| Provincial cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo | |
|---|---|
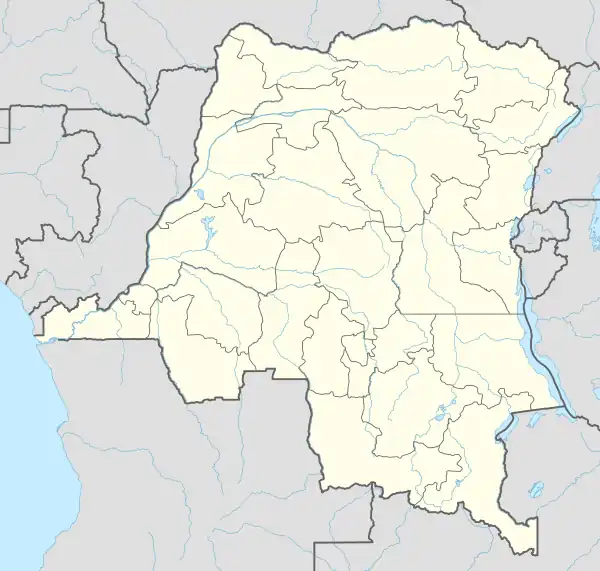 Boma Matadi Kenge Bandundu Kikwit Tshikapa Kananga Mbuji-Mayi Lusambo Kabinda Mwene-Ditu Kamina Kolwezi Lubumbashi Likasi Kalemie Kindu Bukavu Goma Butembo Beni Bunia Inongo Mbandaka Boende Kisangani Lisala Gemena Zongo Gbadolite Buta Isiro Cities marked in red are provincial capitals (Note: click mark for city article) | |
| Category | 2nd-level administrative division of a unitary state |
| Location | DR Congo |
| Found in | Province |
| Number | 32 (as of 2018) |
| Additional status |
|
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |
The cities of the Democratic Republic of the Congo are administrative divisions of provinces with the exception of Kinshasa which itself has the status of a province. Cities are further divided into communes. They are led by mayors except for Kinshasa which is led by a governor.
Provincial cities
The 25 provinces of DR Congo are divided into 32 cities (fr. villes, sing. ville) and 145 territories (fr. territoires, sing. territoire).[1] Each provincial division is also a constituency of the National Assembly as well as of the Provincial Assembly of its province.[2]
Each city is led by a mayor (fr. maire) and is further divided into communes with each commune led by a burgomaster (fr. bourgmestre).[3] Currently mayors, burgomasters, and their deputies are appointed by the government.[4] Elections to bring about elected local government are scheduled for December 2023—May 2024.
All provincial capitals are, by organic law, cities and do not need to meet the requirement of having a population of at least 100,000.[5]
Kinshasa
The capital city of Kinshasa is a one of a kind administrative division due to article 2 of the Constitution which makes it a division of the country and gives it the status of a province.[6] In practice this means that—like a province—it has a provincial government with an elected governor and an Assembly, but—like a city—it is divided into communes led by burgomasters.[7] Uniquely, its 24 communes are also Provincial Assembly constituencies and are grouped into four National Assembly constituencies.[8]
List of cities
.svg.png.webp) |
|---|
| United Nations Mission |
|
|
Due to the lack of reliable and comparable population figures, electoral districts are allocated seats in proportion to their voter registration numbers. The number of seats allocated to a city in the National Assembly and the Provincial Assembly is one measure of its relative political importance nationally and within its province respectively.
In 2018 cities accounted for 27% of the electorate, or 16% when Kinshasa is excluded.[10]
Cities in the making
In mid-2018, just before the general election, the government upheld the granting of city status to 66 other populated places.[11] It was further decided to make these cities operational in stages.[12] Since then the following ones have had their first mayor appointed and take office:
| Name | Province | # of Com. | Mayor | Coordinates | Pre-2015 Province |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baraka | South Kivu | 3 | Jacques Mmbucwa[13] | 4°06′15″S 29°05′38″E / 4.1041°S 29.094°E | South Kivu |
| Kamituga | South Kivu | 2 | Alexandre Bundya[13] | 3°04′S 28°11′E / 3.06°S 28.18°E | South Kivu |
| Kasaji | Lualaba | 3 | Georges Kazadi[14] | 10°22′00″S 23°27′00″E / 10.3667°S 23.45°E | Katanga |
| Kasumbalesa | Haut Katanga | 3 | André Kapamba[15] | 12°15′23″S 27°48′10″E / 12.2564°S 27.8028°E | Katanga |
| Lumumbaville (Wembo Nyama) | Sankuru | 2 | Micheline Ayaki[16] | 4°07′56″S 24°30′33″E / 4.1321°S 24.5091°E | Kasaï-Oriental (old) |
| Tshimbulu | Kasaï-Central | 3 | Marcel Mutamba[17] | 6°29′S 22°51′E / 6.48°S 22.85°E | Kasaï Occidental |
| Uvira | South Kivu | 3 | Kiza Muhato[13] | 3°24′16″S 29°08′16″E / 3.4044°S 29.1379°E | South Kivu |
See Also
Notes and references
- ↑ Organic Law No. 08/016, Articles 3–4.
- ↑ Annex I, p. 3; Annex II, p. 14.
- ↑ Organic Law No. 08/016, Articles 41,3,60.
- ↑ Radio Okapi 27 Nov 2022.
- ↑ Organic Law No. 08/016, Article 6.
- ↑ Constitution, Article 2.
- ↑ ADIAC 29 Dec 2022.
- ↑ Annex II, pp. 14, 15; Annex I, pp. 3, 4–5.
- ↑ Annex I, I.4, pp. 8–13; Annex II, II.4, pp. 19–24; Annex III, III.2, pp. 25–37.
- ↑ The total 2018 electorate was 40,371,439 as stated in Annex I.3 p. 7.
- ↑ Digital Congo 25 Jul 2018; Décret n° 18/020; Journal Officiel 20 Jun 2013, Décret n° 13/020–13/030 du 13 juin 2013.
- ↑ Arrêté Interministeriel n° 25/.../2018.
- 1 2 3 La Prunelle RDC 25 Feb 2019.
- ↑ Lualaba ma province 26 Nov 2022.
- ↑ Nzadi News 7 Mar 2019.
- ↑ Provinces 26 RDC 16 Feb 2022.
- ↑ Arrêté Provincial n°01/.../057/2019; 7sur7.cd 17 Sept 2022.
Cited Works
- "Constitution de la Republique Democratique du Congo" [The Constitution of the Democratic Republic of the Congo] (PDF). LEGANET.CD (in French). 20 January 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 February 2019. Retrieved 11 Jan 2020.
- "Loi organique n° 08/016 du 07 octobre 2008 portant composition, organisation et fonctionnement des Entités Territoriales Décentralisées et leurs rapports avec l'Etat et les Provinces" [Organic Law No. 08/016 of 7 October 2008 on the composition, organization and functioning of the Decentralized Territorial Entities and their relations with the State and the Provinces]. LEGANET.CD (in French). Archived from the original on 21 February 2019. Retrieved 11 Jan 2020.
- "Annexe I : De la repartition des sieges pour l'election des deputes nationaux" [Annex I: On the Distribution of Seats for the Election of National Deputies]. Annexes a la loi portant adoption de la repartition des sieges par circonscription electorale pour les elections legislatives (PDF) (in French). CENI. pp. 3–13. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2018. Retrieved 10 May 2019.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help)
- "Annexe II: De la repartition des sieges pour l'election des deputes provinciaux" [Annex II: On the Distribution of Seats for the Election of Provincial Deputies]. Annexes a la loi portant adoption de la repartition des sieges par circonscription electorale pour les elections legislatives (PDF) (in French). CENI. pp. 14–24. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2018. Retrieved 10 May 2019.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help)
- "Annexe III: De la repartition des sieges pour l'election des conseillers municipaux" [Annex III: On the Distribution of Seats for the Election of Commune Councilors]. Annexes a la loi portant adoption de la repartition des sieges par circonscription electorale pour les elections legislatives (PDF) (in French). CENI. pp. 25–37. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2018. Retrieved 10 May 2019.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help)
- Journal officiel de la République Démocratique du Congo (PDF) (in French) (Special ed.). 20 June 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 January 2020. Retrieved 12 Jan 2020.
- "Décret n° 18/020 du 30 mai 2018" (PDF). Journal officiel de la République Démocratique du Congo (in French). 59 (13). col 13-14. 1 July 2019. Retrieved 22 Jan 2020.
- "Arrêté Interministeriel n° 25/CAB/VPM/MININTERSEC/HMS/081/2018 & n° CAB/ME/MIN.DRI/ARN/FKT/007/2018 du 30 Mai 2018" (PDF). www.lualaba.gouv.cd (in French). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 September 2019. Retrieved 22 Jan 2020.
- "Arrêté Provincial n°01/14/CAB/G.P/K.C/MKM/057/2019 du 05 Septembre 2019". Arretes-du-Gouverneur-Kabuya-portant-nomination-titre-interimaire_Maires-Maires-adjoints-Administrateurs-des-territoires.pdf (PDF) (in French). Congo Research Group. 2019. pp. 2–3. Retrieved 13 April 2023.
- Le Potentiel (25 July 2018). "Décentralisation : les autorités traditionnelles de la RDC en colère contre le Premier ministre". Digital Congo (in French). MMC. Archived from the original on 25 July 2018. Retrieved 25 Jan 2020.
- Jean-Luc M. (25 February 2019). "Sud-Kivu : les maires des nouvelles villes d'Uvira et Kamituga installés ce week-end, celui de Baraka ce lundi". La Prunelle RDC (in French). Archived from the original on 28 June 2022. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- "Territoriale-Kasumbalesa : André Kapamba premier maire de la nouvelle ville". Nzadi News (in French). 7 March 2019. Archived from the original on 12 February 2020. Retrieved 15 Feb 2020.
- "RDC : Le Président Félix Tshisekedi dote la mairie de Lumumbaville de matériels de travail". Provinces 26 RDC (in French). 16 February 2022. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- Lumwanga, Stanislas (26 Nov 2022). "Territoriales 2022 : Georges Kazadi et Nana Nseya, deux serviteurs du développement de Kasaji au front". Lualaba ma province (in French). Retrieved 9 April 2023.
- Makoba, Alain Saveur (17 September 2022). "Kasaï-Central : La ville de Tshimbulu menacée de disparition par plus de 25 têtes d'érosions (Société civile)". 7sur7.cd (in French). Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- "RDC : nomination de nouveaux acteurs de la petite territoriale". Radio Okapi (in French). 27 November 2022. Retrieved 8 April 2023.
- Dianzenza, Lucien (29 Dec 2022). "Kinshasa : le gouverneur Ngobila rencontre les nouveaux bourgmestres" (in French). Agence d’information d’Afrique Centrale (ADIAC). Retrieved 9 April 2023.