationally in scientific or mathematical contexts. The lower-case letter v is used as a symbol for:
- Mathematics:
- Degrees of freedom in statistics.
- The greatest fixed point of a function, as commonly used in the μ-calculus.
- Free names of a process, as used in the π-calculus.
- One of the Greeks in mathematical finance, known as "vega".
- The reciprocal of 1 plus the interest rate in finance.
- The p-adic valuation or p-adic order of a number.
- Physics:
- Kinematic viscosity in fluid mechanics.
- The frequency[1] of a wave in physics and other fields; sometimes also spatial frequency; wavenumber
- The specific volume in thermodynamics.
- Poisson's ratio, the ratio of strains perpendicular with and parallel with an applied force.
- Any of three kinds of neutrino in particle physics.
- The number of neutrons released per fission of an atom in nuclear physics.
- Molecular vibrational mode, vx where x is the number of the vibration (a label).
- The true anomaly, an angular parameter that defines the position of a body moving along an orbit (see orbital elements).
- Biology:
- A DNA polymerase found in higher eukaryotes and implicated in translesion synthesis.
- Chemistry:
- Psychology:
- The maximum conditioning possible for an unconditioned stimulus in the Rescorla-Wagner model.
Character encodings
Greek Nu/Coptic Ni
Encodings of Greek Nu and Coptic Ni.[2]
| Preview | Ν | ν | Ⲛ | ⲛ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | GREEK CAPITAL LETTER NU | GREEK SMALL LETTER NU | COPTIC CAPITAL LETTER NI | COPTIC SMALL LETTER NI | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 925 | U+039D | 957 | U+03BD | 11418 | U+2C9A | 11419 | U+2C9B |
| UTF-8 | 206 157 | CE 9D | 206 189 | CE BD | 226 178 154 | E2 B2 9A | 226 178 155 | E2 B2 9B |
| Numeric character reference | Ν | Ν | ν | ν | Ⲛ | Ⲛ | ⲛ | ⲛ |
| Named character reference | Ν | ν | ||||||
| DOS Greek | 140 | 8C | 164 | A4 | ||||
| DOS Greek-2 | 181 | B5 | 231 | E7 | ||||
| Windows 1253 | 205 | CD | 237 | ED | ||||
| TeX | \nu | |||||||
BBX Mathematical Nu
| Preview | 𝚴 | 𝛎 | 𝛮 | 𝜈 | 𝜨 | 𝝂 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | MATHEMATICAL BOLD CAPITAL NU |
MATHEMATICAL BOLD SMALL NU |
MATHEMATICAL ITALIC CAPITAL NU |
MATHEMATICAL ITALIC SMALL NU |
MATHEMATICAL BOLD ITALIC CAPITAL NU |
MATHEMATICAL BOLD ITALIC SMALL NU | ||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 120500 | U+1D6B4 | 120526 | U+1D6CE | 120558 | U+1D6EE | 120584 | U+1D708 | 120616 | U+1D728 | 120642 | U+1D742 |
| UTF-8 | 240 157 154 180 | F0 9D 9A B4 | 240 157 155 142 | F0 9D 9B 8E | 240 157 155 174 | F0 9D 9B AE | 240 157 156 136 | F0 9D 9C 88 | 240 157 156 168 | F0 9D 9C A8 | 240 157 157 130 | F0 9D 9D 82 |
| UTF-16 | 55349 57012 | D835 DEB4 | 55349 57038 | D835 DECE | 55349 57070 | D835 DEEE | 55349 57096 | D835 DF08 | 55349 57128 | D835 DF28 | 55349 57154 | D835 DF42 |
| Numeric character reference | 𝚴 | 𝚴 | 𝛎 | 𝛎 | 𝛮 | 𝛮 | 𝜈 | 𝜈 | 𝜨 | 𝜨 | 𝝂 | 𝝂 |
| Preview | 𝝢 | 𝝼 | 𝞜 | 𝞶 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD CAPITAL NU |
MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD SMALL NU |
MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD ITALIC CAPITAL NU |
MATHEMATICAL SANS-SERIF BOLD ITALIC SMALL NU | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 120674 | U+1D762 | 120700 | U+1D77C | 120732 | U+1D79C | 120758 | U+1D7B6 |
| UTF-8 | 240 157 157 162 | F0 9D 9D A2 | 240 157 157 188 | F0 9D 9D BC | 240 157 158 156 | F0 9D 9E 9C | 240 157 158 182 | F0 9D 9E B6 |
| UTF-16 | 55349 57186 | D835 DF62 | 55349 57212 | D835 DF7C | 55349 57244 | D835 DF9C | 55349 57270 | D835 DFB6 |
| Numeric character reference | 𝝢 | 𝝢 | 𝝼 | 𝝼 | 𝞜 | 𝞜 | 𝞶 | 𝞶 |
These characters are used only as mathematical symbols. Stylized Greek text should be encoded using the normal Greek letters, with markup and formatting to indicate text style.
See also
- Movable nu
- N, v
References
- ↑ See e.g. Planck's formula
- ↑ Unicode Code Charts: Greek and Coptic (Range: 0370-03FF)