| Slovak invasion of Poland | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Invasion of Poland of World War II | |||||||||
 Slovak Minister of Defence Ferdinand Čatloš decorates ethnic Germans in the Slovak Army | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
| Supported by: |
| ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| 6 infantry divisions | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||
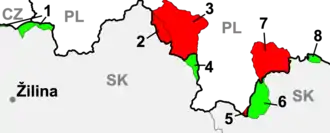
The Slovak invasion of Poland occurred during Nazi Germany's invasion of Poland in September 1939. The recently created Slovak Republic joined the attack, and Field Army Bernolák contributed over 50,000 soldiers in three divisions.[1][2] Since most of the Polish forces were engaged with the German armies, which were more to the north of the southern border, the Slovak invasion met only weak resistance and suffered minimal losses.
Background
On March 14, 1939, the Slovak State was established as a client state of Germany, which initiated the breakup of Czechoslovakia. The south-Slovak part of Czechoslovakia had contained a substantial Hungarian population (Slovakia had been part of the Kingdom of Hungary). It was taken by the Royal Hungarian Army as a result of the First Vienna Award on November 2, 1938.
The official political pretext for the Slovak participation in the Polish Campaign was a small disputed area on the Poland-Slovakia border. Poland had appropriated the area on October 1, 1938, after the previous month's Munich Agreement. In addition, some Polish politicians supported Hungary in its effort to include areas that were inhabited mostly by Hungarians.
During secret discussions with the Germans on July 20–21, 1939, the Slovak government agreed to participate in Germany's planned attack on Poland and to allow Germany to use Slovak territory as the staging area for German troops. On August 26, Slovakia mobilised its armed forces and established a new field army, codenamed "Bernolák", with 51,306 soldiers. Additionally, 160,000 reservists were called up, with 115,000 entering service until September 20, 1939.
Order of battle
The Bernolák army group was led by Slovak Defence Minister Ferdinand Čatloš and had its initial headquarters in Spišská Nová Ves, though after September 8 this was moved to Solivar near Prešov. It consisted of:
- 1st Infantry Division "Jánošík", led by Anton Pulanich in the sector Spišská Nová Ves – Prešov.
- 2nd Infantry Division "Škultéty", led by Alexander Čunderlík in the sector Brezno – Poprad.
- 3rd Infantry Division "Rázus", led by Augustín Malár in the sector east of High Tatra.
- A motorized unit "Kalinčiak" was created on September 5, but the campaign ended before it had arrived at the front.
The group was part of the German Army Group South; was subordinated to the 14th Army, led by Wilhelm List; and contributed to the 14th Army's total of five infantry divisions, three mountain divisions, two panzer divisions and one Luftwaffe division. Bernolák's tasks were to prevent a Polish incursion into Slovakia and to support German troops.
They were opposed by the Polish Karpaty Army (Carpathian Army), which consisted mainly of infantry units with some light artillery support and no tanks.
Campaign
The attack started without a formal declaration of war on September 1, 1939, at 5:00 a.m. The 1st division occupied the village of Javorina and the town of Zakopane and continued toward Nowy Targ to protect the German 2nd Mountain Division from the left.[3]: 50 On September 4 and 5, it engaged in fighting with regular Polish Army units. On September 7, the division stopped its advance 30 km inside Polish territory. Later, the division was pulled back, with one battalion remaining until September 29 to occupy Zakopane, Jurgów and Javorina.
The 2nd Division was kept in reserve and participated only in mopping-up operations in which was supported by the Kalinčiak group. The 3rd Division had to protect 170 km of the Slovak border between Stará Ľubovňa and the border with Hungary. It fought minor skirmishes, and after several days, it moved into Polish territory and ended its advance on September 11.
Two or three Slovak air squadrons (codenamed Ľalia, Lily) were used for reconnaissance, bombing and close support for German fighters. Two Slovak planes were lost (one to anti-aircraft fire, another to an accidental crash), and one Polish plane was shot down. The total Slovak losses during the campaign were 37 dead, 114 wounded and 11 missing.
Aftermath
All Slovak units were pulled back until the end of September 1939. On October 5, a victorious military parade was held in Poprad. The mobilised units were gradually demobilised, and the Army Group Bernolák was disbanded on October 7.
The Slovak Army took around 1,350 civilian prisoners in Poland. In February 1940, around 1,200 of them were handed to Germans and some of the remainders to the Soviets. The rest were kept in a Slovak prison camp in Lešť.
All of the disputed territory, whether in Poland from 1920 or only from 1938, was given to Slovakia, which was confirmed by a Slovak parliamentary resolution on December 22, 1939. That arrangement lasted until 20 May 1945, when the border line was returned to its 1920 position. Since the war was started without a formal declaration of war and there were no longer any Polish prisoners of war held by Slovakia, there was no formal peace treaty between Poland and Slovakia.
Gallery
See also
- Army Karpaty
- List of Czechoslovakia interwar period weapons-Slovak arsenal was those weapons inherited from Czechoslovakia.
- Slovak Air Force (1939–1945)
- List of World War II military equipment of Poland
- List of German military equipment of World War II
References
- ↑ Dowell, Stuart (September 1, 2018). "Slovakian Invasion: the long forgotten story of how Slovak troops helped Hitler defeat Poland". TheFirstNews. Polish Press Agency. Archived from the original on September 19, 2023. Retrieved September 19, 2023.
- ↑ Korkuć, Maciej (September 24, 2020). "Slovak participation in the war. Occupation of Polish mountain regions". Przystanek Historia. Archived from the original on September 19, 2023. Retrieved September 19, 2023.
- ↑ S. J. Zaloga, Poland 1939, Oxford: Osprey, 2002. ISBN 9781841764085.
Further reading
- Charles K. Kliment and Břetislav Nakládal: Germany's First Ally, Schiffer Publishing, 1998, ISBN 0-7643-0589-1. The book covers the Slovak Armed Forces in World War II. 2003 Czech edition, ISBN 80-206-0596-7.
- Igor Baka: Slovensko vo vojne proti Poľsku v roku 1939 (Slovakia during the war against Poland in 1939), Vojenská história, 2005, No 3, pg 26 – 46.
- Igor Baka: Slovenská republika a nacistická agresia proti Poľsku (Slovak Republic and the Nazi Aggression Against Poland), Vojenský historický ústav, 2006, ISBN 978-80-89523-03-0, online.
External links
- Overview of the campaign (in Czech)
- Map of the campaign (in Czech) (archived link)
- Another overview, more military details (in Czech)
.JPG.webp)