 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
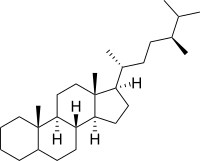
| IUPAC name
Ergostane | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3aS,3bR,5aΞ,9aS,9bS,11aR)-1-[(2R,5S)-5,6-Dimethylheptan-2-yl]-9a,11a-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H50 | |
| Molar mass | 386.708 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Ergostane is a tetracyclic triterpene, also known as 24S-methylcholestane. The compound itself has no known uses; however various functionalized analogues are produced by plants and animals. The most important of these are the heavily derivatised withanolides.[1][2] However simpler forms do exist, such as the sterane campestane (24R-methylcholestane). Along with cholestane and stigmastane, this sterane is used as a biomarker for early eukaryotes.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Glotter, E. (1991). "Withanolides and related ergostane-type steroids". Natural Product Reports. 8 (4): 415–40. doi:10.1039/np9910800415. ISSN 0265-0568. PMID 1787922.
- ↑ Kirson, Isaac; Glotter, Erwin (1981). "Recent Developments in Naturally Occurring Ergostane-Type Steroids. A Review". Journal of Natural Products. 44 (6): 633–647. doi:10.1021/np50018a001. ISSN 0163-3864.
- ↑ Brocks, Jochen J.; Jarrett, Amber J. M.; Sirantoine, Eva; Hallmann, Christian; Hoshino, Yosuke; Liyanage, Tharika (2017). "The rise of algae in Cryogenian oceans and the emergence of animals". Nature. 548 (7669): 578–581. Bibcode:2017Natur.548..578B. doi:10.1038/nature23457. PMID 28813409. S2CID 205258987.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.