 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Intramuscular |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 80.6% |
| Metabolism | Nil |
| Elimination half-life | 2.6 to 2.98 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
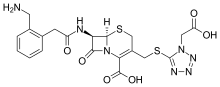
| Formula | C20H21N7O6S2 |
| Molar mass | 519.55 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Ceforanide is a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic.
See also
References
External links
- Crowle A, Sbarbaro J, May M (1988). "Effects of isoniazid and of ceforanide against virulent tubercle bacilli in cultured human macrophages". Tubercle. 69 (1): 15–25. doi:10.1016/0041-3879(88)90036-0. PMID 3140456.
- Campoli-Richards D, Lackner T, Monk J (1987). "Ceforanide. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and clinical efficacy". Drugs. 34 (4): 411–37. doi:10.2165/00003495-198734040-00001. PMID 3315624. S2CID 242440792.
- Cone L, Barton S, Woodard D (1987). "Treatment of scleroma with ceforanide". Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 113 (4): 374–6. doi:10.1001/archotol.1987.01860040036012. PMID 3814386.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.