
Trinity, part of Project Manhattan, was the first ever nuclear explosion.
The nuclear weapons tests of the United States were performed from 1945 to 1992 as part of the nuclear arms race. The United States conducted around 1,054 nuclear tests by official count, including 216 atmospheric, underwater, and space tests.[1][notes 1] Most of the tests took place at the Nevada Test Site (NNSS/NTS) and the Pacific Proving Grounds in the Marshall Islands and off Kiritimati Island in the Pacific, plus three in the Atlantic Ocean. Ten other tests took place at various locations in the United States, including Alaska, Nevada other than the NNSS/NTS, Colorado, Mississippi, and New Mexico.
United States nuclear tests
| Series or years | Years covered | Tests[Summ 1] | Devices fired | Devices with un-known yield | Peace-ful use tests | Non-PTBT tests[Summ 2] | Yield range (kilotons) [Summ 3] | Total yield (kilotons) [Summ 4] | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trinity | 1945 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 21 | 21 | First nuclear weapons test, conducted as part of the Manhattan Project. Tested the Mark 3 Fat Man design. | ||
| Crossroads | 1946 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 21 | 42 | First postwar test series. | ||
| Sandstone | 1948 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 18 to 49 | 104 | The first use of "levitated" cores made of oralloy. Tested components for Mark 4 design. | ||
| Ranger | 1951 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 1 to 22 | 40 | First tests at the Nevada Test Site. Operation originally named "Operation Faust". | ||
| Greenhouse | 1951 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 46 to 225 | 398 | George shot was physics experiment relating to the hydrogen bomb; Item shot was first boosted fission weapon. | ||
| Buster-Jangle | 1951 | 7 | 7 | 7 | small to 31 | 72 | The first series in which troop maneuvers (Desert Rock exercises) were performed. | ||
| Tumbler-Snapper | 1952 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 1 to 31 | 104 | |||
| Ivy | 1952 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 500 to 10,400 | 10,900 | The "Mike" shot was the first multi-megaton thermonuclear weapon. | ||
| Upshot-Knothole | 1953 | 11 | 11 | 11 | small to 61 | 252 | 18,000 men exposed in Desert Rock V up to 26.6 REM. 84 exceeded current yearly limits of 5 REM/yr. | ||
| Castle | 1954 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 110 to 15,000 | 48,200 | Bravo shot inspired secret Project 4.1 to study fallout victims. It over-produced by 250% of expected yield, caused fallout over a wide area. | ||
| Teapot | 1955 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 1 to 43 | 167 | |||
| Wigwam | 1955 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 30 | 30 | 2,000 feet (610 m) underwater | ||
| Project 56 | 1955–1956 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0 to 0 | 0 | |||
| Redwing | 1956 | 17 | 17 | 17 | small to 5,000 | 20,820 | Test with "energy budget". Competition between UCRL and LASL over budget allocation was high. | ||
| Project 57 | 1957 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | The first safety test, asking whether an improperly ignited bomb (as in a plane crash) would cause a nuclear blast. | ||
| Plumbbob | 1957 | 29 | 29 | 25 | 0 to 74 | 345 | Included the largest atmospheric test in CONUS. | ||
| Project 58+58A | 1957 | 4 | 4 | 1 | small to 1 | 1 | Four more safety tests. | ||
| Hardtack I | 1958 | 35 | 35 | 35 | 0 to 9,300 | 35,628 | A series in the Pacific Proving Ground, including three rocket boosted high altitude tests called Operation Newsreel. | ||
| Argus | 1958 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | Also known as Operation Floral before becoming Argus for security reasons. Tested three weapons in the South Atlantic, trying to create an artificial energy belt in the magnetosphere. | ||
| Hardtack II | 1958 | 37 | 37 | 24 | 0 to 22 | 46 | Meant to squeeze all possible testing into the time before Eisenhower's test ban started on 30 October 1958. Planned as "Operation Millrace", changed to HT II when a science panel recommended to "stop testing after the Hardtack series." | ||
| Nougat | 1961–1962 | 44 | 44 | 1 | 2 | small to 67 | 357 | First all-underground test series. Included first Operation Plowshare shot "Gnome" in Carlsbad, New Mexico, which was detonated in an underground salt dome. | |
| Sunbeam | 1962 | 4 | 4 | 4 | small to 2 | 2 | Aka Operation Dominic II. Test of small tactical warheads, including the man-portable "Davy Crockett". Last atmospheric test series. The Army's part of Sunbeam was Operation Ivy Flats. | ||
| Dominic | 1962–1963 | 31 | 31 | 31 | 2 to 8,300 | 34,640 | "Frigate Bird" was the only operational test of a missile "mated" with a live warhead. Series also included three high-altitude tests known as Operation Fishbowl, separated out in this text. | ||
| Fishbowl | 1962 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 9 | 400 to 1,400 | 2,205 | The high altitude rocket part of Operation Dominic. Included several failed tests as the rockets failed for various reasons. | |
| Storax | 1962–1963 | 47 | 47 | 3 | 1 | 1 to 115 | 585 | ||
| Roller Coaster | 1963 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | Storage-transportation safety experiments, measured plutonium dispersal risk. | ||
| Niblick | 1963–1964 | 41 | 43 | 4 | small to 249 | 698 | |||
| Whetstone | 1964–1965 | 46 | 49 | 4 | 1 | small to 51 | 476 | ||
| Flintlock | 1965–1966 | 47 | 49 | 2 | small to 365 | 1,891 | |||
| Latchkey | 1966–1967 | 38 | 38 | 3 | small to 870 | 1,831 | |||
| Crosstie | 1967–1968 | 48 | 57 | 5 | 4 | 2 | small to 1,300 | 3,638 | |
| Bowline | 1968–1969 | 47 | 58 | 2 | 1 | small to 1,150 | 2,152 | ||
| Mandrel | 1969–70 | 52 | 78 | 1 | 2 | small to 1,900 | 5,528 | ||
| Emery | 1970–1971 | 16 | 24 | 2 | small to 220 | 565 | |||
| Grommet | 1971–1972 | 34 | 39 | 1 | small to 4,800 | 5,200 | Included Cannikin, the largest underground explosion ever at 5 Mt, fired under the Aleutian island Amchitka. | ||
| Toggle | 1972–1973 | 28 | 35 | 1 | small to 250 | 958 | |||
| Arbor | 1973–1974 | 18 | 20 | small to 150 | 274 | ||||
| Bedrock | 1974–1975 | 27 | 29 | small to 750 | 2,840 | ||||
| Anvil | 1975–1976 | 21 | 21 | 0 to 1,000 | 5,993 | ||||
| Fulcrum | 1976–1977 | 21 | 24 | small to 140 | 635 | ||||
| Cresset | 1977–1978 | 22 | 23 | 0 to 150 | 1,122 | ||||
| Quicksilver | 1978–1979 | 16 | 16 | 1 to 140 | 717 | ||||
| Tinderbox | 1979–1980 | 14 | 14 | 1 to 140 | 452 | ||||
| Guardian | 1980–1981 | 14 | 14 | 1 to 140 | 322 | ||||
| Praetorian | 1981–1982 | 19 | 20 | 1 to 140 | 938 | ||||
| Phalanx | 1982–1983 | 18 | 19 | 1 to 143 | 365 | ||||
| Fusileer | 1983–1984 | 16 | 16 | small to 150 | 521 | ||||
| Grenadier | 1984–1985 | 16 | 16 | 3 to 150 | 670 | ||||
| Charioteer | 1985–1986 | 16 | 16 | small to 140 | 549 | ||||
| Musketeer | 1986–1987 | 14 | 16 | 3 to 150 | 970 | ||||
| Touchstone | 1987–1988 | 13 | 15 | 2 to 150 | 696 | ||||
| Cornerstone | 1988–1989 | 11 | 17 | 1 to 150 | 436 | ||||
| Aqueduct | 1989–1990 | 10 | 13 | small to 150 | 426 | ||||
| Sculpin | 1990–1991 | 7 | 9 | 2 to 140 | 478 | ||||
| Julin | 1991–1992 | 7 | 9 | small to 100 | 172 | The last test series, cut off by the negotiation of the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty. | |||
| Totals | 1945-Jul-16 to 1992-Sep-23 | 1032 | 1132 | 12 | 27 | 231 | 0 to 15,000 | 196,552 | Total country yield is 36.3% of all nuclear testing. |
- ↑ Includes all tests with potential for nuclear fission or fusion explosion, including combat use, singleton tests, salvo tests, zero yield fails, safety experiments, and bombs incapacitated by accidents but still intended to be fired. It does not include hydronuclear and subcritical tests, and misfires of a device which was subsequently fired successfully.
- ↑ Number of tests which would have been in violation of the Partial Test Ban Treaty of 1963, such as atmospheric, space or underwater tests. Some "peaceful use" cratering tests which should have been violations were protested, and later quietly dropped.
- ↑ "Small" refers to a value greater than zero but less than 0.5 kt.
- ↑ Some yields are described like "< 20 kt"; such are scored at one half of the numeric amount, i.e., yield of 10k in this example. "Unknown yield" adds nothing to the total.
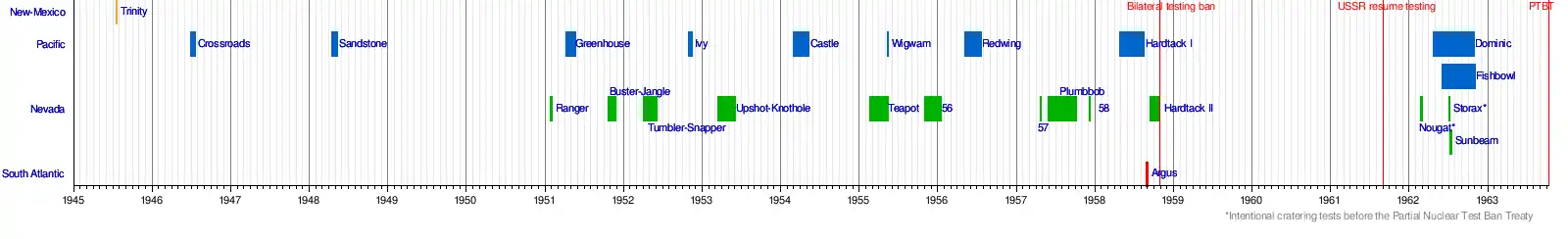
Timeline
Graphical timeline of United States atmospheric nuclear weapons tests. [2]
Notes
- ↑ Discrepancies with the table include 24 tests actually carried out by the United Kingdom at the NTS; four aborted tests in Operation Fishbowl; one test, Anvil/Peninsula, that jammed during lowering in its shaft and was abandoned; and five salvo tests listed as two enumerated tests each because they were treated that way when eventually described to the public, rather than standing on the treaty definition of a salvo test.
References
- ↑ "United States Nuclear Tests: July 1945 through September 1992" (PDF) (DOE/NV-209 REV15). Las Vegas, NV: Department of Energy, Nevada Operations Office. 2000-12-01. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-10-12. Retrieved 2013-12-18.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ United States Nuclear Tests: July 1945 through September 1992 (PDF) (Report). Las Vegas, NV: Department of Energy, Nevada Operations Office. 2000-12-01. DOE/NV-209 REV15. Retrieved 2019-05-05.
Sources
- Yang, Xiaoping; North, Robert; Romney, Carl (August 2000). "CMR Nuclear Explosion Database (Revision 3)". SMDC Monitoring Research.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Andryushi, LA; Voloshin, N.P.; Ilkaev, R.I.; Matushchenko, A.M.; Ryabev, L.D.; Strukov, V.G.; Chernyshev, A.K.; Yudin, Yu.A. Mikhailov, V.N. (ed.). "Catalog of Worldwide Nuclear Testing". Archived from the original on 2013-12-19. Retrieved 2013-03-04.
- Wm Robert Johnston, PhD. "Johnston Archive of Nuclear Weapons". Retrieved 2013-12-31.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.