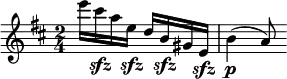
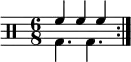
In music, syncopation is a variety of rhythms played together to make a piece of music, making part or all of a tune or piece of music off-beat. More simply, syncopation is "a disturbance or interruption of the regular flow of rhythm": a "placement of rhythmic stresses or accents where they wouldn't normally occur".[1] It is the correlation of at least two sets of time intervals.[2]
Syncopation is used in many musical styles, especially dance music. According to music producer Rick Snoman, "All dance music makes use of syncopation, and it's often a vital element that helps tie the whole track together".[3]
Syncopation can also occur when a strong harmony is simultaneous with a weak beat, for instance, when a 7th-chord is played on the second beat of 3
4 measure or a dominant chord is played at the fourth beat of a 4
4 measure. The latter occurs frequently in tonal cadences for 18th- and early-19th-century music and is the usual conclusion of any section.
A hemiola (the equivalent Latin term is sesquialtera) can also be considered as one straight measure in three with one long chord and one short chord and a syncope in the measure thereafter, with one short chord and one long chord. Usually, the last chord in a hemiola is a (bi-)dominant, and as such a strong harmony on a weak beat, hence a syncope.
Types of syncopation
Technically, "syncopation occurs when a temporary displacement of the regular metrical accent occurs, causing the emphasis to shift from a strong accent to a weak accent".[4] "Syncopation is very simply, a deliberate disruption of the two- or three-beat stress pattern, most often by stressing an off-beat, or a note that is not on the beat."[5]
Suspension
For the following example, there are two points of syncopation where the third beats are sustained from the second beats. In the same way, the first beat of the second bar is sustained from the fourth beat of the first bar.
Though syncopation may be very complex, dense or complex-looking rhythms often contain no syncopation. The following rhythm, though dense, stresses the regular downbeats, 1 and 4 (in 6
8):[5]
However, whether it is a placed rest or an accented note, any point in a piece of music that changes the listener's sense of the downbeat is a point of syncopation because it shifts where the strong and weak accents are built.[5]
Off-beat syncopation
The stress can shift by less than a whole beat, so it occurs on an offbeat, as in the following example, where the stress in the first bar is shifted back by an eighth note (or quaver):

Note how in the sound bite, the piano's notes do not happen at the same time as the drum beat that simply keeps a regular rhythm. In contrast, a standard-rhythm piece would have the notes occur on the beat:
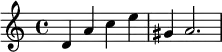
Playing a note ever so slightly before, or after, a beat is another form of syncopation because this produces an unexpected accent:
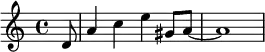
It can be helpful to think of a 4
4 rhythm in eighth notes and count it as "1-and-2-and-3-and-4-and". In general, emphasizing the "and" would be considered the off-beat (syncopated), whereas having the emphasis on the numbers is on-beat.
Anticipated bass
Anticipated bass[6] is a bass tone that comes syncopated shortly before the downbeat, which is used in Son montuno Cuban dance music. Timing can vary, but it usually occurs on the 2+ and the 4 of the 4
4 time, thus anticipating the third and first beats. This pattern is known commonly as the Afro-Cuban bass tumbao.
Transformation
Richard Middleton[7] suggests adding the concept of transformation to Narmour's[8] prosodic rules which create rhythmic successions in order to explain or generate syncopations. "The syncopated pattern is heard 'with reference to', 'in light of', as a remapping of, its partner." He gives examples of various types of syncopation: Latin, backbeat, and before-the-beat. First however, one may listen to the audio example of stress on the "strong" beats, where expected: ⓘ
Latin equivalent of simple 4
4
In the example below, for the first two measures an unsyncopated rhythm is shown in the first measure. The third measure has a syncopated rhythm in which the first and fourth beat are provided as expected, but the accent occurs unexpectedly in between the second and third beats, creating a familiar "Latin rhythm" known as tresillo.
Backbeat transformation of simple 4
4
The accent may be shifted from the first to the second beat in duple meter (and the third to fourth in quadruple), creating the backbeat rhythm:
Different crowds will "clap along" at concerts either on 1 and 3 or on 2 and 4, as above.
"Satisfaction" example
The phrasing of the Rolling Stones' song "Satisfaction" is a good example of syncopation.[5] It is derived here from its theoretic unsyncopated form, a repeated trochee (¯ ˘ ¯ ˘). A backbeat transformation is applied to "I" and "can't", and then a before-the-beat transformation is applied to "can't" and "no".[7]
1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 &
Repeated trochee: ¯ ˘ ¯ ˘
I can't get no – o
Backbeat trans.: ¯ ˘ ¯ ˘
I can't get no – o
Before-the-beat: ¯ ˘ ¯ ˘
I can't get no – o
ⓘ
This demonstrates how each syncopated pattern may be heard as a remapping, "with reference to" or "in light of", an unsyncopated pattern.[7]
History
Syncopation has been an important element of European musical composition since at least the Middle Ages. Many Italian and French compositions of the music of the 14th-century Trecento use syncopation, as in of the following madrigal by Giovanni da Firenze. (See also hocket.)

The refrain "Deo Gratias" from the 15th-century anonymous English "Agincourt Carol" is also characterised by lively syncopation:

According to the Encyclopædia Britannica, "[t]he 15th-century carol repertory is one of the most substantial monuments of English medieval music... The early carols are rhythmically straightforward, in modern 6/8 time; later the basic rhythm is in 3/4, with many cross-rhythms... as in the famous Agincourt carol 'Deo gratias Anglia'. As in other music of the period, the emphasis is not on harmony, but on melody and rhythm."[9]
Composers of the musical High Renaissance Venetian School, such as Giovanni Gabrieli (1557–1612), exploited syncopation for both their secular madrigals and instrumental pieces and also in their choral sacred works, such as the motet Domine, Dominus noster:

Denis Arnold says: "the syncopations of this passage are of a kind which is almost a Gabrieli fingerprint, and they are typical of a general liveliness of rhythm common to Venetian music".[10] The composer Igor Stravinsky, no stranger to syncopation himself, spoke of "those marvellous rhythmic inventions" that feature in Gabrieli's music.[11]
J. S. Bach and George Handel used syncopated rhythms as an inherent part of their compositions. One of the best-known examples of syncopation in music from the Baroque era was the "Hornpipe" from Handel's Water Music (1733).

Christopher Hogwood (2005, p. 37) describes the Hornpipe as “possibly the most memorable movement in the collection, combining instrumental brilliance and rhythmic vitality… Woven amongst the running quavers are the insistent off-beat syncopations that symbolise confidence for Handel.”[12] Bach's Brandenburg Concerto No. 4 features striking deviations from the established rhythmic norm in its first and third movements. According to Malcolm Boyd, each ritornello section of the first movement, "is clinched with an Epilog of syncopated antiphony":[13]

Boyd also hears the coda to the third movement as "remarkable... for the way the rhythm of the initial phrase of the fugue subject is expressed... with the accent thrown on to the second of the two minims (now staccato)":[14]

Haydn, Mozart, Beethoven, and Schubert used syncopation to create variety especially in their symphonies. The beginning movement of Beethoven's Eroica Symphony No. 3 exemplifies powerfully the uses of syncopation in a piece in triple time. After producing a pattern of three beats to a bar at the outset, Beethoven disrupts it through syncopation in a number of ways:
(1) By displacing the rhythmic emphasis to a weak part of the beat, as in the first violin part in bars 7–9:
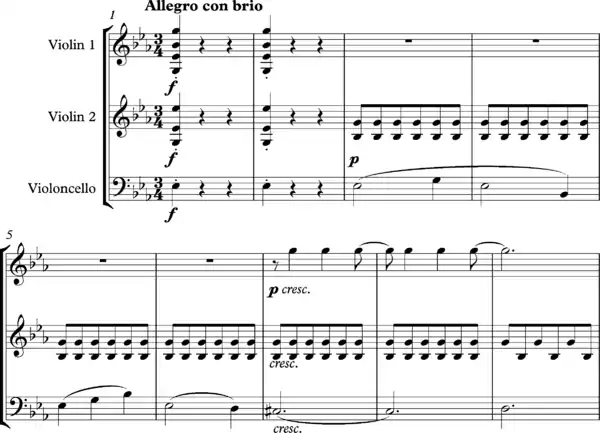

Richard Taruskin describes here how "the first violins, entering immediately after the C sharp, are made palpably to totter for two bars".[15]
(2) By placing accents on normally weak beats, as in bars 25–26 and 28–35:

This "long sequence of syncopated sforzandi"[15] recurs later during the development section of this movement, in a passage that Antony Hopkins describes as "a rhythmic pattern that rides roughshod over the properties of a normal three-in-a bar".[16]
(3) By inserting silences (rests) at points where a listener might expect strong beats, in the words of George Grove, "nine bars of discords given fortissimo on the weak beats of the bar":[17]

See also
- Anacrusis
- Counting (music)
- Syncopation (dance)
- Syncope and epenthesis, analogous linguistic concepts where vocal rhythm causes the loss or addition of sounds to a word
- Hemiola
- Cross-beat
- Nu metal, a subgenre of heavy metal music created in the 1990s, utilizing syncopated rhythms.
- The Syncopated Clock
References
- ↑ Hoffman, Miles (1997). "Syncopation". National Symphony Orchestra. NPR. Retrieved 13 July 2009.
- ↑ Patterson, William Morrison (1917). "Rhythm of Prose" (Introductory Outline). Columbia University Press.
- ↑ Snoman, Rick (2004). Dance Music Manual: Toys, Tools, and Techniques. Taylor & Francis. p. 44. ISBN 0-240-51915-9.
- ↑ Reed, Ted (1997). Progressive Steps to Syncopation for the Modern Drummer. Alfred. p. 33. ISBN 0-88284-795-3..
- 1 2 3 4 Day, Holly; Pilhofer, Michael (2007). Music Theory For Dummies. Wiley. pp. 58–60. ISBN 978-0-7645-7838-0..
- ↑ Peter Manuel (Autumn–Winter 1985). "The anticipated bass in Cuban popular music". Latin American Music Review. 6 (2): 249–261. doi:10.2307/780203. JSTOR 780203.
- 1 2 3 Middleton, Richard (2002) [1990]. Studying Popular Music. Philadelphia: Open University Press. pp. 212–213. ISBN 0-335-15275-9..
- ↑ Narmour (1980). pp. 147–153.
{{cite book}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) Cited in Middleton 2002, pp. 212–213 - ↑ "Carol". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 14 March 2019.
- ↑ Arnold, Denis (1979). Giovanni Gabrieli. Oxford University Press. p. 93.
- ↑ Stravinsky, Igor; Craft, Robert (1959). Conversations with Igor Stravinsky. London: Faber. p. 91.
- ↑ Hogwood, Christopher (2005). Handel: Water Music and Music for the Royal Fireworks. Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ Boyd 1993, p. 53.
- ↑ Boyd 1993, p. 85.
- 1 2 Taruskin, Richard (2010). The Oxford History of Western Music. Oxford University Press. p. 658.
- ↑ Hopkins, Antony (1981). The Nine Symphonies of Beethoven. London: Heinemann. p. 75.
- ↑ Grove, George (1896). Beethoven and his Nine Symphonies. London: Novello. p. 61.
Sources
- Boyd, Malcolm (1993). Bach: The Brandenburg Concertos. Cambridge University Press.
Further reading
- Seyer, Philip; Allan B. Novick; Paul Harmon (1997). What Makes Music Work. Forest Hill Music. ISBN 0-9651344-0-7.
External links
- Syncopation in dance and music
- On syncopation (in Dutch)