 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
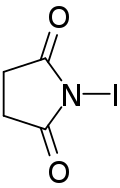
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Iodopyrrolidine-2,5-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 113917 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.475 |
| EC Number |
|
| 122896 | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4INO2 | |
| Molar mass | 224.985 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 2.245 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 202–206 °C (396–403 °F; 475–479 K)(dec.) [1] |
| Soluble in Dioxane, THF, MeCN; Insoluble in ether, CCl4 | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
N-Iodosuccinimide (NIS) is a reagent used in organic chemistry for the iodination of alkenes and as a mild oxidant.[2][3]
NIS is the iodine analog of N-chlorosuccinimide (NCS) and N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) which are used for similar applications.
References
- ↑ "N-Iodosuccinimide". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ↑ Scott C. Virgil; Zeng, Ying; Kong, Fanzuo; Pigza, Julie A. (2001). "N-Iodosuccinimide". E-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.ri038.pub3. ISBN 0471936235.
- ↑ "N-Iodosuccinimide - Huateng Pharma".
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.