| Braunig Lake | |
|---|---|
 | |
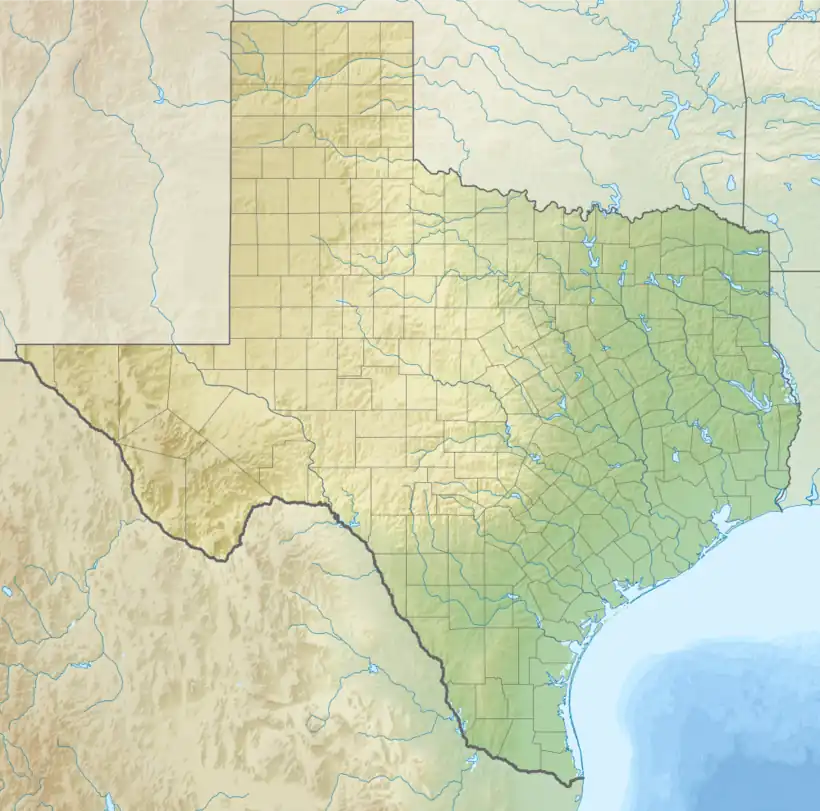 Braunig Lake  Braunig Lake | |
| Location | San Antonio, Texas |
| Coordinates | 29°15.16′N 98°22.58′W / 29.25267°N 98.37633°W |
| Type | Power plant cooling reservoir |
| Primary inflows | Calaveras Creek and Chupaderas Creek |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Surface area | 1,350 acres (550 ha) |
| Max. depth | 50 ft (15 m) |
| Water volume | 26,500 acre⋅ft (0.0327 km3) |
| Surface elevation | 506 ft (154 m) |
Victor Braunig Lake, formerly known as East Lake, is a reservoir on Calaveras Creek and Chupaderas Creek 17 miles (27 kilometres) south of Downtown San Antonio, Texas, USA. The reservoir was formed in 1962 by the construction of a dam to provide a cooling pond for a power plant to supply additional electrical supply to the city of San Antonio. Victor Braunig (1890-1982) was an employee from 1910 becoming in 1949 the general manager of the San Antonio City Public Service Board, the predecessor of CPS Energy. The dam and lake are managed by CPS Energy of San Antonio. Together with Calaveras Lake, Braunig Lake was one of the first projects in the nation to use treated wastewater for power plant cooling. The reservoir is partly filled with wastewater that has undergone both primary and secondary treatment at a San Antonio Water System treatment plant. Braunig Lake also serves as a venue for recreation, including fishing and boating.
Fish and plant life
Braunig Lake has been stocked with species of fish intended to improve the utility of the reservoir for recreational fishing. Fish present in Braunig Lake include red drum, hybrid striped bass, catfish, and largemouth bass.
Recreational uses
Thousand Trails Management Services operates a public park facility at the lake. The park features facilities for camping, picknicking, fishing, boating, and hiking. Swimming is prohibited.
See also
References
External links
- Braunig Lake - Texas Parks & Wildlife
- Braunig Lake Park
- Victor Braunig Lake from the Handbook of Texas Online