This is a non-exhaustive list of Arduino boards and compatible systems. It lists boards in these categories:
- Released under the official Arduino name
- Arduino "shield" compatible
- Development-environment compatible
- Based on non-Atmel processors
Where different from the Arduino base feature set, compatibility, features, and licensing details are included.
Official
Many versions of the official Arduino hardware have been commercially produced to date:[1][2]
| Name | Processor | Format | Host interface | I/O | Release date | Notes | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | Frequency | Dimensions | Voltage | Flash (KB) | EEPROM (KB) | SRAM (KB) | Headers(Fem/Male)
pins vs soldering |
Digital I/O (pins) | Digital I/O with PWM (pins) | Analog input (pins) | Analog output pins | ||||||
| Arduino Uno WiFi rev 2[3] | ATMEGA4809, NINA-W132 Wi-Fi module from u-blox, ECC608 crypto device
|
16 MHz | Arduino / Genuino | 68.6 mm x 53.4 mm [ 2.7 in x 2.1 in ] | USB-A | 32U4 | 5 V | 48 | 0.25 | 6 | FH | 14 | 5 | 6 | 0 | AnnouncedMay 17, 2018 | Contains six-axis accelerometer, gyroscope the NINA/esp32 module supports Wi-Fi and support Bluetooth as Beta feature[4] |
| Arduino / Genuino MKR1000 | ATSAMW25 (made of SAMD21 Cortex-M0+ 32 bit ARM MCU,
WINC1500 2.4 GHz 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi, and ECC508 crypto device ) |
48 MHz | minimal | 61.5 mm × 25 mm [ 2.4 in × 1.0 in ] | USB | 3.3 V | 256 | No | 32 | 8 | 12 | 7 | 1 | Announced: April 2, 2016 | |||
| Arduino MKR Zero | ATSAMD21G18A | 48 MHz | minimal | USB | 3.3 V | 256 | No | 32 | |||||||||
| Arduino 101[5] Genuino 101 |
Intel® Curie™ module[6] two tiny cores, an x86 (Quark SE) and an ARC | 32 MHz | Arduino / Genuino | 68.6 mm × 53.4 mm [ 2.7 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | 3.3 V | 196 | 24 | 14 | 4 | 6 | October 16, 2015 | Contains six-axis accelerometer, gyroscope and Bluetooth | ||||
| Arduino Zero[7] | ATSAMD21G18A[8] | 48 MHz | Arduino | 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm [ 2.7 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | Native & EDBG Debug | 3.3 V | 256 | 0 to 16 Kb emulation | 32 | 14 | 12 | 6 | 1 | Released June 15, 2015[9]
Announced
May 15, 2014[10] |
Beta test started in Aug 1, 2014,[11] 32-bit architecture | |
| Arduino Due[12][13] | ATSAM3X8E[14] (Cortex-M3) | 84 MHz | Mega | 101.6 mm × 53.3 mm [ 4 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | 16U2[15] + native host[16] | 3.3 V | 512 | 0[17] | 96 | 54 | 12 | 12 | 2 | October 22, 2012[18] |  The first Arduino board based on an ARM processor. Features 2 channel 12-bit DAC, 84 MHz clock frequency, 32-bit architecture, 512 KB flash and 96 KB SRAM. Unlike most Arduino boards, it operates on 3.3 V and is not 5 V tolerant. | |
| Arduino Yún[19] | ATmega32U4,[20] Atheros AR9331 |
16 MHz, 400 MHz |
Arduino | 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm [ 2.7 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | 5 V | 32 KB, 16 MB |
1 KB, 0 KB |
2.5 KB, 64 MB |
14 | 6 | 12 | September 10, 2013[21] | Arduino Yún is the combination of a classic Arduino Leonardo (based on the ATmega32U4 processor) with a Wi-Fi system on a chip (SoC) running Linino, a MIPS Linux based on OpenWrt. | |||
| Arduino Leonardo[22] | ATmega32U4[20] | 16 MHz | Arduino | 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm [ 2.7 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | 32U4[20] | 5 V | 32 | 1 | 2.5 | 20 | 7 | 12 | July 23, 2012[23] |  The Leonardo uses the ATmega32U4 processor, which has a USB controller built-in, eliminating one chip as compared to previous Arduinos. | ||
| Arduino Uno[24] | ATmega328P[25] | 16 MHz | Arduino | 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm [ 2.7 in × 2.1 in ] | USB-A | 8U2[26] (Rev1&2)/
16U2[15] (Rev3) |
5 V | 32 | 1 | 2 | FM | 14 | 6 | 6 | September 24, 2010[27] |  This uses the same ATmega328 as late-model Duemilanove, but whereas the Duemilanove used an FTDI chip for USB, the Uno uses an ATmega16U2 (ATmega8U2 before rev3) programmed as a serial converter. | |
| Arduino Mega2560[28] | ATmega2560[29] | 16 MHz | Mega | 101.6 mm × 53.3 mm [ 4 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | 8U2[26] (Rev1&2)/
16U2[15] (Rev3) |
5 V | 256 | 4 | 8 | FH | 54 | 15 | 16 | September 24, 2010[27] |  Total memory of 256 KB. Uses the ATmega16U2 (ATmega8U2 before Rev3) USB chip. Most shields that were designed for the Duemilanove, Diecimila, or Uno will fit, but a few shields will not fit because of interference with the extra pins. | |
| Arduino Ethernet[30] | ATmega328[31] | 16 MHz | Arduino | 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm [ 2.7 in × 2.1 in ] | Ethernet serial interface | Wiznet Ethernet | 5 V | 32 | 1 | 2 | 14 | 4 | 6 | July 13, 2011[32] |  Based on the same WIZnet W5100 chip as the Arduino Ethernet Shield.[33] A serial interface is provided for programming, but no USB interface. Late versions of this board support Power over Ethernet (PoE). | ||
| Arduino Fio[34] | ATmega328P[25] | 8 MHz | minimal | 66.0 mm × 27.9 mm [ 2.6 in × 1.1 in ] | XBee Serial | 3.3 V | 32 | 1 | 2 | 14 | 6 | 8 | March 18, 2010[35] | 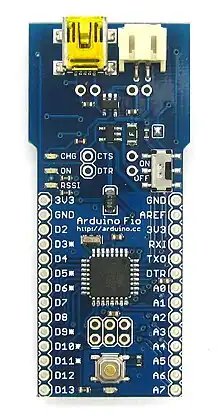 Includes XBee socket on bottom of board.[34] | |||
| Arduino Nano[36] | ATmega328[31] (ATmega168 before v3.0[37]) |
16 MHz | minimal | 43.18 mm × 18.54 mm [ 1.70 in × 0.73 in ] | USB-mini | FTDI FT232R[38] | 5 V | 16/32 | 0.5/1 | 1/2 | MH & soldering | 14 | 6 | 8 | May 15, 2008[39] | 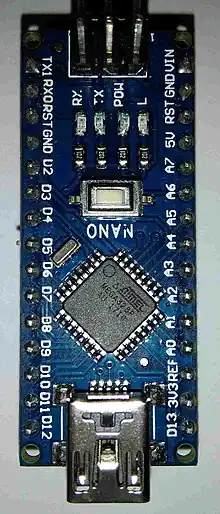 This small USB-powered version of the Arduino uses a surface-mounted processor. | |
| LilyPad Arduino[40] | ATmega168V or ATmega328V | 8 MHz | wearable | 51 mm ⌀ [ 2 in ⌀ ] | 2.7-5.5 V | 16 | 0.5 | 1 | 14 | 6 | 6 | October 17, 2007[41] |  This minimalist design is for wearable applications. | ||||
| Arduino Pro[42] | ATmega168 or ATmega328[42] | 16 MHz | Arduino | 52.1 mm × 53.3 mm [ 2.05 in × 2.1 in ] | UART serial, I²C (TWI), SPI | FTDI | 5 V or 3.3 V | 16/32 | 0.5/1 | 1/2 | 14 | 6 | 6 | August 23, 2008[43] |  Designed and manufactured by SparkFun Electronics for use in semi-permanent installations. | ||
| Arduino Mega ADK[44] | ATmega2560[29] | 16 MHz | Mega | 101.6 mm × 53.3 mm [ 4 in × 2.1 in ] | 8U2[26]
|
5 V | 256 | 4 | 8 | 54 | 14 | 16 | July 13, 2011[32] | ||||
| Arduino Esplora[45] | ATmega32U4[20] | 16 MHz | 165.1 mm × 61.0 mm [ 6.5 in × 2.4 in ] | 32U4[20] | 5 V | 32 | 1 | 2.5 | December 10, 2012 | Analog joystick, four buttons, several sensors, 2 TinkerKit inputs and 2 outputs, LCD connector | |||||||
| Arduino Micro[46] | ATmega32U4[20] | 16 MHz | Mini | 17.8 mm × 48.3 mm [ 0.7 in × 1.9 in ] | USB | 5 V | 32 | 1 | 2.5 | Soldering | 20 | 7 | 12 | November 8, 2012[47] |  This Arduino was co-designed by Adafruit. | ||
| Arduino Pro Mini | ATmega328P | 8 MHz (3.3V), 16 MHz (5V) | Mini | 17.8 mm × 33.0 mm [ 0.7 in × 1.3 in ] | Six-pin serial header | 5 V / 3.3 V | 32 | 1 | 2 | Soldering | 14 | 6 | 6 | August 23, 2008[43] | Designed and manufactured by SparkFun Electronics. | ||
See also list of Official Arduino Boards in wikidata
Superseded
The following have been superseded by later and more capable versions from Arduino.
| Name | Processor | Format | Host interface | I/O | Release date | Notes | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | Frequency | Dimensions | Voltage | Flash (KB) | EEPROM (KB) | SRAM (KB) | Digital I/O (pins) | Digital I/O with PWM (pins) | Analog input (pins) | ||||||
| Serial Arduino[48] | ATmega8[49] | 16 MHz | Arduino | 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm [ 3.2 in × 2.1 in ] | DE-9 serial connection | native | March 30, 2005[50] |  The first board labelled "Arduino". | |||||||
| Arduino USB[1] | ATmega8[49] | 16 MHz | Arduino | 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm [ 3.2 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | FTDI FT232BM |  Arduino USB v2.0 | ||||||||
| Arduino Extreme[1] | ATmega8[49] | 16 MHz | Arduino | 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm [ 3.2 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | The Arduino Extreme uses many more surface mount components than previous USB Arduino boards and comes with female pin headers.[1] | |||||||||
| Arduino NG (Nuova Generazione)[1] | ATmega8[49] | 16 MHz | Arduino | 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm [ 3.2 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | FTDI FT232RL |  | ||||||||
| Arduino NG plus | ATmega168[37] | 16 MHz | Arduino | 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm [ 3.2 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | ||||||||||
| Arduino BT (Bluetooth)[51] | ATmega168[37] ATmega328[31] |
16 MHz | Arduino | 81.3 mm × 53.3 mm [ 3.2 in × 2.1 in ] | Bluetooth | Bluegiga WT11 Bluetooth | 5 V | 32 | 1 | 2 | 14 | 4 | 6 | October 22, 2007[52] |  Similar to the Arduino NG, this has a Bluetooth module rather than a serial interface.[51] Programming is carried out via Bluetooth. |
| Arduino Diecimila[53] | ATmega168 (DIP-28)[37] | 16 MHz | Arduino | 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm [ 2.7 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | FTDI | 5 V | 16 | 0.5 | 1 | 14 | 6 | 6 | October 22, 2007[52] |  |
| Arduino Duemilanove (2009)[54] | ATmega168,[37] ATmega328P (ATmega328 for newer version) |
16 MHz | Arduino | 68.6 mm × 53.3 mm [ 2.7 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | FTDI | 5 V | 16/32 | 0.5/1 | 1/2 | 14 | 6 | 6 | October 19, 2008[55] |  Improved: automatically switching between USB and external power, eliminating jumper |
| Arduino Mega[56] | ATmega1280[57] | 16 MHz | Mega | 101.6 mm × 53.3 mm [ 4 in × 2.1 in ] | USB | FTDI | 5 V | 128 | 4 | 8 | 54 | 14 | 16 | March 26, 2009[58] |  Uses a surface-mounted ATmega1280 for additional I/O and memory.[59] |
| Arduino Mini[60] | ATmega168[37] (Pro uses ATmega328) | 8 MHz (3.3 V model) or 16 MHz (5 V model) | 17.8 mm × 33.0 mm [ 0.7 in × 1.3 in ] | 5 | 16 | 0.5 | 1 | 14 | 6 | 6 | August 23, 2008[43] |  This miniature version of the Arduino uses a surface-mounted processor. | |||
Compatible
Although the hardware and software designs are freely available under copyleft licenses, the developers have requested that the name "Arduino" be exclusive to the official product and not be used for derivative works without permission. The official policy document on the use of the Arduino name emphasizes that the project is open to incorporating work by others into the official product.[2]
As a result of the protected naming conventions of the Arduino, a group of Arduino users forked the Arduino Diecimila, releasing an equivalent board called Freeduino. The name "Freeduino" is not trademarked and is free to use for any purpose.[61]
Several Arduino-compatible products commercially released have avoided the "Arduino" name by using "-duino" name variants.[61]
Footprint-compatible
The following boards are fully or almost fully compatible with both the Arduino hardware and software, including being able to accept "shield" daughterboards.
| Name | Processor | Maker | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seeeduino V4.2 [62] | ATmega328P | Seeed Studio | Seeeduino V4.2 is an Arduino-compatible board, which is based on ATmega328P MCU, Arduino UNO bootloader, and with an ATmega16U2 as a UART-to-USB converter. The three on-board Grove interface can make your board connect to over 300 Grove modules. |
| Seeeduino Cortex-M0+] | SAMD21 Cortex-M0+ | Seeed Studio | The Seeeduino Cortex-M0+ features an Atmel SAMD21 MCU which is based on a 32-bit ARM® Cortex®-M0+ processor. With the help of this powerful core, SAMD21 is much more powerful than AVR and can achieve many functions and more complex calculations that cannot be implemented on AVR chips. |
| Seeeduino Lotus V1.1 | ATmega328P | Seeed Studio | Seeeduino Lotus V1.0 is a 2 in 1 solution of the Seeeduino board and base shield. |
| Seeeduino Lotus Cortex-M0+ | SAMD21 Cortex-M0+ | Seeed Studio | SMART™ SAM D21 is a series of low-power microcontrollers using the 32-bit ARM® Cortex®-M0+ processor with 256 KB flash and 32 KB of SRAM. The Seeeduino Lotus Cortex-M0+ can be considered as a combination of Seeeduino and Base Shield. |
| Seeeduino LoRaWAN | SAMD21 Cortex-M0+ | Seeed Studio | LoRaWAN Class A/C Ultra long range communication Ultra low power consumption Arduino programming (based on Arduino Zero bootloader). Embedded with lithium battery management chip 4 Grove connectors onboard |
| Seeeduino LoRaWAN W/GPS | SAMD21 Cortex-M0+ | Seeed Studio | LoRaWAN Class A/C Ultra long range of communication GPS communication Ultra low power consumption Arduino programming (based on Arduino Zero bootloader). Embedded with lithim battery management chip 4 Grove connectors onboard |
| Seeeduino Lite | ATmega32U4 | Seeed Studio | Built around the ATmega32U4 chip Provide up to 20 Digital I/Os On board switch for 3. 3V and 5 V dual working mode 2 built-in Grove interface Built-in Micro USB for power supply and programming |
| Seeeduino Ethernet | ATmega328P | Seeed Studio | Seeeduino Ethernet is a compact and multifunctional development platform, which merges data logging and processing, device control and Ethernet communication together into one |
| Seeeduino Cloud | ATmega32U4 | Seeed Studio | Built on Dragino Wi-Fi IoT module HE and ATmega32U4 Compatible with Arduino Yun Support 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi, 802.11 b/g/n Built-in Ethernet port and USB 2.0 Running OpenWrt system |
| Seeeduino Stalker V3.1 | ATmega328P | Seeed Studio | Upgraded from Seeeduino Stalker V3.0 Lower power consumption (down to 100uA in sleep mode) Extra toggle switch for X-bee area 2 extra toggle switches for selecting the INT pin connected to RTC 3.3 V and 5 V dual mode |
| evive | ATmega2560[29] | STEMpedia | Built on top of Arduino MEGA 2560 R3.[63] Designed for STEM educational, and prototyping purpose.
Compatible with Arduino Uno for all the Arduino Shields. Additional features:
|
| Canaduino Uno Bone | Atmega328P-PU | Universal Solder | Do-it-yourself Arduino Uno R3 compatible footprint and connections.
Additional features:
|
| ST1 | ATmega328 | Sanjay Technologies (sanjaytechnologies.co.in)[64] | Compatible with Arduino Uno Rev3 - added features:
Compatible with Arduino Uno R3. |
| ST Freeduino Robotics Board | ATmega328 | Sanjay Technologies (sanjaytechnologies.co.in)[65] | Compatible with Arduino with servo ports - added features:
External DC power socket (7 VDC to 20 VDC) or USB powered. On-board 5 V regulator with heatsink area for efficient 1000 mA output. Has built in ICSP port for on the fly programming (P1). Robotics ready (has 4 servo ports P3 and P2). |
| GSTduino | ATmega328 | Green System Technology[66] | Added features:
Powered via the micro USB connection, or 2.8–5.5 V battery connector Serial communication on pin D0 (RX) and pin D1 (TX). used to receive (RX) and transmit (TX) TTL serial data. These pins are connected to the corresponding pins of the FTDI USB-to-TTL serial chip. By sliding the switch (S1), RX/TX pins can be re-routed to Bluetooth UART connector. |
| Linduino One | ATmega328 | Linear Technology Corporation[67] | Compatible with Arduino Uno. Galvanically isolated USB interface provided by onboard LTM2884 USB Isolation module. |
| InVentor UNO[68] | ATmega328P-PU | Ventor Technologies[69] | Added features:
|
| InvIoT U1 | ATmega328P-PU | InvIoT.com[70] |  inviot U1 (arduino-compatible) all-in-one board with LCD, rotary encoder, RTC DS3231, EEPROM, buzzer, push buttons, RGB Led, NRF24 plug, and ESP8266 plug.
|
| Bluno | ATmega328 | DFRobot.com | Added features:
|
| AVR.duino U+ | ATmega328 | SlicMicro.com |  Compatible With Arduino Uno Rev3
|
| SainSmart UNO[71] | ATmega328 | SainSmart[72] |  Compatible with Arduino |
| SainSmart Mega 2560[73] | ATmega2560[29] | SainSmart[72] |  Compatible with Arduino |
| Freaduino MEGA2560[74] | ATmega2560[29] | ElecFreaks[75] |
|
| SainSmart UNO R3[76] | ATmega328-AU | SainSmart[72] |  Development board compatible with Arduino UNO R3 |
| AVR-Duino[77] | TavIR[78] | Another Arduino/Mega compatible board. | |
| Brasuíno[79] | Holoscópio[80] |  Based on the Uno with rearranged LEDs and reset button, mini-USB connector, and altered pin 13 circuitry so that the LED and resistor do not interfere with pin function when acting as an input. The Brasuíno was designed using KiCad, and is licensed as GPLv2. Based on the Uno with rearranged LEDs and reset button, mini-USB connector, and altered pin 13 circuitry so that the LED and resistor do not interfere with pin function when acting as an input. The Brasuíno was designed using KiCad, and is licensed as GPLv2. | |
| ChibiDuino2[81] | ATmega328 | TiisaiDipJp[81] |  Japanese Arduino compatible kit using Uno board setting. Includes two mini-B USB sockets, 1602 LCD socket, 5 V or 3.3 V power selection, breadboard area. Japanese Arduino compatible kit using Uno board setting. Includes two mini-B USB sockets, 1602 LCD socket, 5 V or 3.3 V power selection, breadboard area. |
| Cosmo Black Star[82] | ATmega328 | JT5[83] | Arduino layout-compatible board. Based on the Arduino Duemilanove. |
| CraftDuino[84] | Manufactured and sold by RoboCraft Team. | ||
| CT UNO | ATmega328P | Cytron Technologies | CT-UNO features:
|
| CT ARM (Cytron ARM Cortex M0) | NUC131LD2AE (32-bit ARM Cortex-M0) | Cytron Technologies | CT-ARM features:
|
| Diavolino[85] | Evil Mad Scientist Laboratories |  Arduino layout-compatible board, designed for use with a USB-TTL serial cable. Arduino layout-compatible board, designed for use with a USB-TTL serial cable. | |
| DuinoBot v1.x[86] | ATmega32U4 | RobotGroup Argentina[87] | Arduino fully compatible board, with integrated power supply and controllers designed for robotics. Compatible as well with the system "Multiplo" |
| eJackino[88] | Kit by CQ publisher in Japan. | Similar to Seeeduino, eJackino can use universal boards as shields. On back side, there is a "Akihabara station" silk, just like Italia on Arduino. | |
| gizDuino Version 5.0V | Atmega168, Atmega328 | e-gizmo | Arduino compatible
USB to serial made by prolific Locally made in the Philippines. |
| Elektor Platino[89] universal AVR board | ATmega8, ATmega16, ATmega32, ATmega88, ATmega164, ATmega168, ATmega324, ATmega328, ATmega644, ATmega1284 | Elektor | Platino is an Arduino compatible board that supports 28-pin and 40-pin AVR devices. The board features multiple footprints for user interface elements like LCDs, pushbuttons, rotary encoders, LEDs and buzzer, supported by an extensive library. Bootloaders are available for all supported processors. On its backside are Arduino shield compatible connectors plus other extension connectors. |
| fayaduino Series[90] | fayalab[91] | Manufactured and sold by Taiwan-based kit company fayalab, with 100% compatible design to Genuino/Arduino. | |
| Freeduino MaxSerial[90] | Manufactured and sold assembled or as a kit by Fundamental Logic until May 2010. | A board with a standard DE-9 serial port. | |
| Freeduino SB[92] | ATmega328 | Solarbotics Ltd.[93] |  Compatible with the Duemilanove. Compatible with the Duemilanove. |
| Freeduino Through-Hole[94] | Manufactured and sold as a kit by NKC Electronics. | The design avoids surface-mount soldering. | |
| Illuminato Genesis[95] | ATmega644 | Provides 64 KB of flash, 4 KB of RAM and 42 general I/O pins. Hardware and firmware are open source. | |
| InduinoR3[96] (Previously Known as InduinoX) | ATmega168/ATmega 328/ATmega 8 | Simple Labs[97] | A low cost Arduino clone using the ATmega168/ATmega 328/ATmega 8 and designed for prototyping, it includes onboard peripherals such as an RGB LED, switches, IR LED, TSOP and LDR. |
| Japanino[98] | ATmega168[37] | A kit by Otonano Kagaku publisher in Japan. | The board and a POV kit were included in Vol. 27 of the eponymous series. It is unique in having a regular size USB A connector. |
| 1000Pads Luigino[99] | Minimalistic version of Arduino: small, without serial converter. Available as a kit, board only or assembled. Smaller than Arduino, with different footprint. | ||
| Luigino328[100] | ATmega328 | It has an improved automatic voltage selector, resolves problems during programming caused by shields that use the serial port, with an automatic serial port selector, and has the LM1117 voltage regulator. | |
| metaboard[101] | Developed by Metalab, a hackerspace in Vienna. | Designed to have a very low complexity and price. Hardware and firmware are open source. | |
| Rascal | AT91SAM9G20 (ARM9) | Rascal Micro[102] | It is compatible with Arduino shields, but it is programmed in Python rather than C++. It has an embedded webserver. |
| Raspduino[103] | ATmega328 | Bitwizard[104] | Fully Arduino compatible board, that fits perfectly on a Raspberry Pi, and can be programmed through the Raspberry Pi's serial interface. It also breaks out the Raspberry Pi's SPI and I²C interfaces, or can be used as a stand-alone Arduino when powered with the external power header. |
| Romeo 2012[105] | ATmega328 | DFRobot[106] | An all-in-one Arduino with motor controller. Compatible with the Arduino Uno.  |
| Roboduino[107] | 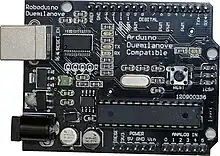 Designed for robotics. All connections have neighboring power buses (not pictured) for servos and sensors. Additional headers for power and serial communication are provided. It was developed by Curious Inventor, LLC. Designed for robotics. All connections have neighboring power buses (not pictured) for servos and sensors. Additional headers for power and serial communication are provided. It was developed by Curious Inventor, LLC. | ||
| SunDuino[108] | ATmega8/88/168/328/16/32/324/644 and PIC18F2550/4550 PIC32MX320F128 and ButterFLY, STM32Discovery | Lothar Team Arduino PRO Compatible boards. (Poland) | Another Arduino compatible board, software- and hardware-compatible. |
| TwentyTen[109] | Freetronics[110] |  Based on the Duemilanove, with a prototyping area, rearranged LEDs, mini-USB connector, and altered pin 13 circuitry so LED and resistor do not interfere with pin function when acting as an input. Based on the Duemilanove, with a prototyping area, rearranged LEDs, mini-USB connector, and altered pin 13 circuitry so LED and resistor do not interfere with pin function when acting as an input. | |
| UDOO | Atmel SAM3X8E | SECO Inc. | Android-Linux-Arduino compatible board. |
| Volksduino[111] | Applied Platonics[112] | A low cost, high power, shield-compatible, complete Arduino-compatible board kit. Based on the Duemilanove, it comes with a 5 V / 1 A voltage regulator (optional 3.3 V regulator). Designed for low component count and for ease of assembly. | |
| Wiseduino[113] | Includes a DS1307 RTC with backup battery, a 24LC256 EEPROM and a connector for XBee adapter for wireless communication. | ||
| Xaduino | ATXmega128A3U | OBDIIworld | 8/16 bit Xmega core @ 32 MHz. 8 KB SRAM. 37 Digital I/O. 3.3 V. 2 DAC. Output 3.3 V pin: 500 mA, 5 V 500 mA. |
| YourDuinoRoboRED | Atmel 328 | Yourduino.com[114] | Includes 14 color-coded 3-pin connectors for direct cable connection of servos, electronic bricks, etc., and six color-coded3-pin connectors to analog inputs for electronic bricks, etc. Provides improved 3.3 V regulator supplying 500 mA, and optional 3.3 V operation. Switching regulator provides 5 V 2 A from up to 20 V external supply.
|
| YourDuinoRobo1[115] | Atmel 328 | Yourduino.com[114] | Includes 6 color-coded 3-pin connectors for direct cable connection of servos, electronic bricks, etc., and 6 3-pin connectors to analog inputs for electronic bricks, etc. Provides improved 3.3 V regulator supplying 500 mA, and optional 3.3 V operation. |
| ZArdino[116] | ATMega328 | A kit created by Peter Ing | A South African Arduino-compatible board derived from the Duemilanove, it features mostly through-hole construction except for the SMD FT232RL IC, power selection switches, option for a Phoenix power connector instead of DC jack, extra I/O pads for using Veroboard as shields. Designed for easy assembly in countries where exotic components are hard to find. PCB layout and board now available on Circuitmaker as Open Source Hardware |
| Zigduino[117] | ATmega128RFA1 | Logos Electromechanical[118] |  Integrates Zigbee (IEEE 802.15.4). It can be used with other 802.15.4 network standards as well as Zigbee. It is the same shape as the Duemilanove, includes an external RPSMA jack on the side of the board opposite the power jack, and is compatible with shields that work with other 3.3 V boards. Integrates Zigbee (IEEE 802.15.4). It can be used with other 802.15.4 network standards as well as Zigbee. It is the same shape as the Duemilanove, includes an external RPSMA jack on the side of the board opposite the power jack, and is compatible with shields that work with other 3.3 V boards. |
| EtherTen[119] | ATmega328P | Freetronics | Fixed SPI behaviour on Ethernet chip, D13 pin isolated with a MOSFET of which can also be used as an input. |
| EtherMega[120] | ATmega2560[29] | Freetronics | Fixed SPI behaviour on Ethernet chip, Micro SD card slot, D13 pin isolated with a MOSFET of which can also be used as an input. |
| USBDroid[121] | ATmega328P | Freetronics | Can act as a host for an Android device and is compatible with the Android Open Accessory Development Kit, Micro SD card slot, D13 pin isolated with a MOSFET of which can also be used as an input. |
| Eleven[122] | ATmega328P | Freetronics | Arduino Uno compatible, D13 pin isolated with a MOSFET of which can also be used as an input. |
| KitTen[123] | ATmega328P | Freetronics | Includes both 3.3 V and 5 V regulators for shields, D13 pin isolated with a MOSFET of which can also be used as an input. Can be connect to Arduino using CAT5 cable.[124] |
| EtherDue[125] | ATSAM3X8E[14] (Cortex-M3) | Freetronics | Arduino Due with onboard Ethernet, software-compatible with Arduino Ethernet shield, D13 pin isolated with a MOSFET of which can also be used as an input. |
| TAIJIUINO Due Pro[126] | ATSAM3X8E[14] (Cortex-M3) | Elechouse | Mostly compatible with Arduino Due. Includes RMII signals via a connector to allow access to the microcontroller's native Ethernet MAC. |
| ShieldBuddy TC275[127] | Infineon Aurix TC275TP | Hitex UK | Uses Arduino Due form factor and largely compatible pin allocation. Runs at 5 V, but can be modified to run at 3.3 V. Triple-core, 32-bit, 200 MHz Aurix processor. 4 MB flash, 550 kB SRAM, 128 kB DataFlash. Optional CIC61508 safety monitor. Arduino IDE supported via add-in, plus Eclipse-based tools with multicore debugger. |
| MBZ Pro WiFi | Atmega328P-PU | MaxBlitz | 
MBZ Pro Mega is an Arduino compatible stand-alone board with a prototyping area and built-in Wi-Fi. Featuring a compact design, it helps to shrink Arduino projects and make it permanent.
|
| Rhino Mega 2560[128] | ATmega2560[29] | Cyrola Inc. |  Arduino Uno compatible board powered by ATmega2560. D0/D1 can be changed to D19/D18. It enables to multiple serial communication.[129] A4/A5 are not connected to SDA/SCL same as Arduino Mega. |
| Mega 2560 PRO (Embed) | ATmega2560-16AU | RobotDyn | Embed version of Mega 2560 CH340G/ATmega2560 - compatible with Arduino Mega 2560 board. Built on the Atmel ATmega2560 microcontroller and USB-UART interface chip CH340G.
Board have compact size 38x55 mm. It is good solution, to make your final project on solder proto-board. Board for functionality similar to the Arduino Mega 2560. It is embed board, but the same stable, and uses the original chips ATmega2560 (16 MHz). The board used the chip CH340G as converter UART-USB. When working in the frequency 12 MHz, giving a stable result of data exchange (need install drivers to computer). Mega PRO (Embed) 2560 CH340G / ATmega2560 - connects to the computer via microUSB cable (used for almost all Android smartphones). |
| MiniZed | Zynq 7Z007S | Avnet, Inc. | Compatible with Arduino shields and Pmod extension cards. ARM Cortex-A9 CPU (max frequency 667 MHz) and FPGA fabric, 512 Mb RAM, 8 Gb eMMC storage, on-board Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, USB 2.0 host. |
Special purpose compatible
Special purpose Arduino-compatible boards add additional hardware optimised for a specific application. It is kind of like having an Arduino and a shield on a single board. Some are Shield compatible, others are not.
| Name | Processor | Shield-compatible? | Host interface | Maker | Additions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Io:duino[130] | AT90CAN128 | yes | USB with FTDI serial chip | Railstars | Adds built-in CAN support through the AT90CAN128 micro processor, dual RJ45 jacks, and optional bus termination. Designed specifically for model railroading applications using the OpenLCB networking protocol, the hardware is sufficiently generic for use with other low-speed CAN networks. OUT OF BUSINESS 17 Dec 2014. All designs supposedly on GitHub, but Io:duino is not present. (https://web.archive.org/web/20160516101800/http://railstars.com/blog/) |
| DFRobotShop Rover[131] | ATmega328 | This is a minimalist tracked platform based on the Arduino Duemilanove. Has an ATmega328 with Arduino bootloader, a dual H-bridge and additional prototyping space and headers. It is compatible with many shields, though four digital pins are used when operating the motor controller. Has an onboard voltage regulator, additional LEDs, a temperature sensor, and a light sensor. Part of the DFRobotShop Rover kit. | |||
| Faraduino[132] | ATmega328 | Yes | USB with FTDI serial chip | Developed by Middlesex University Teaching Resources.[133] |  Simple shield-compatible board, with onboard discrete transistor H-bridges and screw terminals to drive two small DC motors from pins 4–7.[134] Has headers for three servos on pins 9–11. Simple shield-compatible board, with onboard discrete transistor H-bridges and screw terminals to drive two small DC motors from pins 4–7.[134] Has headers for three servos on pins 9–11.  Also sold with the Faraduino buggy kit[135] and Faraconnect shield[136] as a simple school-level teaching robot. Also sold with the Faraduino buggy kit[135] and Faraconnect shield[136] as a simple school-level teaching robot. |
| Motoruino[137] | ATmega328 | Yes | Serial only, 6-pin header | Guibot |  Has L293D twin H-bridge. Has L293D twin H-bridge. |
| Alternator Regulator[138] | ATmega64M1 | No | USB with FTDI serial chip | Open source Alternator Regulator suitable for 12 V to 48 V systems with many different battery chemistries (lead-acid, LiFeP04, etc.). Multi stage (3, 4), fully configurable. Features battery voltage and current measurement to assure complete and safe battery charging as well as CAN support for communications with other devices and status output (including "NMEA2000" like messages).
Programmable using Arduino IDE with ATmegaxxM1 board type ( https://github.com/thomasonw/ATmegaxxM1-C1 ) More (including source and CAD files): | |
| ArduPilot[139] |  An Arduino-compatible board designed for auto-piloting and autonomous navigation of aircraft, cars, and boats. It uses GPS for navigation and thermopile sensors or an IMU for stabilization. An Arduino-compatible board designed for auto-piloting and autonomous navigation of aircraft, cars, and boats. It uses GPS for navigation and thermopile sensors or an IMU for stabilization. | ||||
| ArduIMU[139] | An Arduino-compatible board designed for inertial measurement and inertial navigation of aircraft, cars, and boats. It uses the ATmega128RFA1 and a variety of sensors IMU for various applications. | ||||
| FlyDuino Mega[140] | ATmega 2560[29] | Serial only, 6-pin header | Paul Bake | An Arduino Mega 2560 compatible board designed for auto-piloting and autonomous navigation of multirotor aircraft. Designed to be stacked with sensor bobs and boards with several breakout boards available. | |
| Colibri[141] | ATmega168[37] | No | Serial only | JT5[83] | Universal platform for wireless data transmission in the frequency band 868 MHz. The board combines features of Arduino Mini and the radio EZRadioPRO for receiving and transmitting data. With DataFlash. |
| JeeNode[142] | ATmega328 | 6-pin header | Jeelabs | Includes a wireless radio module, called the RFM12B by HopeRF | |
| ArduPhone[143] | ATmega1284P | yes | USB | Freetronics | Cellular phone kit, ADH8066 GSM module, Micro SD slot, 16 key matrix keyboard, LiPo charger and microphone/speaker connectors. |
| WTFDUINO[144] | ATmega328P | No | USB & CH340G | Calum Knott | "The world needs a more confusing Arduino" |
| Tah[145] | ATmega32U4 | Yes | USB | Revealing Hour Creations[146] | Stock Arduino Leonardo with a built-in BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) 4.0. Has Arduino compatibility with its breakout shield. |
| WIOT Archived 2014-01-11 at the Wayback Machine | ATmega32U4 | No | USB | ubld.it | WIOT is an Open Source, rechargeable, Li-Ion battery powered, Arduino compatible, development board designed around the ATmega32U4 processor and ESP8266 Wi-Fi Module.
|
| XLR8 | Altera MAX10 10M08 FPGA | Yes, with exceptions | USB | Alorium Technology | FPGA-based drop-in replacement for Arduino UNO R3; offers faster clock rates and overall applications speed, higher-performance through vendor-supplied hardware-specific library functions utilizing FPGA; half of FPGA's space remains available for further customizations including ones written by end user |
| Arduino Uno*Pro Archived 2017-06-23 at the Wayback Machine | ATmega1284 | No | USB | Hobbytronics | Replaces the Arduino Uno's ATmega328 chip with the ATmega1284, drastically expanding memory. |
Industrial grade
| Name | Model | Processor | Voltage | Host interface | I/O | Maker | Additions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controllino[147] | Mini | ATmega328 | 12 V or 24 V | USB | 8x analog/digital inputs, 6x relay outputs, 8x digital outputs | Controllino / Conelcom GmbH | Once successful Kickstarter project, CONTROLLINO is now used by over 800 companies in the industry automation, automotive and aerospace field.  CONTROLLINO Mini. |
| Maxi | ATmega2560 | Ethernet/USB | 12x analog/digital inputs, 10x relay outputs, 12x digital outputs | ||||
| Mega | 12x analog/digital inputs, 10x relay outputs, 12x digital outputs | ||||||
| FA-DUINO[148] | 12RA | Mega2560 | 24 V | RS-232 | 8x inputs, 4x relays | Comfile Technology | |
| 24RA | 16x inputs, 8x relays | ||||||
| ARDBOX[149] | ATmega32U4 | 12-24 V | USB | 10x inputs, 10x outputs | Industrial Shields | Uses Arduino Leonardo board | |
| Industruino[150] | Atmega 32u4 or Atmega AT90USB1286 | 6.5-32 V | USB | 8x shared digital input/output, 4x analog inputs, 2x analog outputs | Industruino | Arduino compatible industrial controller housed in DIN rail casing, designed for industrial automation in small to medium-sized businesses. | |
| Iono[151] | No integral board | 11–30 V | USB / 6-pin header | 6x inputs, 6x outputs | Sfera Labs | iono is a general-purpose industrial controller based on Arduino, suitable for professional use (e.g. industrial automation, building automation). It features wide-range power supply, analog/digital inputs with robust protection circuits, power relays with double-winding latching bistable coils, 0÷10 V analog output, DIN rail case. | |
Software-compatibility only
These boards are compatible with the Arduino software, but they do not accept standard shields. They have different connectors for power and I/O, such as a series of pins on the underside of the board for use with breadboards for prototyping, or more specific connectors. One of the important choices made by Arduino-compatible board designers is whether or not to include USB circuitry in the board. For many Arduino tasks, the USB circuitry is redundant once the device has been programmed, so that circuitry can be placed in the cable between development PC and board, thus making each instance of the board less expensive, potentially smaller, and more power efficient.
| Name | Processor | Maker | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seeeduino XIAO | SAMD21G18 Cortex-M0+ | Seeed Studio | Seeeduino XIAO is the smallest Arduino compatible board in Seeeduino Family. It is an Arduino microcontroller that is embedded with the SAMD21 microchip. The interfaces of Seeeduino XIAO is rich enough in such a tiny Dev. Board as well. |
| Seeeduino Nano | ATmega328P | Seeed Studio | The Seeeduino Nano is a compact board similar to the Seeeduino V4.2/Arduino UNO, and it is fully compatible with Arduino Nano on pinout and sizes. |
| Seeeduino Mega[152] | ATmega2560[29] | Seeed Studio | Built around ATmega 2560 @ 16 MHz Massive GPIOs: 70 digital I/Os, 16 analog inputs and 4 UARTs, etc. Small form factor, 30% smaller than Arduino Mega 3.3 V and 5 V dual mode. Can be powered through a battery or through an AC to DC adaptor |
| Ardweeny[153] | Solarbotics | An inexpensive, even more compact breadboardable device. | |
| Banguino[154] | ATmega328 | Dimitech |  |
| SAM15x15 | SAMD21G18 | avdweb | 
|
| Canique MK2[155] | ATmega328P | Canique | A very power efficient breadboard friendly Arduino compatible board with onboard RFM69W/RFM69HW transceiver and a stock speed of 16 MHz @ 3.3 V. You can solder your own antenna or connect an antenna via U.FL connector. |
| Bare Bones Board[156] (BBB) and Really Bare Bones Board[157] (RBBB) | Modern Device | Compact inexpensive Arduino-compatible board suitable for breadboarding. | |
| BBFUINO (Breadboard Friendly Arduino Compatible) | ATmega328P | Cytron Technologies | BBFuino come with the ATmega328 controller, loaded with Optiboot (Arduino UNO's bootloader), compatible with Arduino IDE and sample code, design to fit breadboard for prototyping and learning, lower down the cost by taking out the USB to UART IC, so the board has the basic component to operate. |
| BlockDuino[158] | ATmega8 ATmega328 | Blockduino | An Arduino-Diecimila-compatible board with serial connection to Blocks (shields).[159] |
| Boarduino[160] | ATmega168 or ATmega328 | Adafruit |  |
| Breaduino[161] | Applied Platonics[112] | A complete, very low cost Arduino-compatible kit that can be assembled entirely on a breadboard. | |
| Dasduino series[162] | ATmega328, ESP32, ESP8266, STM32 | Soldered Electronics | Inexpensive series of fully compatible Arduino boards for education and hobbyists, designed and manufactured in Croatia. |
| Cardboarduino[163] | ATmega168[37] | Inspired by the Paperduino, an ultra low-cost Arduino compatible, built on printed posterboard, rather than a PCB. | |
| Crumbuino-Nano[164] | ATmega328 | chip45.com/[165] | The Crumbuino-Nano is a low-cost module comparable to the Arduino-Nano and can be used as Arduino-Nano in the Arduino-IDE. The Arduino bootloader is preloaded, hence the module is ready-to-use. The documentation shows the pin mapping of Arduino-naming to module pinout. |
| Crumbuino-Mega[166] | ATmega2560[29] | chip45.com/[165] | The Crumbuino-Mega is a low-cost module comparable to the Arduino-Mega 2560 and can be used as Arduino-Mega 2560 in the Arduino-IDE. The Arduino bootloader is preloaded, hence the module is ready-to-use. The documentation shows the pin mapping of Arduino-naming to module pinout. |
| Cuteduino | ATtiny85 | Cytron Technologies | Cuteduino Features:
|
| Digispark[167] | ATtiny85 | Digistump[168] |  Digispark |
| DragonFly[169] | ATmega1280[57] | A compact board with Molex connectors, aimed at environments where vibration could be an issue. DragonFly features the ATmega1280 and have all 86 I/O lines pinned out to connectors. | |
| Femtoduino[170] | ATmega328P-MU | Femtoduino[171] |  Femtoduino PCB vs Dime |
| Freeduino USB Mega 2560[172] | ATmega2560[29] | Bhasha Technologies[173] |  Freeduino USB Mega 2560, designed in India with Male headers (coming soon with Female Headers). Suitable for use in project, R&D, device and applications |
| Freeduino Lite v2[174] | ATmega8/168/328 | Bhasha Technologies[173] | Freeduino Lite v2 is a low cost, Freeduino with no USB and serial port. Needs FTDI USB Cable or FTDI Breakout board for programming. Uses through hole components and has male headers. |
| Freeduino Serial[175] | ATmega8/168/328 | Bhasha Technologies[173] | Freeduino Serial is a low cost Freeduino board with serial DB9 connector. Uses the MAX232 chip for serial connectivty. |
| Freeduino NANO[171] | ATmega328 | Bhasha Technologies[173] |  Freeduino nano designed in India, completely breadboard friendly, elegant and compact design. |
| iDuino[170] | A USB board for breadboarding, manufactured and sold as a kit by Fundamental Logic. | ||
| IMUduino[176] | ATmega32U4 | Femtoduino.com[177] | The world's first wireless 3D position, inertia, and orientation beacon. Designed in the San Francisco bay area, this board provides a 10-DoF IMU with on-board ATmega32U4 chip (the same as the Arduino Leonardo). |
| JeeNode[178] | ATmega328P | JeeLabs[179] |  |
| LCDuino[181] | ATmega328P | Geppetto Electronics | A combination of an ATmega328P and an I²C based RGB backlit LCD interface (software compatible with the Adafruit RGB LCD shield), along with a USB serial programming interface done as a "backpack" module for the LCD. |
| LEDuino[182] | A board with enhanced I²C, DCC decoder and CAN-bus interfaces. Manufactured using surface mount and sold assembled by Siliconrailway. | ||
| Moteino[183] | ATmega328P | LowPowerLab[184] |   These are the different types of available Moteino boards and their transceiver options. |
| Narrow | Atmega644 / Atmega1284 | Pandauino? |

|
| NavSpark[186] | Venus822 (Leon3 SPARC V8 compatible, 100 MHz 32-bit RISC) | SkyTraq[187] | The modified Arduino IDE allows the compiled user sketch to be uploaded onto the processor either with or without the proprietary GNSS software. NavSpark has 17 GPIO pins, which include two UARTs, 1 I²C, 1 SPI, 1 PWM, and a trigger. The first UART is usually used by the GNSS software to output NMEA 0183 data, although this can be disabled. This UART communicates over USB through a PL2303 serial converter and the transmit output is also made available on a pin. A 1 pulse per second signal is produced on a dedicated pin when a valid fix has been made.
There is a GPS-only version, a combined GPS/GLONASS version, and a GPS/Beidou version. An adaptor board adds a JST connector for a lithium-ion battery, a charger for the battery, and a microSD card slot connected to the SPI pins. |
| NB1A[188] | An Arduino-compatible board that includes a battery backed up real-time clock and a four channel DAC. Most Arduino-compatible boards require an additional shield for these resources. | ||
| NB2A[189] | Sanguino-compatible board that includes a battery backed up real-time clock and a two channel DAC. Sanguino's feature the ATmega644P, which has additional memory, I/O lines and a second UART. | ||
| Nymph[190] | ATmega328P | A compact board with Molex connectors, aimed at environments where vibration could be an issue. | |
| Oak Micros om328p[191] | An Arduino Duemilanove compacted down to a breadboardable device (36 mm x 18 mm) that can be inserted into a standard 600 mil 28-pin socket, with USB capability, ATmega328P, and 6 onboard LEDs. | ||
| OpenTag[192] | ATmega328P | Loggerhead Instruments |   Arduino-compatible microSD motion datalogging board with accelerometer, magnetometer, gyroscope, pressure, temperature and real-time clock. Arduino-compatible microSD motion datalogging board with accelerometer, magnetometer, gyroscope, pressure, temperature and real-time clock. |
| Paperduino[193] | ATmega168 | An ultra low-cost Arduino compatible, built on a printed paper and cardboard substrate, rather than a PCB. | |
| Photon[194] | STM32F205[195] (Cortex-M3) | Particle | An ARM-based Wi-Fi development kit with a Broadcom BCM43362 Wi-Fi chip supporting 802.11b/g/n. |
| PicoDuino[196] | ATtiny85 | Peter Misenko |  PicoDuino size demonstration.
|
| Pro Micro[197] | ATmega32U4 | Sparkfun and clones | A popular low-cost compact Arduino-compatible board. Available in 3.3 V and 5 V versions. |
| Rainbowduino[198] | An Arduino-compatible board designed specifically for driving LEDs. It is generally used to drive an 8x8 RGB LED matrix using row scanning, but it can be used for other things. | ||
| Sanguino[199] | ATmega644 |  | |
| Sippino[200] | SpikenzieLabs | A miniature Arduino compatible board with all of the digital and analog I/O pins brought out into a single line of pins (SIP). Available as a kit, intended for use with a solderless breadboard. | |
| SODAQ Mbili[201] | ATmega1284P | SODAQ |  SODAQ, an Arduino Compatible Solar Powered sensor board Specifications:
|
| Sparrow[202] | ATmega328P | Open Home Automation | Arduino compatible board designed specifically for RF mesh network experiments. It features 10 I/Os, a 10-pin ISP programming connector, a connector for a standard LCD display (in 4 bit mode) and a connector for a 2.4 GHz RF module. |
| Spider Controller[203] | Arduino Mega compatible board designed specifically for robots requiring large numbers of servos. A built in 3 A switchmode power supply allows servos to plug directly into the board. Pin spacing allows making custom shields from standard prototype board. | ||
| Stickduino[204] | Similar to a USB key. | ||
| Teensy 2.0[205] | ATmega32U4 8 bit AVR 16 MHz[206] | PJRC |  Teensy 2.0 microcontroller |
| Teensy 2.0++[207] | AT90USB1286 8 bit AVR 16 MHz[206] | PJRC |  Teensy++ 2.0 microcontroller |
| Teensy 3.0[208] | MK20DX128 32 bit ARM Cortex-M4 48 MHz[206] | PJRC | A very small board based on the Freescale MK20DX128VLH5 CPU. It has 34 I/O pins; 16 KB RAM; 128 KB of flash; 16-bit ADC; 3xUARTs, SPI, I²C, I²S, Touch and other I/O capability. Version 3.0 is not recommended for new designs. |
| Teensy 3.1/3.2[209] | MK20DX256 32 bit ARM Cortex-M4 72 MHz[206] | PJRC | Same form factor as Teensy 3.0. Based on the Freescale MK20DX256VLH7 CPU. It has 34 I/O pins; 64 KB RAM; 256 KB of flash; 2x16-bit ADC; 12-bit DAC; 3xUARTs, SPI, 2xI²C, I²S, CAN bus, Touch and other I/O capability. All digital pins are 5 volt tolerant. Teensy 3.2 adds a more powerful 3.3 volt regulator, with the ability to directly power ESP8266 Wi-Fi, WIZ820io Ethernet and other power-hungry 3.3 V add-on boards. |
| Teensy 3.5[210] | MK64FX512VMD12 32 bit ARM Cortex-M4F 120 MHz[206] | PJRC | Form factor compatible with Teensy 3.0/3.1/3.2, with more pins directly available. Based on the NXP/Freescale MK64FX512VMD12 CPU. It has 58 I/O pins; 256 KB RAM; 512 KB of flash; 27 analog inputs on 2x16-bit ADC; 2x12-bit DAC; 17 timers (20 PWM outputs); 6xUARTs, 3xSPI, 3xI²C, 2xI²S, CAN bus, On-board Micro SD Card, Touch and other I/O capability. All digital pins are 5 volt tolerant. |
| Teensy 3.6[210] | MK66FX1M0VMD18 32 bit ARM Cortex-M4F 160 MHz[206] | PJRC | Form factor compatible with Teensy 3.0/3.1/3.2, with more pins directly available. Based on the NXP/Freescale MK66FX1M0VMD18 CPU. It has 58 I/O pins; 256 KB RAM; 1024 KB of flash; 25 analog inputs on 2x16-bit ADC; 2x12-bit DAC; 19 timers (22 PWM outputs); 6xUARTs, 3xSPI, 3xI²C, 2xI²S, CAN bus, 2nd USB (Host mode supported); On-board Micro SD Card, Touch and other I/O capability. I/O pins are not 5 V tolerant. |
| Teensy 4.0[210] | i.MXRT1062 32 bit ARM Cortex-M7 600 MHz by NXP Semiconductors[206] | PJRC | The Teensy 4.0 has an NXP i.MXRT1062 ARM Cortex-M7 at 600 MHz with 1024 KB RAM (512 KB is tightly coupled), 2048 KB flash (64K reserved for recovery & EEPROM emulation), two USB ports, both 480 Mbit/s, three CAN bus channels (one with CAN FD), two I²S Digital Audio, 1 S/PDIF Digital Audio, 1 SDIO (4 bit) native SD, SPI, all with 16 word FIFO, 3 I²C, all with 4 byte FIFO, 7 serial, all with 4 byte FIFO, 32 general purpose DMA channels, 31 PWM pins, 40 digital pins, all interrupt capable, 14 analog pins, 2 ADCs on chip, Cryptographic Acceleration, Random Number Generator, Pixel Processing Pipeline, Peripheral cross triggering and more in a tiny 1.4 by 0.7 inch Teensy 3.0/3.1/3.2 form factor |
| Teensy LC[211] | MKL26Z64VFT4 ARM Cortex-M0+ 48 MHz[211] | PJRC | A lower cost version of the Teensy 3.1/3.2. It has 27 I/O pins; 64 KB of flash; 12-bit DAC; 3xUARTs, 2xSPI, 2xI²C, I²S, Touch and other I/O capability. I/O pins are not 5 V tolerant. No FIFOs on serial 1 and serial2. Fewer hardware timers. |
| TinyDuino[212] | ATmega328P | TinyCircuits[213] |  |
| TinyLily[214] | ATmega328P | TinyCircuits[213] |  |
| Trinket[215] | ATtiny85 | Adafruit | Requires updates to Arduino IDE (or download special version) and driver under Windows. Includes regulator for battery power away from PC. Very low cost. |
| Wireless Widget[216] | A compact (35 mm x 70 mm), low voltage, battery powered Arduino-compatible board with onboard wireless capable of ranges up to 120 m. The Wireless Widget was designed for both portable and low cost Wireless sensor network applications. | ||
| Whisper Node AVR[217] | ATmega328P | Wisen - Talk² |  On field tests the Whisper Node was able to communicate on distances over 1 km line-of-sight and can run for years on battery, making a great platform for remote sensing and IoT applications. |
| Whisper Node LoRa[218] | ATmega328P | Wisen - Talk² |  |
| ZB1[219] | An Arduino-compatible board that includes a Zigbee radio (XBee). The ZB1 can be powered by USB, a wall adapter or an external battery source. It is designed for low-cost Wireless sensor network applications. | ||
| SunDuino2[108] | ATmega16/32/324/644 | An open source enhanced Arduino-compatible board that uses an ATmega16/32/324/644 instead of an ATmega168. This provides 16/32/64 KB of flash, and 32 general I/O pins in a 40-pin DIP device. | |
| OpenEnergyMonitor emonTx[220] | ATmega328 |  | |
| panStamp[222] | ATmega328 | panStamp[222] |  |
| Microduino[224][225] | ATmega168/328/644/1284 | Microduino Studio | 1" x 1.1" small, stackable, low-cost Arduino-compatible board with a uniformed U-shape 27-pin standard interface. |
| Versalino Uno[226] | ATmega328P | Virtuabotix |  Versalino Uno 1.1 |
| LeoStick[227] | ATmega32U4 | Freetronics | Compact version of the Arduino Leonardo (which can be plugged straight into a USB port without a cable) and has a buzzer and a 3-in-1 RGB LED. |
| Wattuino Nanite[228][229] | ATtiny85/ATtiny841 | Watterott electronic | Very small size and microUSB plug for programming (Micronucleus USB Bootloader). Requires special board package for the Arduino IDE. |
| Wattuino Pro Mini PB[230] | ATmega328PB | Watterott electronic | An Arduino Pro Mini compatible board with the new ATmega328PB. Requires special board package for the Arduino IDE. |
| eDOTcore | ATmega328P-PU | antiElectron | An ATmega328P-PU based Arduino compatible board with embedded DS3231 RTC
|
| PICO[231] | ATmega32U4 | MellBell Electronics | A successful Kickstarter project[232] |
| uChip | SAMD21E18 | Itaca Innovation |  uChip mounted on a breadboard |
| Nucleo boards | STM8 / STM32 | ST | 
|
| Blue Pill board | STM32 | ST | 
|
| Rhino Mini 328PB[233] | ATmega328PB-AU | Cyrola Inc. |
 Arduino compatible board with MiniCore. Designed for a prototyping board. A secondary UART. On-grid pin layout. Pogo pin clip connectivity. |
| Rhino WAN[234] | STM32L082CZ | Cyrola Inc. |
 Murata CMWX1ZZABZ-078 based Arduino compatible board. LoRaWAN™ connectivity. |
Non-ATmega
The following non-ATmega boards accept Arduino shield daughter boards. The microcontrollers are not compatible with the official Arduino IDE, but they do provide a version of the Arduino IDE and compatible software libraries.
| Name | Processor | Host interface | Maker | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIC.duino Net | PIC18F67J60 | Ethernet or serial | SlicMicro |
Pin compatible with Arduino but uses the Ethernet enabled PIC microcontroller to connect to the Internet. Allows sending of email, display of javascript enabled webpages, and remote web based access and control from around the world. |
| Leaflabs Maple[235] | STM32 (Cortex-M3) | USB | LeafLabs[236] |  |
| Microchip chipKIT Uno32, Max32, WF32, DP32 | PIC32 | USB | Digilent[242] | 32-bit MIPS-M4K PIC32MX processor boards (40-80 MHz). The Arduino libraries have been implemented natively for the PIC32MX and these kits run in a fork of the standard Arduino IDE, MPIDE[243] and are compatible to most shields.[244][245][246] |
| Microchip chipKIT Wi-Fire | PIC32MZ | USB | Digilent[242] | 32-bit MIPS-M4K PIC32MZ processor boards (200 MHz). The Arduino libraries have been implemented natively for the PIC32MZ and these kits run in a fork of the standard Arduino IDE, MPIDE[243] and are compatible to most shields.[244][245][246] |
| Freescale Freedom[247] | Kinetis-L (Cortex-M0+) | USB | Freescale[248] | A 48 MHz 32-bit ARM Cortex-M0+-based microcontroller (Freescale MKL25Z128VLK4[249]) with USB support, compatibility with Arduino shields and 64 GP I/O pins. Board embeds the new ARM OpenSDA debug and programming interface through USB and is compatible with the majority of the ARM IDE suppliers. |
| PRO Family[250] | ARM Cortex LPC1114 LPC1751 LPC1756 | USB | Coridium[251] | up to 200 MHz dual core ARM Cortex-M4F, ARM Cortex-M3 and ARM7TDMI-based shield-compatible boards, programmable in BASIC or C with sketch support with open source MakeItC utilities. All boards have 5 V tolerant I/Os. |
| Energia | MSP430 | USB | Texas Instruments | The Energia project integrates this with the Arduino IDE.[252][253] |
| Sakura board[254] | Renesas RX63N | USB | Renesas/Wakamatsu Tsusho Co., Ltd | Web compiler with sketch support,[255] Ethernet interface |
| HiFive1[256] | SiFive E31 32 bit RISC-V | USB | SiFive |  HiFive1 board |
Non-Arduino
The following boards accept Arduino shield daughter boards. They do not use microcontrollers compatible with the Arduino IDE,[257] nor do they provide an alternative implementation of the Arduino IDE and software libraries.
| Name | Processor | Maker | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADICUP3028 | ADuCM3029 (Cortex™-M3 ) | Analog Devices | The EVAL-ADICUP3029 is an Arduino Uno form factor compatible platform based on the ultra low power ADuCM3029 32-bit ARM Cortex™-M3 microcontroller. The platform is designed to be a development and prototyping vehicle to get design ideas from concept to production with a minimal risk and faster time to market. The EVAL-ADICUP3029 is designed for IOT (Internet of Things) applications in mind, and therefore comes with on board Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5.0 capabilities. A free version of CrossCore Embedded Studios (an Eclipse-based Analog Devices Interactive Development Environment) is supplied to the designer for debugging and application development. Add-on hardware modules, MCU drivers and software application examples help form a complete ecosystem that designers can leverage into their final product. |
| ADICUP360 | ADuCM360
(Cortex M3) |
Analog Devices | Arduino form factor compatible ARM Cortex-M3 Development Platform: 24-bit data acquisition system that incorporates dual high performance, multichannel sigma-delta (Σ-Δ) analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), a 32-bit ARM Cortex™-M3 processor, and flash/EEPROM memory on a single chip. The platform has an Arduino-Due compatible form factor and has two additional PMOD connectors. It is accompanied by an Eclipse-based development environment. |
| DAQduino | PIC18F2550 or
PIC18F2553 |
PICcircuit.com | DAQduino is iCP12 usbStick that built in Arduino form of external ports connection. With these I/O ports, user can easily plug in different type of 3rd party Arduino extension boards with direct connection to USB port and SmartDAQ software. Great tool for parallel USB I/O control, signals monitoring (6 ch. oscilloscope) and data acquisition. |
| CIKU | PIC18F4550 | Cytron Technologies | CIKU Features:
|
| Chipino[258] | PIC16F886-I/SP[259] | Howtronics[260] | Chipino is an electronics prototyping platform based on a Microchip PIC microcontroller. It was designed to use the same footprint and connection scheme as the official Arduino boards to allow Arduino shields to be used with Chipino. |
| Bambino 210 | NXP LPC4330 | Microint USA | Dual core ARM Cortex-M4/M0, 264 KB SRAM, 4 MB flash, mbed HDK, Arduino-compatible headers. The Bambino 210E has the same features as the 210, but adds a 10/100 Ethernet port, 8 MB flash, microSD socket, and Xbee Socket |
| Cypress PSoC 4 Pioneer Kit (CY8CKIT-042) | Cypress PSoC4 CY8C4245AXI-483 | Cypress | The PSoC 4 Pioneer Kit is a development platform enabling users to design with the ARM Cortex-M0 PSoC®4 device family. The kit features the PSoC 4200 device family as the main processor and includes a PSoC 5LP (ARM Cortex-M3 processor) to perform programming and debugging. The kit is supported using PSoC Creator, which is a free IDE for embedded development targeting the PSoC 3/4/5LP device families. In the summer of 2013 Cypress supported the kit with a 100 projects in 100 days campaign on the community forums at Element14. |
| Arduino Shield Compatible Propeller Board[261] | Parallax Propeller | Parallax | Based on the Parallax Propeller; interfaces with standard Arduino shields. The Propeller comes with a free IDE called "propeller tool", and an alternative IDE tool is available.[262] |
| Amicus18[263] | PIC | Amicus18 is an embedded system platform based on PIC architecture (18F25K20). Can be programmed with any programming language, though the Amicus IDE is free and complete. | |
| Cortino[264] | ARM STM32 | Development system for a 32-bit ARM Cortex-M3-based microcontroller. | |
| Pinguino[265] | PIC | Board based on a PIC microcontroller, with native USB support and compatibility with the Arduino programming language plus an IDE built with Python and sdcc as compiler. | |
| Unduino[266] | PIC | A board based on the dsPIC33FJ128MC202 microcontroller, with integrated motor control peripherals. | |
| Netduino[267] | Cortex-M4 (STM32F4)
(ARM7) |
Wilderness Labs | 168 MHz Cortex-M4 (STM32F4) with up to 1,408 KB of code storage and 164 KB of RAM. On-board USB, Ethernet, Wi-Fi, SD card slot. Support for the .NET Micro Framework. Development environment is MS Visual Studio and C#. Pin compatible with Arduino shields although drivers are required for some shields.[267] |
| Vinculo[268] | Vinculum II | FTDI USB development board for the FTDI Vinculum II microcontroller. | |
| FEZ Domino,[269] FEZ Panda,[270] and FEZ Panda II[271] | ARM | 72 MHz 32-bit ARM (GHI Electronics USBizi chips) micro-controller boards with support for the .NET Micro Framework. Pin compatible with Arduino shields, although drivers are required for some shields.[272] | |
| TheUno[273] | Freescale S08DZ60 | MyFreescaleWebPage[273] |  |
| BigBrother[273] | Freescale MCF51AC256 | MyFreescaleWebPage[273] |  |
| BigBrother-USB[273] | Freescale MCF51JM128 | MyFreescaleWebPage[273] |  |
| Firebird32[274] | Coldfire | Freescale 32-bit Coldfire MCF51JM128 based Arduino Shield Compatible development board. Programmable in StickOS BASIC, and C or assembly language using Flexisframework or CodeWarrior with a step-by-step debugger. The Firebird32 is also available in a special model based on the 8-bit MC9S08JM60. | |
| Stampduino[275] | PIC or Parallax SX | Parallax | Arduino Shield compatible BASIC Stamp 2 board, interfaces with most standard Arduino shields, and comes with a free IDE. |
| SunDuinoPIC[108] | PIC18F2550 or PIC18F4550 | Microchip PIC Arduino hardware compatible board. Based PINGUINO Project. USB HID Bootloader. | |
| Breeze[276][277] | PIC | Breeze boards are prototyping platforms for 28-pin PIC microcontrollers. They come with a PIC18F25K22 (USB-UART interface) or PIC18F25J50 (direct USB interface), however almost any 28-pin PIC can be used with the platform. |
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Arduino - Boards". Arduino.cc. 2009-03-01. Archived from the original on 2013-01-23. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "Arduino - HomePage". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-21. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "ARDUINO UNO WiFi REV2". store.arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2018-12-18. Retrieved 2018-12-17.
- ↑ "Firmware Update 1.2.1 - available now, with BLE mode". forum.arduino.cc. 13 November 2018. Archived from the original on 2018-12-18. Retrieved 2018-12-17.
- ↑ "Arduino Official Store | Boards Shields Kits Accessories". Archived from the original on 2015-10-23. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ↑ "Intel® Curie™ Module: Unleashing Wearable Device Innovation". intel.com. Archived from the original on 2015-09-06. Retrieved 2015-08-15.
- ↑ "Arduino Official Store | Boards Shields Kits Accessories". Archived from the original on 2016-12-29. Retrieved 2016-12-19.
- ↑ "ATSAMD21G18;". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2015-11-24. Retrieved 2014-08-12.
- ↑ "Arduino Zero now available for purchase!". 15 June 2015. Archived from the original on 2016-03-18. Retrieved 2016-12-19.
- ↑ "Meet Arduino ZERO - the new board jointly developed by Arduino and Atmel". 15 May 2014. Archived from the original on 2017-05-10. Retrieved 2016-12-19.
- ↑ "20 Arduino ZERO Dev. Edition available for beta-testing - Join us!". August 2014. Archived from the original on 2017-07-18. Retrieved 2016-12-19.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardDue". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-17. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ Chirgwin, Richard (2011-09-20). "Arduino to add ARM board this year". The Register. Archived from the original on September 23, 2011. Retrieved September 20, 2011.
- 1 2 3 "AT91SAM3X8E;". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2012-12-08. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- 1 2 3 "ATmega16U2". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-04. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "SAM3U4E". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-30. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "atmel.com". atmel.com. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Arduino Due is finally here". Arduino.cc. 2012-10-22. Archived from the original on 2013-04-26. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Boards". Archived from the original on 2016-12-28. Retrieved 2016-12-19.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "ATmega32U4". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-04. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Updating about Arduino Yún (Video preview!) and Arduino Robot". 21 August 2013. Archived from the original on 2017-05-10. Retrieved 2016-12-19.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardLeonardo". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-21. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Massimo Introduces Arduino Leonardo". Arduino.cc. 2012-07-23. Archived from the original on 2013-05-02. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardUno". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-21. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "ATmega328P". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-22. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- 1 2 3 "ATmega8U2". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-29. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- 1 2 "Arduino Blog- Dinner is Ready". Arduino.cc. 2010-09-24. Archived from the original on 2013-05-27. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardMega2560". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-21. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "ATmega2560". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-29. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardEthernet". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- 1 2 3 "ATmega328". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-13. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- 1 2 "Arduino Blog- Arduino Ethernet, ADK Available for purchase". Arduino.cc. 2011-07-13. Archived from the original on 2013-07-18. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoEthernetShield". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-28. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "Arduino - ArduinoBoardFio". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Arduino FIO presented at Uno Punto Zero". Arduino.cc. 2010-03-18. Archived from the original on 2013-09-24. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardNano". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "ATmega168". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-29. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "FT232R". ftdichip.com. Archived from the original on 2014-08-16. Retrieved 2014-08-14.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Arduino Nano: all-in-one design for breadboard use". Arduino.cc. 2008-05-15. Archived from the original on 2013-06-01. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardLilyPad". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- LilyPad Arduino and Arduino 0010". Arduino.cc. 2007-10-17. Archived from the original on 2013-10-22. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- 1 2 "arduino.cc". Archived from the original on 2016-12-22. Retrieved 2016-12-19.
- 1 2 3 "Arduino Blog- Arduino Pro and Pro Mini". Arduino.cc. 2008-08-23. Archived from the original on 2015-01-12. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardADK". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardEsplora". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardMicro". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- New Arduino Micro available". Arduino.cc. 2012-11-08. Archived from the original on 2013-04-27. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardSerial". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-02-04. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 3 4 "ATmega8". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2014-08-09. Retrieved 2014-08-14.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardSerial". Archived from the original on 2013-02-04. Retrieved 17 May 2021.
- 1 2 "Arduino - ArduinoBoardBluetooth". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-27. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "Arduino Blog- Arduino Diecimila and BT reference designs now available". Arduino.cc. 2007-10-22. Archived from the original on 2015-01-12. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardDiecimila". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardDuemilanove". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-22. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Arduino Duemilanove". Arduino.cc. 2008-10-19. Archived from the original on 2014-07-18. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardMega". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-21. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "ATmega1280". Atmel.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-04. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino Blog- Arduino Mega: bigger, more powerful, still blue". Arduino.cc. 2009-03-26. Archived from the original on 2014-01-16. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- ↑ "Arduino - ArduinoBoardMega". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-21. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "ArduinoBoardProMini". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-18.
- 1 2 "Freeduino Open Source Hardware Files". Freeduino.org. Archived from the original on 2008-04-10. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Seeeduino V3.0 (Atmega 328P) [ARD130D2P] - $22.50 : Seeed Studio Bazaar, Boost ideas, extend the reach". Seeedstudio.com. Archived from the original on 9 November 2014. Retrieved 9 Nov 2014.
- ↑ "evive Features - One Stop Solution for Maker needs for DIY, STEM Project". STEMpedia. Retrieved 2020-08-03.
- ↑ "Canaduino Uno Bone "FULL" - Arduino Uno R3 compatible Atmega328P-PU – Universal-Solder". Archived from the original on 2016-12-20. Retrieved 2016-12-12.
- ↑ "ST Freeduino Robotics Board - Home". Archived from the original on 2016-12-03. Retrieved 2016-12-06.
- ↑ "GSTduino – Arduino Compatible Special Purpose Board". greensystemtech.com. Archived from the original on 2016-10-26. Retrieved 2016-10-26.
- ↑ "Meet Linduino | Analog Devices". Archived from the original on 2015-02-19. Retrieved 2015-02-19.
- ↑ "InVentor UNO - Arduino UNO Compatible Board : Ventor, Online Price in India". Archived from the original on 2014-12-26. Retrieved 2014-12-26.
- ↑ "Ventor Technologies India, Online Electronic Component Shop". Archived from the original on 2014-12-26. Retrieved 2014-12-26.
- ↑ "Page Redirection". Archived from the original on 2016-11-16. Retrieved 2016-11-16.
- ↑ "SainSmart UNO". sainsmart.com. Archived from the original on 2012-12-14. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 3 "SainSmart-Open Hardware Company". sainsmart.com. Archived from the original on 2012-12-25. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "SainSmart Mega 2560". sainsmart.com. Archived from the original on 2012-12-14. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-04-02. Retrieved 2015-03-15.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Electronic Design, Electronics Components, Development Platform - ElecFreaks". Archived from the original on 2015-03-14. Retrieved 2015-03-15.
- ↑ "SainSmart UNO R3". sainsmart.com. Archived from the original on 2013-03-04. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Tavir-AVR. "Tavir-AVR :: Bascom, Arduino, Wiring - Programozás, Fórum, ingyenes mintaalkalmazások, könyvek". Avr.tavir.hu. Archived from the original on 2013-03-08. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "TavIR : Mikrokontroller világ | A gyakorlati tudás tárháza" (in Hungarian). Tavir.hu. Archived from the original on 2013-01-26. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Brasuíno". Brasuino.holoscopio.com. Archived from the original on 2011-07-11. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Holoscópio". Holoscopio.com. 2011-07-18. Archived from the original on 2009-02-25. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "Chibiduino2". tiisai.dip.jp. Archived from the original on 12 October 2013. Retrieved 17 Aug 2013.
- ↑ "Arduino совместимая платформа "Cosmo Black Star" :: платы Arduino". Jt5.ru. Archived from the original on 2013-01-16. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "JT5 :: инжиниринговая компания специализирующая на разработке и производстве электронных устройств". Jt5.ru. Archived from the original on 2013-04-26. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "CraftDuino / RoboCraft.ru / RoboCraft". Robocraft.ru. 20 October 2009. Archived from the original on 2013-01-16. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Evil Mad Scientist Laboratories | Making the world a better place, one Evil Mad Scientist at a time". Archived from the original on May 11, 2012.
- ↑ "Electronics | multiplo Robot Building System". Multiplo.org. Archived from the original on 2012-12-14. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "multiplo Robot Building System |". Multiplo.org. Archived from the original on 2013-03-27. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "アーデュイーノ互換マイコン・ボードを作る". Shop.cqpub.co.jp. Archived from the original on 2012-10-21. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Platino - Versatile Board for AVR Microcontrollers [100892 & 150555] | Elektor Labs". www.elektor-labs.com. Retrieved 2015-11-04.
- 1 2 "MaxSerial : Fundamental Logic WebStore, Electronic Kits and Components". Store.fundamentallogic.com. 2010-05-30. Archived from the original on 2008-08-12. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "fayalab inc. | fayalab inc". www.fayalab.com. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2016-02-18.
- ↑ "SB-Freeduino". Solarbotics. Archived from the original on 2012-02-15. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Solarbotics". Solarbotics. Archived from the original on 2013-01-15. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Freeduino USB complete KIT (Arduino Duemilanove Compatible)". Nkcelectronics.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-28. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Illuminato::Genesis". Liquidware. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "InduinoR3". Induino Wiki. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- ↑ "Simple Labs | Simplifying Technology". Build.simplelabs.co.in. Archived from the original on 2012-03-30. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Vol.27 テクノ工作セット(8ビットマイコン+光残像キット) | 大人の科学マガジン | 大人の科学.net". Otonanokagaku.net. Archived from the original on 2012-12-28. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "990.110". Droids.it. Archived from the original on 2015-01-12. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "990.023 Luigino328 - User Manual [EN]". Droids.it. Archived from the original on 2013-06-05. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Metaboard – Metalab" (in German). Metalab.at. Archived from the original on 2013-05-26. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "small computers for art and science". Rascal Micro. Archived from the original on 2013-01-20. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Raspduino". BitWizard WIKI. Archived from the original on March 31, 2013. Retrieved January 23, 2013.
- ↑ "BitWizard". Bitwizard.nl. Archived from the original on 2013-01-06. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "DFRduino Romeo-All in one Controller V1.1(SKU:DFR0004) - Robot Wiki". Dfrobot.com. Archived from the original on 2013-06-29. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "DFRobot-An Online Opensource Robot and Hardware Shop". Dfrobot.com. Archived from the original on 2012-06-29. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Tools, Parts, Kits for DIY'ers". Curious Inventor. Archived from the original on 2010-03-12. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 3 "SunDUINO Nowy wymiar elektroniki". Sunduino.pl. Archived from the original on 2013-01-11. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ TwentyTen (100% Arduino Compatible). "Parts & Kits for Arduino Online, Buy Microcontroller Boards, Electronic Components for Arduino - TwentyTen (100% Arduino Compatible)". Freetronics. Archived from the original on 2013-02-22. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Parts & Kits for Arduino Online, Buy Microcontroller Boards, Electronic Components for Arduino - Welcome". Freetronics. Archived from the original on 2013-01-15. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Volksduino: complete low-cost Arduino clone". Appliedplatonics.com. Archived from the original on 2011-07-07. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "Applied Platonics". Applied Platonics. Archived from the original on 2011-07-20. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Wise time with Arduino". Timewitharduino.blogspot.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-13. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "YourDuino". YourDuino. Archived from the original on 2012-01-02. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "YourDuinoRobo1 (Upgraded Arduino Compatible)". Arduino-direct.com. Archived from the original on 2014-08-07. Retrieved 2014-09-23.
- ↑ "geekstudio.co.za". Archived from the original on 2010-11-07. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Zigduino r1 - Logos Electromechanical". Logos-electro.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-31. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Products & Services - Logos Electromechanical". Logos-electro.com. 1999-02-22. Archived from the original on 2013-01-16. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "EtherTen Arduino compatible with onboard Ethernet". Archived from the original on 2014-07-15. Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ "EtherMega (100% Arduino Mega 2560 compatible with onboard Ethernet)". Archived from the original on 2014-07-15. Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ "USBDroid (Arduino Uno compatible with onboard Android/USB Host)". Archived from the original on 2014-07-15. Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ "Eleven (100% Arduino Uno Compatible)". Archived from the original on 2014-07-15. Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ "KitTen (Arduino-compatible kit)". Archived from the original on 2014-07-15. Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ "CATkit". Archived from the original on 2015-02-22. Retrieved 2014-11-20.
- ↑ "EtherDue (100% Arduino Due compatible with onboard Ethernet)". Archived from the original on 2014-07-15. Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ "TAIJIUINO Due Pro -- Compatible with Arduino Due [ARD_BD_PRP] - $43.90 : Elechouse, Arduino Play House". Archived from the original on 2014-12-23. Retrieved 2014-12-23.
- ↑ http://www.hitex.co.uk/index.php?id=3650
- ↑ "サイローラ株式会社 | 製品案内 | Rhino Mega 2560 (Arduino Compatible)". Archived from the original on 2018-04-28. Retrieved 2018-04-28.
- ↑ "Use Multiple Serial Ports on the Arduino Mega | Arduino Documentation". Archived from the original on 2018-05-07. Retrieved 2018-05-07.
- ↑ "Io:duino". Railstars. Archived from the original on 2013-02-02. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "DFRobotShop Rover V2 - Arduino Compatible Tracked Robot (Basic Kit)". RobotShop. Archived from the original on 2013-01-25. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Mindsets online". Mindsets online. 2007-03-01. Archived from the original on 2013-03-21. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Mindsets online.co.uk". Mindsets online.co.uk. 2007-03-01. Archived from the original on 2013-01-16. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "mindsetsonline.co.uk" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 21, 2012.
- ↑ "Bump and Reverse Robot Kit (Faraduino) - Faraduino". Mindsets online. 2007-03-01. Archived from the original on 2013-03-20. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Faraconnect Shield (Faraduino) - Faraduino". Mindsets online. 2007-03-01. Archived from the original on 2013-03-20. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Motoruino | GUIBOT". Guibot.pt. Archived from the original on 2013-01-05. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino based Alternator Regulator". arduinoalternatorregulator.blogspot.com. Archived from the original on 2017-04-06. Retrieved 2017-04-05.
- 1 2 Anderson, Chris (2009-01-21). "ArduPilot (Legacy) main page". DIY Drones. Archived from the original on 2013-01-22. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Flyduino Shop - Multirotor, Multicopter Teile & Zubehör für Quadrocopter, Hexacopter, Octocopter - Motore, Rahmen, FCs & ESCs". Flyduino.net. Archived from the original on 2013-01-11. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino совместимая платформа "Колибри" с RF радиомодулем 868 MHz :: платы Arduino". Jt5.ru. 2012-03-30. Archived from the original on 2013-01-01. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "JeeNode - JeeLabs Hardware - JeeLabs . net". Jeelabs.net. Archived from the original on 2013-01-24. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "ArduPhone Arduino Compatible Cellphone". Archived from the original on 2014-07-15. Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ http://wtfduino.co.uk Archived 2015-12-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "The domain name tah.io is for sale | Undeveloped". Archived from the original on 2018-12-06. Retrieved 2019-08-17.
- ↑ "Revealing Hour Creations". Archived from the original on 2018-12-11. Retrieved 2019-08-17.
- ↑ "Controllino". Archived from the original on 15 August 2016. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- ↑ "FA-DUINO-12RA (INDUSTRIAL ARDUINO)". Archived from the original on 16 July 2016. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- ↑ "ARDBOX". Archived from the original on 17 July 2016. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- ↑ "Industruino". Archived from the original on 14 June 2015. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- ↑ "iono". Archived from the original on 2016-08-19. Retrieved 2016-06-16.
- ↑ "Seeeduino Mega [ARD121D2P] - $43.00 : Seeed Studio Bazaar, Boost ideas, extend the reach". Seeedstudio.com. Archived from the original on 2013-06-13. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Ardweeny". Solarbotics. Archived from the original on 2012-02-15. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Banguino". Dimitech. Archived from the original on 2 September 2014. Retrieved 14 Jun 2014.
- ↑ canique.com, Official page of Canique MK2
- ↑ "Bare Bones Board (BBB) Kit | Modern Device". Shop.moderndevice.com. Archived from the original on 2013-03-13. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "RBBB Kit | Modern Device". Shop.moderndevice.com. Archived from the original on 2013-03-09. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "аналог Arduino, но другой.;)". Blockduino. Archived from the original on 2015-01-12. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Каталог блоков от BlockDuino". Blockduino.org. Archived from the original on 2015-01-12. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Boarduino - Breadboard-compatible Arduino Clone". Ladyada.net. 2011-08-15. Archived from the original on 2013-06-27. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Breaduino: the all-breadboard Arduino clone". Appliedplatonics.com. Archived from the original on 2011-07-07. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Dasduino Arduino Compatible boards". SolderedElectronics. Archived from the original on 2023-04-02. Retrieved 2023-06-06.
- ↑ "chip45.com".
- ↑ "chip45.com".
- 1 2 "Microcontroller Modules, Boards, Tools and Accessories for Atmel AVR ATmega Xmega Processors". Chip45.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-26. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Electronics for Hobbyists". Circuit Monkey. Archived from the original on 2012-03-30. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Digispark USB Development Board". Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- ↑
- "Digispark USB Development Board". Digistump. Archived from the original on 2023-03-12. Retrieved 2014-06-05.
- "digispark". wiki. digistump. Retrieved 28 March 2023.
- ↑ "DragonFly - ATmega1280 Arduino Bundle - Circuit Monkey". Circuitmonkey.com. Archived from the original on 2014-11-04. Retrieved 2014-11-04.
- 1 2 "iDuino Complete Kit [iDuino-3-kit] - $21.00 : Fundamental Logic WebStore, Electronic Kits and Components". Spiffie.org. 2010-05-30. Archived from the original on 2012-12-09. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 Albino, Alejandro (2012-04-21). "Smallest Arduino". Femtoduino. Archived from the original on 2013-01-17. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "freeduino lite v2". Bhashatech.com. Archived from the original on 2012-11-02. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 3 4 "Bhasha Technologies". Bhashatech.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Freeduino Serial India". Bhashatech.com. 2009-08-23. Archived from the original on 2012-01-15. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Femtoduino: an ultrasmall (20.7x15.2 mm) libre Arduino compatible board". Varesano.net. Archived from the original on 2011-02-18. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Archived 2014-11-07 at the Wayback Machine, specifications
- ↑ Archived 2014-11-07 at the Wayback Machine, Femtoduino.com website
- ↑ "JN - JeeLabs Hardware - JeeLabs . net". Jeelabs.net. Archived from the original on 2012-06-15. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Computing stuff tied to the physical world (2013-01-19). "JeeLabs". JeeLabs. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Wiki - JeeLabs Hardware - JeeLabs . net". Jeelabs.net. Archived from the original on 2013-01-23. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Archived 2016-02-02 at the Wayback Machine, LCDuino blog
- ↑ "Silicon Railway. Small, powerful, and versatile at a reasonable cost". Siliconrailway.com. Archived from the original on 2012-10-15. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ lowpowerlab.com Archived 2013-04-04 at the Wayback Machine, All about Moteino
- ↑ "lowpowerlab.com". Archived from the original on 2013-04-17. Retrieved 2013-04-19.
- ↑ Archived 2013-09-26 at the Wayback Machine DualOptiboot
- ↑ "SkyTraq". Archived from the original on 2014-04-21. Retrieved 2014-06-05.
- ↑ "Wiblocks - NB1A - ATmega328 + DAC + RTC". Wiblocks.luciani.org. Archived from the original on 2012-10-31. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Wiblocks - NB2 System". Wiblocks.luciani.org. Archived from the original on 2012-10-02. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Electronics for Hobbyists". Circuit Monkey. Archived from the original on 2012-03-30. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "om328p". Oak Micros. Archived from the original on 2012-10-23. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "OpenTag Board". Loggerhead Instruments. Archived from the original on 9 November 2014. Retrieved 9 Nov 2014.
- ↑ "Guilherme Martins : PAPERduino's design". Lab.guilhermemartins.net. 6 May 2009. Archived from the original on 2013-01-13. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Particle Store". Particle. Archived from the original on 2015-09-28. Retrieved 2015-09-28.
- ↑ "STM32F2x5". st.com. Archived from the original on 2015-09-29. Retrieved 2015-09-28.
- ↑ "Picoduino". Peter Misenko. Archived from the original on 6 June 2014. Retrieved 4 June 2014.
- ↑ "Pro Micro - 5V/16MHz - DEV-12640 - SparkFun Electronics". Archived from the original on 2016-06-13. Retrieved 2016-06-26.
- ↑ "Rainbowduino LED driver platform - Atmega 328 Rainbowduino LED driver platform - Plug and Shine! [ARD127D2P] - $24.90 : Seeed Studio Bazaar, Boost ideas, extend the reach". Seeedstudio.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-06. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "What Is Sanguino?". Sanguino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Sippino". SpikenzieLabs. 2011. Archived from the original on 15 August 2014. Retrieved 9 Nov 2014.
- ↑ "SODAQ board". odaq.net. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 2 Oct 2013.
- ↑ "Sparrow prototyping board". open-homeautomation.com. Archived from the original on 2013-09-17. Retrieved 2013-05-13.
- ↑ "Red Back Spider robot controller | Let's Make Robots!". Letsmakerobots.com. Archived from the original on 2013-02-02. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "StickDuino - USB Stick Sized Arduino Clone". Spiffie.org. Archived from the original on 2013-01-13. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Archived 2016-03-22 at the Wayback Machine PJRC Teensy 2.0
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Archived 2016-03-25 at the Wayback Machine PJRC teensy variants, https://www.pjrc.com/store/teensy40.html
- ↑ Archived 2016-03-26 at the Wayback Machine PJRC Teensy 2.0++
- ↑ Archived 2016-03-28 at the Wayback Machine, PRJC Teensy 3.0
- ↑ Archived 2016-03-19 at the Wayback Machine PJRC Teensy 3.1/3.2
- 1 2 3 "Teensy Technical Specs Comparison Table". Archived from the original on 2019-02-13. Retrieved 2019-04-06.
- 1 2 "TeensyLC". Archived from the original on 2016-03-30. Retrieved 2016-03-24.
- ↑ "TinyDuino". TinyCircuits. Archived from the original on 2013-12-07. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "A Maker of Tiny Open Source Circuits". TinyCircuits. Archived from the original on 2013-01-12. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "TinyLily". TinyCircuits. Archived from the original on 2013-01-22. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Introducing Trinket". Archived from the original on 2014-07-28. Retrieved 2014-07-23.
- ↑ "strobit - Strobit Wireless Widget Open Hardware Project - Google Project Hosting". Archived from the original on 2013-02-07. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Product: Talk² Whisper Node – AVR". Talk² by Wisen. 2016-02-03. Archived from the original on 2017-09-06. Retrieved 2016-12-14.
- ↑ "Whisper Node - LoRa". Wisen. Archived from the original on 2017-07-28. Retrieved 2017-07-27.
- ↑ "Wiblocks - ZB1 System". Wiblocks.luciani.org. Archived from the original on 2013-01-28. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ OpenEnergyMonitor. "emonTx". OpenEnergyMonitor. Archived from the original on 2013-01-26. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Project:Nanode - London Hackspace". Wiki.london.hackspace.org.uk. Archived from the original on 2012-10-29. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 3 "Wireless Arduino-compatible miniatures". panStamp. Archived from the original on 2013-01-31. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Lagarto: open automation platform". panstamp. Archived from the original on December 18, 2013. Retrieved March 17, 2015.
- ↑ "Microduino Wiki(English)". www.microduino.net. Archived from the original on 12 January 2015. Retrieved 10 Oct 2013.
- ↑ "Microduino Wiki(中文)". www.microduino.net. Archived from the original on 2013-11-13. Retrieved 10 Oct 2013.
- ↑ "Versalino-Uno". Archived from the original on 2014-05-07. Retrieved 2014-05-07.
- ↑ "LeoStick (Arduino Compatible)". Archived from the original on 2014-07-14. Retrieved 2014-07-14.
- ↑ "GitHub - watterott/Wattuino: Arduino compatible Boards and Modules based on Microchip ATSAMW25, ATmega328, ATmega328PB, ATtiny841, ATtiny85". GitHub. Archived from the original on 2018-06-11. Retrieved 2015-11-04.
- ↑ "GitHub - watterott/Wattuino: Arduino compatible Boards and Modules based on Microchip ATSAMW25, ATmega328, ATmega328PB, ATtiny841, ATtiny85". GitHub. Archived from the original on 2018-06-11. Retrieved 2015-11-04.
- ↑ "GitHub - watterott/Wattuino: Arduino compatible Boards and Modules based on Microchip ATSAMW25, ATmega328, ATmega328PB, ATtiny841, ATtiny85". GitHub. Archived from the original on 2018-06-11. Retrieved 2015-11-04.
- ↑ "PICO". MellBell. Archived from the original on 2018-05-21. Retrieved 2018-05-20.
- ↑ "PICO: The world's smallest Arduino compatible board!". Kickstarter. Archived from the original on 2018-05-21. Retrieved 2018-05-20.
- ↑ "サイローラ株式会社 | 製品案内 | Rhino Mini 328PB (Arduino Compatible)". www.cyrola.co.jp. Archived from the original on 2020-10-02. Retrieved 2020-08-04.
- ↑ "MCU Module with LoRa Radio". www.cyrola.co.jp.
- ↑ "leaflabs.com". leaflabs.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-23. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "leaflabs.com". leaflabs.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-15. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "st.com". Archived from the original on 2009-03-26. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "leaflabs/maple-ide · GitHub". Github.com. Archived from the original on 2010-05-05. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Arduino - Reference". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-21. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "leaflabs/libmaple · GitHub". Github.com. Archived from the original on 2016-02-02. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "GitHub - rogerclarkmelbourne/Arduino_STM32: Arduino STM32. Hardware files to support STM32 boards, on Arduino IDE 1.6.12 including LeafLabs Maple and other generic STM32F103 boards. There is also Alpha suppory for GD32F103 based boards". GitHub. Archived from the original on 2016-12-28. Retrieved 2016-10-01.
- 1 2 "Digital Design Engineer's Source". Digilent Inc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-16. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "chipKIT32/chipKIT32-MAX · GitHub". Github.com. Archived from the original on 2016-02-02. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "Digital Design Engineer's Source". Digilent Inc. Archived from the original on 2013-05-04. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "Digital Design Engineer's Source". Digilent Inc. Archived from the original on 2012-11-26. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- 1 2 "chipKIT Uno32: first impressions and benchmarks". Hackaday.com. 2011-05-27. Archived from the original on 2013-03-03. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Freescale Freedom Development Platform for Kinetis KL14, KL15, KL24, KL25 MCUs". Archived from the original on 6 October 2014.
- ↑ "Welcome to Freescale - Freescale Semiconductor". Freescale.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-15. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "KL2 Product Summary Page". Freescale.com. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Coridium". Coridiumcorp.com. Archived from the original on 2013-02-18. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Coridium". Coridiumcorp.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-28. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Use Arduino code on a TI Launchpad MSP430". Instructables. 14 August 2012. Archived from the original on 6 May 2013. Retrieved 19 May 2013.
- ↑ "Energia". Github. Archived from the original on 2015-02-14. Retrieved 2015-03-17.
- ↑ "Sakura board homepage". Gadget Renesas project. Archived from the original on 2013-10-24. Retrieved 2013-10-28.
- ↑ "Feature description of board and web compiler". Renesas. Archived from the original on 2013-06-25. Retrieved 2013-10-28.
- ↑ "SiFive - HiFive1". Archived from the original on 2017-02-26. Retrieved 2017-02-26.
- ↑ "Arduino - Software". Arduino.cc. Archived from the original on 2013-01-21. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "CHIPINO - The Microchip PIC Based Arduino Style Module". Chipino.com. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 15 November 2014.
- ↑ "CHIPINO-FAQ". Chipino.com. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 15 November 2014.
- ↑ "CHIPINO". Howtronics.com. Howtronics. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 15 November 2014.
- ↑ "propellerpowered.com". Archived from the original on 2011-08-25. Retrieved 2011-08-13.
- ↑ "QuickStart 1: Comparison of Programming Tools". Parallax Semiconductor. Archived from the original on 2013-05-22. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Mitchell, Graham (2010-06-09). "Introducing The Amicus18 [195] | Amicus18 Beginner Guides | Amicus18". Digital-diy.com. Archived from the original on 2010-09-20. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Bugblat Cortino". Bugblat.com. 2012-01-04. Archived from the original on 2012-11-12. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "PINGUINO Project". Hackinglab.org. 2010-08-26. Archived from the original on 2013-05-18. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ unduino.com Archived 2012-10-28 at the Wayback Machine
- 1 2 "Netduino". Wilderness Labs. Archived from the original on 2017-09-21.
- ↑ "Development Modules". Ftdichip.com. Archived from the original on 2013-01-16. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "FEZ Domino". GHI Electronics. Archived from the original on 2012-11-30. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "FEZ Panda". GHI Electronics. Archived from the original on 2012-10-24. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ FEZ Cerbuino Bee. "FEZ Panda II". GHI Electronics. Archived from the original on 2013-01-15. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "Comparison". TinyCLR.com. Archived from the original on March 11, 2011. Retrieved August 13, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "MyFreescaleWebPage". MyFreescaleWebPage. Archived from the original on 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ "firebird32.com". Archived from the original on 2011-07-04. Retrieved 2011-08-13.
- ↑ "parallax.com". Archived from the original on November 12, 2012.
- ↑ Breeze Boards Archived 2015-01-12 at the Wayback Machine Dizzy Enterprises website
- ↑ Arduino clone with mikroBUS socket Archived 2012-12-01 at the Wayback Machine mikroElektronika news article
Further reading
| Library resources about List of Arduino boards and compatible systems |
- Evans, Martin; Noble, Joshua; Hochenbaum, Jordan (August 28, 2012). Arduino in Action (1st ed.). Manning. p. 300. ISBN 978-1617290244.
- McComb, Gordon (June 5, 2012). Arduino Robot Bonanza (1st ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 40. ISBN 978-0-07-178277-7.
- Olsson, Tony (May 30, 2012). Arduino Wearables (1st ed.). Apress. p. 400. ISBN 978-1-4302-4359-5.
- Anderson, Rick; Cervo, Dan (May 16, 2012). Pro Arduino (1st ed.). Apress. p. 350. ISBN 978-1-4302-3939-0.
- Wilcher, Don (April 30, 2012). Learn Electronics with Arduino (1st ed.). Apress. p. 350. ISBN 978-1-4302-4266-6.
- Melgar, Enrique Ramos; Diez, Ciriaco Castro Diez (March 26, 2012). Arduino and Kinect Projects: Design, Build, Blow Their Minds (1st ed.). Apress. p. 350. ISBN 978-1-4302-4167-6.
- Böhmer, Mario (March 26, 2012). Beginning Android ADK with Arduino (1st ed.). Apress. p. 350. ISBN 978-1-4302-4197-3.
- Jepson, Brian; Igoe, Tom (March 22, 2012). Getting Started with NFC: Contactless Communication with Android, Arduino, and Processing (1st ed.). O'Reilly Media/Make. p. 30. ISBN 978-1-4493-0852-0.
- Doukas, Charalampos (March 14, 2012). Arduino, Sensors, and the Cloud (1st ed.). Apress. p. 350. ISBN 978-1-4302-4125-6. Archived from the original on May 10, 2012.
- Riley, Mike (March 7, 2012). Programming Your Home: Automate with Arduino, Android, and Your Computer (1st ed.). Pragmatic Bookshelf. p. 200. ISBN 978-1-934356-90-6.
- Igoe, Tom (February 22, 2012). Getting Started with RFID: Identify Objects in the Physical World with Arduino (1st ed.). O'Reilly Media. p. 40. ISBN 978-1-4493-2418-6.
- Borenstein, Greg (February 3, 2012). Making Things See: 3D vision with Kinect, Processing, Arduino, and MakerBot (1st ed.). O'Reilly Media. p. 440. ISBN 978-1-4493-0707-3.
- Noble, Joshua (January 30, 2012). Programming Interactivity (2nd ed.). O'Reilly Media. p. 726. ISBN 978-1-4493-1144-5.
- Margolis, Michael (December 30, 2011). Arduino Cookbook (2nd ed.). O'Reilly Media. p. 724. ISBN 978-1-4493-1387-6.
- Premeaux, Emery; Evans, Brian (December 7, 2011). Arduino Projects to Save the World (1st ed.). Apress. p. 256. ISBN 978-1-4302-3623-8.
- Wheat, Dale (November 16, 2011). Arduino Internals (1st ed.). Apress. p. 392. ISBN 978-1-4302-3882-9.
- Monk, Simon (November 15, 2011). Arduino + Android Projects for the Evil Genius: Control Arduino with Your Smartphone or Tablet (1st ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 224. ISBN 978-0-07-177596-0.
- Timmis, Harold (November 9, 2011). Practical Arduino Engineering (1st ed.). Apress. p. 328. ISBN 978-1-4302-3885-0.
- Monk, Simon (November 8, 2011). Programming Arduino: Getting Started With Sketches (1st ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 176. ISBN 978-0-07-178422-1.
- Evans, Brian (October 17, 2011). Beginning Arduino Programming (1st ed.). Apress. p. 272. ISBN 978-1-4302-3777-8.
- Igoe, Tom (September 26, 2011). Making Things Talk: Using Sensors, Networks, and Arduino to see, hear, and feel your world (2nd ed.). O'Reilly Media/Make. p. 496. ISBN 978-1-4493-9243-7.
- Allan, Alasdair (September 22, 2011). iOS Sensor Apps with Arduino: Wiring the iPhone and iPad into the Internet of Things (1st ed.). O'Reilly Media. p. 126. ISBN 978-1-4493-0848-3.
- Banzi, Massimo (September 20, 2011). Getting Started with Arduino (2nd ed.). O'Reilly Media/Make. p. 128. ISBN 978-1-4493-0987-9.
- Smith, Alan G (August 19, 2011). Introduction to Arduino: A piece of cake (PDF) (1st ed.). CreateSpace. p. 170. ISBN 978-1-4636-9834-8.
- Warren, John-David; Adams, Josh; Molle, Harald (July 18, 2011). Arduino Robotics (1st ed.). Apress. p. 450. ISBN 978-1-4302-3183-7. Archived from the original on 2010-12-05. Retrieved 2013-05-21.
- Karvinen, Tero; Karvinen, Kimmo (April 6, 2011). Make: Arduino Bots and Gadgets: Six Embedded Projects with Open Source Hardware and Software (1st ed.). O'Reilly Media/Make. p. 296. ISBN 978-1-4493-8971-0.
- Margolis, Michael (March 15, 2011). Arduino Cookbook (1st ed.). O'Reilly Media. p. 660. ISBN 978-0-596-80247-9.
- Schmidt, Maik (March 10, 2011). Arduino: A Quick Start Guide (1st ed.). The Pragmatic Bookshelf. p. 296. ISBN 978-1-934356-66-1. Archived from the original on September 2, 2015. Retrieved May 21, 2013.
- Faludi, Robert (January 4, 2011). Building Wireless Sensor Networks: with ZigBee, XBee, Arduino, and Processing (1st ed.). O'Reilly Media. p. 320. ISBN 978-0-596-80774-0. Archived from the original on January 26, 2013.
- McRoberts, Michael (December 20, 2010). Beginning Arduino (1st ed.). Apress. p. 350. ISBN 978-1-4302-3240-7. Retrieved 2013-05-21.
- Monk, Simon (August 23, 2010). 30 Arduino Projects for the Evil Genius (1st ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 208. ISBN 978-0-07-174133-0.
- F. Barrett, Steven; Thornton, Mitchell (April 30, 2010). Arduino Microcontroller Processing for Everyone! (1st ed.). Morgan and Claypool Publishers. p. 344. ISBN 978-1-60845-437-2. Archived from the original on January 26, 2013.
- Pardue, Joe (January 15, 2010). An Arduino Workshop (1st ed.). Smiley Micros. p. 214. ISBN 978-0-9766822-2-6. Archived from the original on 2012-03-14. Retrieved 2013-05-21.
- Oxer, Jonathan; Blemings, Hugh (December 28, 2009). Practical Arduino: Cool Projects for Open Source Hardware (1st ed.). Apress. p. 450. ISBN 978-1-4302-2477-8. Archived from the original on 2010-12-05. Retrieved 2013-05-21.
- Noble, Joshua (July 15, 2009). Programming Interactivity: A Designer's Guide to Processing, Arduino, and openFrameworks (1st ed.). O'Reilly Media. p. 736. ISBN 978-0-596-15414-1.
External links
 Media related to Arduino compatibles at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Arduino compatibles at Wikimedia Commons


_Board_by_ubld.it.png.webp)

