| Gene therapy | |
|---|---|
| Target gene | Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase |
| Clinical data | |
| Other names | PTC-AADC |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| DrugBank | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
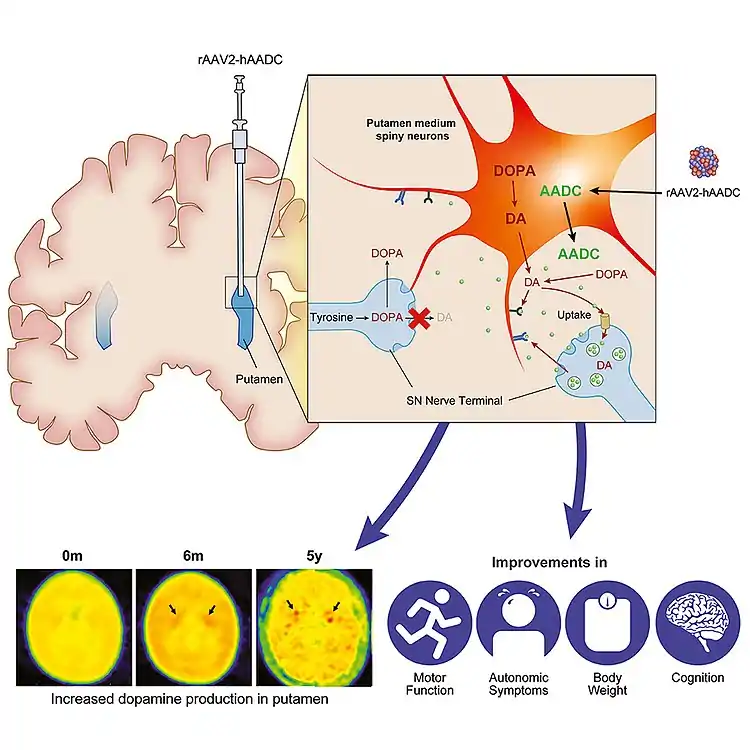
Eladocagene exuparvovec, sold under the brand name Upstaza, is a gene therapy product for the treatment of aromatic L‑amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency.[1][2][3] It infuses the gene encoding for the human AADC enzyme into the putamen region of the brain.[1][2] The subsequent expression of AADC results in dopamine production and, as a result, development of motor function in patients with AADC deficiency.[1]
The most common side effects include initial insomnia, irritability and dyskinesia.[1]
Eladocagene exuparvovec was approved for medical use in the European Union in July 2022.[1]
Medical uses
Eladocagene exuparvovec is indicated for the treatment of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency.[1]
Society and culture
Eladocagene exuparvovec is the international nonproprietary name (INN).[4]
Legal status
On 19 May 2022, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization under exceptional circumstances for the medicinal product Upstaza, intended for the treatment of aromatic L‑amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) deficiency.[5][6] As Upstaza is an advanced therapy medicinal product, the CHMP positive opinion is based on an assessment by the Committee for Advanced Therapies.[5] The applicant for this medicinal product is PTC Therapeutics International Limited.[5] Eladocagene exuparvovec was approved for medical use in the European Union in July 2022.[1][7]
Figures
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Upstaza EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 13 April 2022. Retrieved 3 March 2023. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- 1 2 "Eladocagene exuparvovec for aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency". National Institute for Health and Care Research. 13 January 2022. Retrieved 22 May 2022.
- ↑ "PTC Therapeutics Announces Results from Long-Term AADC Deficiency Gene Therapy Treatment Demonstrating Sustained Improvements". PTC Therapeutics (Press release). 24 October 2019. Retrieved 22 May 2022.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2019). "International nonproprietary names for pharmaceutical substances (INN): recommended INN: list 81". WHO Drug Information. 33 (1). hdl:10665/330896.
- 1 2 3 "Upstaza: Pending EC decision". European Medicines Agency. 19 May 2022. Archived from the original on 25 May 2022. Retrieved 22 May 2022. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ↑ "PTC Therapeutics Receives Positive CHMP Opinion for Upstaza for the Treatment of AADC Deficiency". PTC Therapeutics (Press release). 20 May 2022. Retrieved 22 May 2022.
- ↑ "Upstaza Product information". Union Register of medicinal products. Retrieved 3 March 2023.
- ↑ Tai CH, Lee NC, Chien YH, Byrne BJ, Muramatsu SI, Tseng SH, Hwu WL (February 2022). "Long-term efficacy and safety of eladocagene exuparvovec in patients with AADC deficiency". Molecular Therapy. 30 (2): 509–518. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.11.005. PMC 8822132. PMID 34763085.
Further reading
- Tai CH, Lee NC, Chien YH, Byrne BJ, Muramatsu SI, Tseng SH, et al. (February 2022). "Long-term efficacy and safety of eladocagene exuparvovec in patients with AADC deficiency". Mol Ther. 30 (2): 509–518. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.11.005. PMC 8822132. PMID 34763085.
External links
- "Eladocagene exuparvovec". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.