| Bergstraße-Odenwald | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Location | Odenwald |
| Coordinates | 49°41′39″N 9°10′31″E / 49.69410°N 9.17526°E |
| Designation | NP-00001 |
| Established | 1960 |
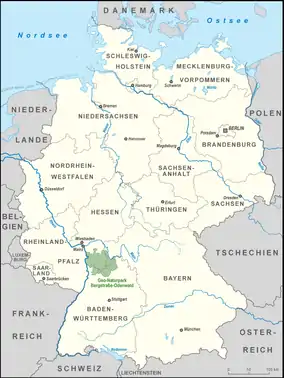
The Bergstraße-Odenwald Nature Park (German: Geo-Naturpark Bergstraße-Odenwald) is a nature park in southern Germany with an area of 3,500 km² that lies between the rivers Rhine, Main (river) and Neckar. In the south it overlaps in places with the Neckar Valley-Odenwald Nature Park on the territory of Baden-Württemberg. In the east it meets the Bavarian Spessart Nature Park at the River Main. The nature park covers parts of the states of Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria and Hesse.
Sights
- Messel Pit,
- Lorsch Abbey,
- Kühkopf-Knoblochsaue, Stockstadt am Rhein
- Odenwald Limes
- Felsenmeer near Reichenbach, Lautertal (Odenwald)
- Obrunn Gorge between Höchst im Odenwald and Rimhorn
- Heidelberg and Heidelberg Castle
- Lösswand von Haarlass in Heidelberg, the first scientific description of which by Karl Cäsar von Leonhard in 1824 led to the introduction of the term loess
- Katzenbuckel – at 626 metres, the highest point in the Odenwald
- Odenwald Open Air Museum in Walldürn-Gottersdorf
- Eberstadt Stalactite Cave near Buchen (Odenwald)
- Bergstraße Nature Conservation Centre near Bensheim
- Marie in der Kohlbach Pit, a visitor mine, near Hohensachsen
- Anna Elisabeth Pit, another visitor mine, near Schriesheim
Gallery
.jpg.webp) Autumn in Ober-Hambach. |
 Blossoming trees in Alt-Lechtern. |
 Beerfelden bike park. |
 Winter in Lindenfels. |
 Heppenheim. |
 Hiking in the Dürr-Ellenbacher valley, Wald-Michelbach. |
 Eberbach castle. |
See also
References
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bergstraße-Odenwald Nature Park.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.



