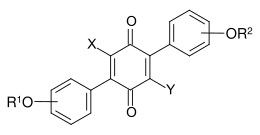
Terphenylquinones are fungal dyes from the group of phenyl-substituted p-benzoquinones having the following general structure.[1]
General chemical structure of terphenylquinones
Also derivatives with a central o-benzoquinone structure are known.
Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of terphenylquinones is carried out by dimerization of substituted oxophenylpropanoic acids (phenylpyruvic acids).
Occurrence
Terphenylquinones are typical constituents of the Boletales.
Examples
Name Structure CAS-Nr. Origin Polyporic acid 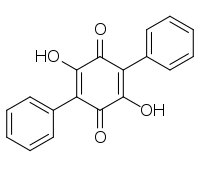
548-59-4 Polypore of the order Aphyllophorales, lichen Yarrumia coronata[2] Atromentin 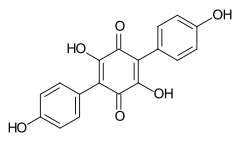
519-67-5 Paxillus atrotomentosus (Basidiomycota)[3] Aurantiacin 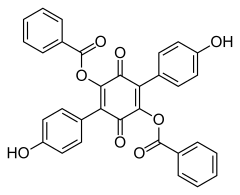
548-32-3 Hydnellum aurantiacum (Basidiomycota)[4] Phlebiarubron 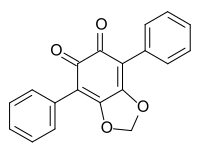
7204-23-1 Cultures of Phlebia strigosozonata and Punctularia atropurpurascens (Basidiomycota)[5] Spiromentin B 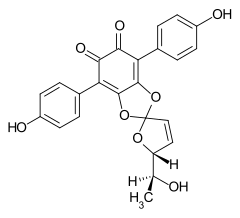
121254-56-6 Tapinella atrotomentosa (Basidiomycota) and cultures of Tapinella panuoides[6]
See also
References
- ↑ Burkhard Fugmann, ed. (1997), RÖMPP Lexikon Naturstoffe, 1. Auflage, 1997 (in German) (1. ed.), Stuttgart: Georg Thieme Verlag, p. 638, ISBN 3-13-749901-1
- ↑ Entry on Polyporsäure. at: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved 3. September 2019.
- ↑ Entry on Atromentin. at: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved 3. September 2019.
- ↑ Entry on Aurantiacin. at: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved 3. September 2019.
- ↑ Entry on Phlebiarubron. at: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved 3. September 2019.
- ↑ Entry on Spiromentine. at: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, retrieved 3. September 2019.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.