
The River Ems is a much-sluiced, six miles (9.7 km) river that is located in the far west of the county of West Sussex, England.The last one and a half miles (2.4 km), of this river, delimits eastern Hampshire, before flowing into the sea at Chichester Harbour.
The river was so named, the "Ems", by a chronicler in the Tudor period.
Source
Over the centuries various cartographers and chroniclers have suggested a variety of sources for the Ems.[1] According to research by David J. Rudkin the River Ems has its source about one and a half miles (2 km) east of Stoughton.[1]
From source to the sea
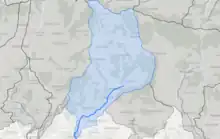
The River Ems has a catchment area of over 60 square kilometres (6,000 ha), and its upper reaches drain the South Downs.[2]Along the county-limits part, of its west bank, is the old town portion of Emsworth that contains mainly pre-1900-built buildings. The Ems flows south west through Walderton as a broad-catchment winterbourne.[1] It runs past:
- the hamlet that includes well-preserved Lordington House
- Racton Monument which has nearby in Racton hamlet the church for Lordington
- A copse, Ractonpark Dell
- the village of Westbourne, has the westmost section of the Ems, in Sussex. Westbourne receives a year-round brook from the north and that descends under the railway at Emsworth (in Hampshire), becomes tidal, drains Brook Meadow to Peter and Slipper Mill Ponds from where it discharges into the sea. At lower tides it helps forms at the head of Emsworth Channel in the harbour; its last few metres enable access to Emworth Marina, the other former tidal mill pond.[3][4]
There is little or no surface water in prolonged dry periods as the downstream springs have lowered the level of the water-table. However when the underlying aquifers are full, the rain runs off and the stream system starts to function.[5]
Etymology
It is sometimes thought that the town of Emsworth derives its name from that of the River Ems, this is not correct as before the 16th Century the stream was originally called the Bourne.[lower-alpha 1] The river was renamed by the 16th century chronicler Raphael Holinshed. Many of the towns and villages that the River Ems runs through or past still have Bourne as a suffix. e.g.:Westbourne.[7][8]
The Emille cometh first between Racton and Stansted, then down to Emilswort or Emmesworth, and so into the Ocean. Separating Sussex from Hampshire almost from the very head.
Notes
References
- 1 2 3 Rudkin 1984, p. 7.
- ↑ Environment Agency 2021.
- ↑ Ordnance Survey 1912, LX 6. 1910 revision.
- ↑ Rudkin 1984, Ch.2-Ch.5.
- ↑ Cole, Howard & Moore 2009.
- ↑ Lower 1864, pp. 263–264.
- ↑ Reger 1967, p. 17.
- ↑ Holinshed 1577, p. 21.
Citations
- Cole, S.J.; Howard, P.J.; Moore, R.J. (2009), Hydrological Modelling for the Rivers Lavant and Ems, Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, pp. 1–109
- Environment Agency (2021). "Ems Water Body". Department of Environment and Rural Affairs. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- Holinshed, Raphael (1577). The firste volume of the chronicles of England, Scotlande, and Irelande etc. Vol. 1. London: Imprinted for Iohn Hunne. OCLC 10105970.
- Lower, Mark Anthony (1864). Mark Antony Lower (ed.). "The Ems" (PDF). Sussex Archaeological Collections Relating to the History and Antiquities of the County. The Rivers of Sussex II. Lewes: SAC. XVI: 263–268.

- Ordnance Survey (1912). Sussex LX.6 (includes: Havant; Westbourne)Revised: 1910, Published: 1912 (Map). Ordnance Survey England & Wales County Series : Parish edition 1:2500.
- Reger, A J C (1967). A Short History of Emsworth and Warblington. Portsmouth: Pott and Horsey. p. 17.
- Rudkin, David J (1984). The River Ems and related Watercourses. Westbourne. OCLC 499701376.
