 Flag of the Stillaguamish Tribe of Indians | |
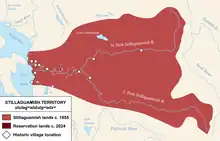 Historical (1855) and current reservation lands of the Stillaguamish Tribe | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 237 enrolled members[1] | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Languages | |
| English, Lushootseed[2] | |
| Religion | |
| traditional tribal religion |
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Lushootseed-speaking peoples of Puget Sound |
|---|
 |
The Stillaguamish Tribe of Indians, formerly known as the Stillaguamish Tribe of Washington, is a federally recognized tribe of Stillaguamish people. They are a tribe of Southern Coast Salish indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest located in Washington.[3]
Other Stillaguamish people are enrolled in the Tulalip Tribes.[4]
Name
The name has been used since 1850 to refer to indigenous peoples living along the Stillaguamish River. In 1855, they used the name Stoluck-wa-mish, which is how they sign the Point Elliott Treaty.[1]
Reservation
The Stillaguamish Tribe's trust lands are located in Snohomish County, Washington.[1] The tribe was granted a 64-acre (26 ha) reservation by the federal government in 2014.[5]
Government
The Tribe's constitution, approved by the Tribal Council on January 31, 1953, provides for the administrative responsibilities of Tribal government to be handled by the popularly elected six-member Stillaguamish Tribal Council. The Tribal Council is composed of a Chairman, Vice Chairman, Treasurer, Secretary, and two Members.[6]
As of June 2023, the Stillaguamish Tribal Council/Board of Directors is as follows:
- Chairman: Eric White
- Vice Chairman: Jeremy Smith
- Treasurer: Gary Tatro
- Secretary: Kadi Bizyayeva
- Member: Joshua Wells
- Member: Stacy White
The Tribe petitioned the federal government for recognition in 1974; it was granted on October 27, 1976.
Language
English is commonly spoken by the tribe. Formerly tribal members spoke Lushootseed, a Central Salish language. The language is written in the Latin script and a dictionary and grammar have been written in the Lushootseed.[2]
Economic Development

The Stillaguamish Tribal Business Development Department develops and works in partnership with the Board of Directors for the tribe's businesses that include River Rock Tobacco & Fuel and the Angel of the Winds Casino Resort, all located in Arlington.[7][8]
Notes
- 1 2 3 "Stillaguamish Tribe." Northwest Portland Area Indian Health Board. Retrieved September 26, 2013.
- 1 2 "Lushootseed." Ethnologue. Retrieved September 26, 2013.
- ↑ Pritzker 203
- ↑ Pritzker 201
- ↑ Bray, Kari (August 25, 2014). "Stillaguamish Tribe gets 'long overdue' reservation". The Everett Herald. Retrieved April 15, 2017.
- ↑ "Tribal Government." Stillaguamish Tribe of Indians. Retrieved July 31, 2023.
- ↑ "Stillaguamish Tribal Enterprise Corporation." Retrieved September 26, 2013.
- ↑ "Angel of the Winds Casino." 500 Nations. Retrieved September 26, 2013.
References
- Pritzker, Barry M. A Native American Encyclopedia: History, Culture, and Peoples. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000. ISBN 978-0-19-513877-1.
External links
- Stillaguamish Tribe of Indians, official website
- Esther Ross and the Struggle for Stillaguamish Identity, review by Carter Jones Meyer