 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cyclohexa-1,2,3-triene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H6 | |
| Molar mass | 78.114 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
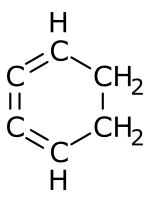
1,2,3-Cyclohexatriene is an unstable chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6.[1] It is an unusual isomer of benzene in which the three double bonds are cumulated.
In 1990, 1,2,3-cyclohexatriene was first prepared by reacting a cyclohexadiene derivative with cesium fluoride.[2] The product was too reactive to be isolated on its own, so its existence was confirmed by trapping via a cycloaddition reaction.
 Preparation and trapping of 1,2,3-cyclohexatriene reaction
Preparation and trapping of 1,2,3-cyclohexatriene reaction
1,2,3-Cyclohexatriene and its derivatives undergo a variety of reactions including cycloadditions, nucleophilic additions, and σ-bond insertions,[3] and therefore they can be versatile reagents for organic synthesis.[4]
References
- ↑ "Benzene's forgotten isomer takes centre stage in organic synthesis". May 2, 2023.
- ↑ Shakespeare, William C.; Johnson, Richard P. (1990). "1,2,3-cyclohexatriene and cyclohexen-3-yne: Two new highly strained C6H6 isomers". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 112 (23): 8578–8579. doi:10.1021/ja00179a050.
- ↑ Kelleghan, Andrew V.; Bulger, Ana S.; Witkowski, Dominick C.; Garg, Neil K. (2023). "Strain-promoted reactions of 1,2,3-cyclohexatriene and its derivatives". Nature. 618 (7966): 748–754. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06075-8. PMC 10460091. PMID 37075803. S2CID 258237506.
- ↑ "A fresh look at 1,2,3-cyclohexatriene shows it could be used as a versatile reagent in organic synthesis". May 3, 2023.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.