 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
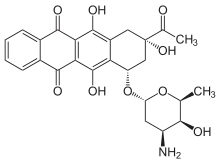
| Other names | 9-acetyl-7-(4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydropyran-2-yl)oxy-6,9,11-trihydroxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-dione |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a691004 |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 97% |
| Elimination half-life | 22 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H27NO9 |
| Molar mass | 497.500 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Idarubicin /ˌaɪdəˈruːbɪsɪn/ or 4-demethoxydaunorubicin is an anthracycline antileukemic drug. It inserts[1] itself into DNA and prevents DNA unwinding by interfering with the enzyme topoisomerase II. It is an analog of daunorubicin, but the absence of a methoxy group increases its fat solubility and cellular uptake.[2] Similar to other anthracyclines, it also induces histone eviction from chromatin.[3]
It belongs to the family of drugs called antitumor antibiotics.
It is currently combined with cytosine arabinoside as a first line treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.[4]
It is used for treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast crisis.[5]
It is distributed under the trade names Zavedos (UK) and Idamycin (USA).
Side effects
Diarrhea, stomach cramps, nausea and vomiting are common among patients treated with idarubicin.[6]
References
- ↑ Miller JP, Stoodley RJ (2013). "Studies directed towards anthracyclinone syntheses: The use of d-glucose as a chiral auxiliary in asymmetric Diels–Alder reactions". J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 17: 29–42. doi:10.1016/j.jscs.2011.02.019.
- ↑ "Idamycin Package insert" (PDF). Pfizer. January 2006.
- ↑ Pang B, Qiao X, Janssen L, Velds A, Groothuis T, Kerkhoven R, et al. (2013). "Drug-induced histone eviction from open chromatin contributes to the chemotherapeutic effects of doxorubicin". Nature Communications. 4: 1908. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4.1908P. doi:10.1038/ncomms2921. PMC 3674280. PMID 23715267.
- ↑ Arwanih EY, Louisa M, Rinaldi I, Wanandi SI (December 2022). "Resistance Mechanism of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells Against Daunorubicin and Cytarabine: A Literature Review". Cureus. 14 (12): e33165. doi:10.7759/cureus.33165. PMC 9885730. PMID 36726936.
- ↑ Katzung BG (2017-11-30). Basic & clinical pharmacology. McGraw-Hill Education. ISBN 9781259641152. OCLC 1009849139.
- ↑ "Idarubicin Side Effects: Common, Severe, Long Term". Drugs.com. Retrieved 2019-06-21.
External links
- Idarubicin bound to proteins in the PDB