 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hydroxypropanedial | |
| Other names
Hydroxymalonaldehyde 2-Hydroxypropanedial Reductone Tartronaldehyde 2-Hydroxymalonaldehyde 2-Hydroxymalondialdehyde Glucose-reductone Tartronal Tartronic aldehyde Triose reductone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4O3 | |
| Molar mass | 88.062 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.38 g/mL |
| Melting point | 149 °C (300 °F; 422 K) (decomposes)[1] |
| Boiling point | 274 °C (525 °F; 547 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkenals |
4-Hydroxynonenal |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Glucic acid is an acid produced by the action of acids on cane-sugar or of alkalis on glucose.
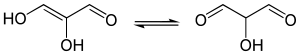 Tautomeric forms of glucic acid
Tautomeric forms of glucic acid
References
- ↑ Holker, J. R. (1955). "Oxidation of Some Enediols with Selenium Dioxide". J. Chem. Soc.: 579–580. doi:10.1039/JR9550000574.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.