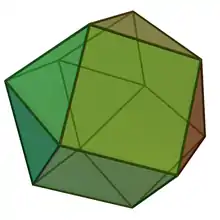
| Cuboctahedron | |
|---|---|
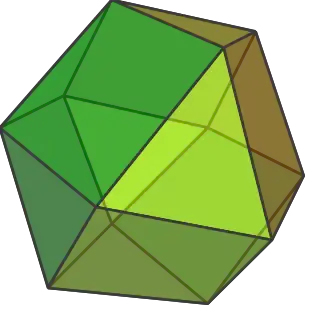 (Click here for rotating model) | |
| Type | Archimedean solid Uniform polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 14, E = 24, V = 12 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 8{3}+6{4} |
| Conway notation | aC aaT |
| Schläfli symbols | r{4,3} or rr{3,3} or |
| t1{4,3} or t0,2{3,3} | |
| Wythoff symbol | 2 | 3 4 3 3 | 2 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | Oh, B3, [4,3], (*432), order 48 Td, [3,3], (*332), order 24 |
| Rotation group | O, [4,3]+, (432), order 24 |
| Dihedral angle | |
| References | U07, C19, W11 |
| Properties | Semiregular convex quasiregular |
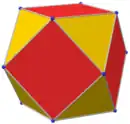 Colored faces |
 3.4.3.4 (Vertex figure) |
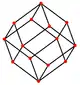
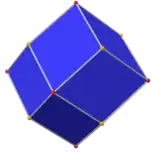 Rhombic dodecahedron (dual polyhedron) |
 Net |
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it is a quasiregular polyhedron, i.e. an Archimedean solid that is not only vertex-transitive but also edge-transitive.[1] It is radially equilateral.
Its dual polyhedron is the rhombic dodecahedron.
The cuboctahedron was probably known to Plato: Heron's Definitiones quotes Archimedes as saying that Plato knew of a solid made of 8 triangles and 6 squares.[2]
Synonyms
- Vector Equilibrium (Buckminster Fuller) because its center-to-vertex radius equals its edge length (it has radial equilateral symmetry). Fuller also called a cuboctahedron built of rigid struts and flexible vertices a jitterbug; this object can be progressively transformed into an icosahedron, octahedron, and tetrahedron by folding along the diagonals of its square sides.[3]
- With Oh symmetry, order 48, it is a rectified cube or rectified octahedron (Norman Johnson)
- With Td symmetry, order 24, it is a cantellated tetrahedron or rhombitetratetrahedron.
- With D3d symmetry, order 12, it is a triangular gyrobicupola.
Orthogonal projections
The cuboctahedron has four special orthogonal projections, centered on a vertex, an edge, and the two types of faces, triangular and square. The last two correspond to the B2 and A2 Coxeter planes. The skew projections show a square and hexagon passing through the center of the cuboctahedron.
| Square Face |
Triangular Face |
Vertex | Edge | Skew | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| [4] | [6] | [2] | [2] | ||
| Rhombic dodecahedron (Dual polyhedron) | |||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Spherical tiling
.png.webp)
The cuboctahedron can also be represented as a spherical tiling, and projected onto the plane via a stereographic projection. This projection is conformal, preserving angles but not areas or lengths. Straight lines on the sphere are projected as circular arcs on the plane.
 |
 |
 |
 |
| orthographic projection | square-centered | triangle-centered | Vertex centered |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stereographic projection | |||
Structure
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a cuboctahedron (of edge length √2) centered at the origin[4] are:
- (±1,±1,0)
- (±1,0,±1)
- (0,±1,±1)
An alternate set of coordinates can be made in 4-space, as 12 permutations of:
- (0,1,1,2)
This construction exists as one of 16 orthant facets of the cantellated 16-cell.
Root vectors
The cuboctahedron's 12 vertices can represent the root vectors of the simple Lie group A3. With the addition of 6 vertices of the octahedron, these vertices represent the 18 root vectors of the simple Lie group B3.
Metric properties
The area A and the volume V of the cuboctahedron of edge length a are:
Dissection
Tetrahedra and Octahedra
The cuboctahedron can be dissected into 6 square pyramids and 8 tetrahedra meeting at a central point. This dissection is expressed in the tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb where pairs of square pyramids are combined into octahedra.
Irregular polyhedra
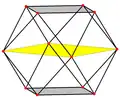
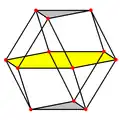
The cuboctahedron can be dissected into two triangular cupolas by a common hexagon passing through the center of the cuboctahedron.[lower-alpha 1] If these two triangular cupolas are twisted so triangles and squares line up, Johnson solid J27, the triangular orthobicupola, is created.
Geometric relations

Radial equilateral symmetry
In a cuboctahedron, the long radius (center to vertex) is the same as the edge length; thus its long diameter (vertex to opposite vertex) is 2 edge lengths. Its center is like the apical vertex of a pyramid: one edge length away from all the other vertices. (In the case of the cuboctahedron, the center is in fact the apex of 6 square and 8 triangular pyramids). This radial equilateral symmetry is a property of only a few uniform polytopes, including the two-dimensional hexagon, the three-dimensional cuboctahedron, and the four-dimensional 24-cell and 8-cell (tesseract). Radially equilateral polytopes are those which can be constructed, with their long radii, from equilateral triangles which meet at the center of the polytope, each contributing two radii and an edge. Therefore, all the interior elements which meet at the center of these polytopes have equilateral triangle inward faces, as in the dissection of the cuboctahedron into 6 square pyramids and 8 tetrahedra.
Each of these radially equilateral polytopes also occurs as cells of a characteristic space-filling tessellation: the tiling of regular hexagons, the rectified cubic honeycomb (of alternating cuboctahedra and octahedra), the 24-cell honeycomb and the tesseractic honeycomb, respectively. Each tessellation has a dual tessellation; the cell centers in a tessellation are cell vertices in its dual tessellation. The densest known regular sphere-packing in two, three and four dimensions uses the cell centers of one of these tessellations as sphere centers.
A cuboctahedron has octahedral symmetry. Its first stellation is the compound of a cube and its dual octahedron, with the vertices of the cuboctahedron located at the midpoints of the edges of either.
Constructions
A cuboctahedron can be obtained by taking an equatorial cross section of a four-dimensional 24-cell or 16-cell. A hexagon or a square can be obtained by taking an equatorial cross section of a cuboctahedron.
The cuboctahedron is a rectified cube and also a rectified octahedron.
It is also a cantellated tetrahedron. With this construction it is given the Wythoff symbol: 3 3 | 2. 
A skew cantellation of the tetrahedron produces a solid with faces parallel to those of the cuboctahedron, namely eight triangles of two sizes, and six rectangles. While its edges are unequal, this solid remains vertex-uniform: the solid has the full tetrahedral symmetry group and its vertices are equivalent under that group.
The edges of a cuboctahedron form four regular hexagons. If the cuboctahedron is cut in the plane of one of these hexagons, each half is a triangular cupola, one of the Johnson solids; the cuboctahedron itself thus can also be called a triangular gyrobicupola, the simplest of a series (other than the gyrobifastigium or "digonal gyrobicupola"). If the halves are put back together with a twist, so that triangles meet triangles and squares meet squares, the result is another Johnson solid, the triangular orthobicupola, also called an anticuboctahedron.
Both triangular bicupolae are important in sphere packing. The distance from the solid's center to its vertices is equal to its edge length. Each central sphere can have up to twelve neighbors, and in a face-centered cubic lattice these take the positions of a cuboctahedron's vertices. In a hexagonal close-packed lattice they correspond to the corners of the triangular orthobicupola. In both cases the central sphere takes the position of the solid's center.
Cuboctahedra appear as cells in three of the convex uniform honeycombs and in nine of the convex uniform 4-polytopes.
The volume of the cuboctahedron is 5/6 of that of the enclosing cube and 5/8 of that of the enclosing octahedron.
Vertex arrangement
Because it is radially equilateral, the cuboctahedron's center can be treated as a 13th canonical apical vertex, one edge length distant from the 12 ordinary vertices, as the apex of a canonical pyramid is one edge length equidistant from its other vertices.
The cuboctahedron shares its edges and vertex arrangement with two nonconvex uniform polyhedra: the cubohemioctahedron (having the square faces in common) and the octahemioctahedron (having the triangular faces in common), both have four hexagons. It also serves as a cantellated tetrahedron, as being a rectified tetratetrahedron.
 Cuboctahedron |
 its equator |
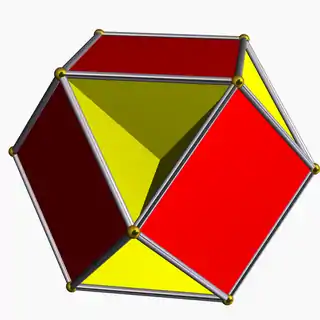 Cubohemioctahedron |
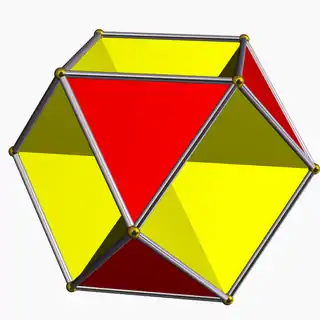 Octahemioctahedron |
The cuboctahedron 2-covers the tetrahemihexahedron,[5] which accordingly has the same abstract vertex figure (two triangles and two squares: 3.4.3.4) and half the vertices, edges, and faces. (The actual vertex figure of the tetrahemihexahedron is 3.4.3/2.4, with the a/2 factor due to the cross.)
 Cuboctahedron |
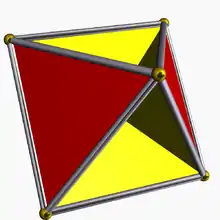 Tetrahemihexahedron |
Kinematics

When interpreted as a framework of rigid flat faces, connected along the edges by hinges, the cuboctahedron is a rigid structure, as are all convex polyhedra, by Cauchy's theorem. However, when the faces are removed, leaving only rigid edges connected by flexible joints at the vertices, the result is not a rigid system (unlike polyhedra whose faces are all triangles, to which Cauchy's theorem applies despite the missing faces).
Adding a central vertex, connected by rigid edges to all the other vertices, subdivides the cuboctahedron into square pyramids and tetrahedra, meeting at the central vertex. Unlike the cuboctahedron itself, the resulting system of edges and joints is rigid, and forms part of the infinite octet truss structure.
Related polytopes
Regular polyhedra
The cuboctahedron is one of a family of uniform polyhedra related to the cube and regular octahedron.
| Uniform octahedral polyhedra | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [4,3], (*432) | [4,3]+ (432) |
[1+,4,3] = [3,3] (*332) |
[3+,4] (3*2) | |||||||
| {4,3} | t{4,3} | r{4,3} r{31,1} |
t{3,4} t{31,1} |
{3,4} {31,1} |
rr{4,3} s2{3,4} |
tr{4,3} | sr{4,3} | h{4,3} {3,3} |
h2{4,3} t{3,3} |
s{3,4} s{31,1} |
= |
= |
= |
||||||||
| Duals to uniform polyhedra | ||||||||||
| V43 | V3.82 | V(3.4)2 | V4.62 | V34 | V3.43 | V4.6.8 | V34.4 | V33 | V3.62 | V35 |
The cuboctahedron also has tetrahedral symmetry with two colors of triangles.
| Family of uniform tetrahedral polyhedra | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [3,3], (*332) | [3,3]+, (332) | ||||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||
| {3,3} | t{3,3} | r{3,3} | t{3,3} | {3,3} | rr{3,3} | tr{3,3} | sr{3,3} |
| Duals to uniform polyhedra | |||||||
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||
| V3.3.3 | V3.6.6 | V3.3.3.3 | V3.6.6 | V3.3.3 | V3.4.3.4 | V4.6.6 | V3.3.3.3.3 |
Quasiregular polyhedra and tilings
The cuboctahedron exists in a sequence of symmetries of quasiregular polyhedra and tilings with vertex configurations (3.n)2, progressing from tilings of the sphere to the Euclidean plane and into the hyperbolic plane. With orbifold notation symmetry of *n32 all of these tilings are wythoff construction within a fundamental domain of symmetry, with generator points at the right angle corner of the domain.[6][7]
| *n32 orbifold symmetries of quasiregular tilings: (3.n)2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Construction |
Spherical | Euclidean | Hyperbolic | ||||
| *332 | *432 | *532 | *632 | *732 | *832... | *∞32 | |
| Quasiregular figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Vertex | (3.3)2 | (3.4)2 | (3.5)2 | (3.6)2 | (3.7)2 | (3.8)2 | (3.∞)2 |
| *n42 symmetry mutations of quasiregular tilings: (4.n)2 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *4n2 [n,4] |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracompact | Noncompact | |||
| *342 [3,4] |
*442 [4,4] |
*542 [5,4] |
*642 [6,4] |
*742 [7,4] |
*842 [8,4]... |
*∞42 [∞,4] |
[ni,4] | |
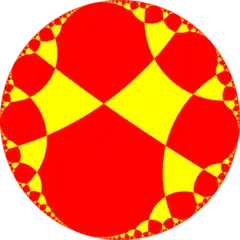
| Figures |  |
 |
 |
 |
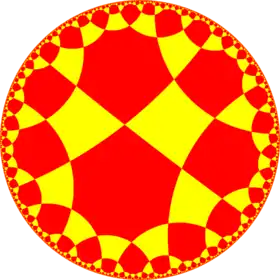 |
 |
 |
|
| Config. | (4.3)2 | (4.4)2 | (4.5)2 | (4.6)2 | (4.7)2 | (4.8)2 | (4.∞)2 | (4.ni)2 |
This polyhedron is topologically related as a part of sequence of cantellated polyhedra with vertex figure (3.4.n.4), and continues as tilings of the hyperbolic plane. These vertex-transitive figures have (*n32) reflectional symmetry.
| *n32 symmetry mutation of expanded tilings: 3.4.n.4 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry *n32 [n,3] |
Spherical | Euclid. | Compact hyperb. | Paracomp. | ||||
| *232 [2,3] |
*332 [3,3] |
*432 [4,3] |
*532 [5,3] |
*632 [6,3] |
*732 [7,3] |
*832 [8,3]... |
*∞32 [∞,3] | |
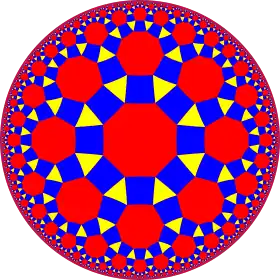
| Figure |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
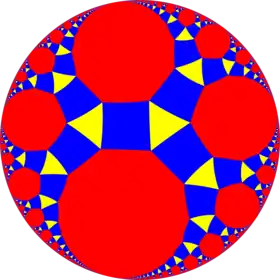 |
| Config. | 3.4.2.4 | 3.4.3.4 | 3.4.4.4 | 3.4.5.4 | 3.4.6.4 | 3.4.7.4 | 3.4.8.4 | 3.4.∞.4 |
4-dimensional polytopes
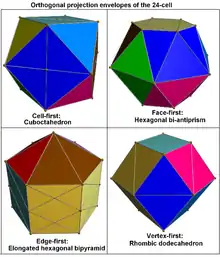
The cuboctahedron can be decomposed into a regular octahedron and eight irregular but equal octahedra in the shape of the convex hull of a cube with two opposite vertices removed. This decomposition of the cuboctahedron corresponds with the cell-first parallel projection of the 24-cell into three dimensions. Under this projection, the cuboctahedron forms the projection envelope, which can be decomposed into six square faces, a regular octahedron, and eight irregular octahedra. These elements correspond with the images of six of the octahedral cells in the 24-cell, the nearest and farthest cells from the 4D viewpoint, and the remaining eight pairs of cells, respectively.
Cuboctahedral graph
| Cuboctahedral graph | |
|---|---|
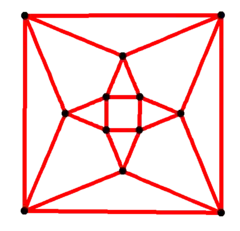 4-fold symmetry | |
| Vertices | 12 |
| Edges | 24 |
| Automorphisms | 48 |
| Properties | |
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a cuboctahedral graph is the graph of vertices and edges of the cuboctahedron, one of the Archimedean solids. It can also be constructed as the line graph of the cube. It has 12 vertices and 24 edges, is locally linear, and is a quartic Archimedean graph.[8]
 6-fold symmetry |
See also
Notes
- ↑ Notice that the cuboctahedron has four hexagonal central planes, inclined at 60° to each other. Like the hexagon, the cuboctahedron can be divided into equilateral triangles which meet at its center: it has radial equilateral symmetry.
References
- ↑ Coxeter 1973, pp. 18–19, §2.3 Quasi-regular polyhedra.
- ↑ Heath, Thomas L. (1931), "A manual of Greek mathematics", Nature, Clarendon, 128 (3235): 739–740, Bibcode:1931Natur.128..739T, doi:10.1038/128739a0, S2CID 3994109
- ↑ "Vector Equilibrium: R. Buckminster Fuller". YouTube.
- ↑ Coxeter 1973, p. 52, §3.7 Coordinates for the vertices of the regular and quasi-regular solids.
- ↑ Richter, David A., Two Models of the Real Projective Plane, archived from the original on 2016-03-03, retrieved 2010-04-15
- ↑ Coxeter 1973, pp. 86–88, §5.7 Wythoff's construction.
- ↑ Two Dimensional symmetry Mutations by Daniel Huson
- ↑ Read, R. C.; Wilson, R. J. (1998), An Atlas of Graphs, Oxford University Press, p. 269
Bibliography
- Coxeter, H.S.M. (1973) [1948]. Regular Polytopes (3rd ed.). New York: Dover.
- Ghyka, Matila (1977). The geometry of art and life ([Nachdr.] ed.). New York: Dover Publications. pp. 51–56, 81–84. ISBN 9780486235424.
- Weisstein, Eric W. (2002). "Cuboctahedron". CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics (2nd ed.). Hoboken: CRC Press. pp. 620–621. ISBN 9781420035223.
- Williams, Robert (1979). The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure: A Source Book of Design. Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-23729-X. (Section 3-9)
- Cromwell, P. Polyhedra, CUP hbk (1997), pbk. (1999). Ch.2 p. 79-86 Archimedean solids
External links
- The Uniform Polyhedra
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Cuboctahedron" ("Archimedean solid") at MathWorld.
- The Cuboctahedron on Hexnet a website devoted to hexagon mathematics.
- Klitzing, Richard. "3D convex uniform polyhedra o3x4o - co".
- Editable printable net of a Cuboctahedron with interactive 3D view