 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CeSe | |
| Appearance | purple solid[1] |
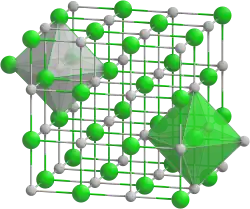
| Structure | |
| NaCl-type (cubic) | |
| Fm3m (No. 225) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Cerium monosulfide Cerium monotelluride |
Related compounds |
Cerium selenide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Cerium monoselenide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CeSe. It exists in the form of Ce3+Se2−(e−).[2]
Preparation
Cerium monoselenide can be obtained by reducing cerium selenide with metallic sodium at 600 °C (or calcium at 1000 °C):[2]
- Ce2Se3 + 2Na → 2CeSe + Na2Se
The reduction of cerium selenide by cerium dihydride can also produce cerium monoselenide:[1]
- Ce2Se3 + CeH2 → 3 CeSe + H2↑
Properties
Like many other rare earth monochalcogenides, Cerium monoselenide has metallic-type electrical conductivity and a NaCl-type crystal structure.[3]
References
- 1 2 Obolonchik, V. A.; Mikhlina, T. M. Synthesis of rare earth metal monoselenides(in Russian). Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR, Neorganicheskie Materialy, 1968. 4(2): 287-8. ISSN:0002-337X
- 1 2 洪广言. 现代化学基础丛书 第36卷 稀土化学导论. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014. pp. 62-63. 2. 稀土硒化物 ISBN 978-7-03-040581-4
- ↑ Smolensky, G. A.; Adamjan, V. E.; Loginov, G. M. (1968-02-01). "Antiferromagnetic Properties of Light Rare Earth Monochalcogenides". Journal of Applied Physics. AIP Publishing. 39 (2): 786–790. doi:10.1063/1.2163619. ISSN 0021-8979.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.