 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N′-Diphenylurea | |
| Other names
1,3-Diphenylurea; Diphenylurea; carbanilide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 782650 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.731 |
| EC Number |
|
| 143821 | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H12N2O | |
| Molar mass | 212.252 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 239–241 °C (462–466 °F; 512–514 K) |
| Boiling point | 262 °C (504 °F; 535 K) |
| -127.5·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H332 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P312, P322, P330, P363, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
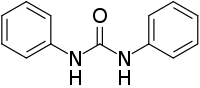
1,3-Diphenylurea is a phenylurea-type compound with the formula (PhNH)2CO (Ph = C6H5). It is a colorless solid that is prepared by transamidation of urea with aniline.
DPU is a cytokinin, a type of plant hormone that induces flower development. It occurs in coconut milk.[1] The cytokinin effect of DPU is relatively low, but other more potent phenylurea-type cytokinins have been reported.[2]
References
- ↑ Shantz, E. M.; Steward, F. C. (1955). "The Identification of Compound A from Coconut Milk as 1,3-Diphenylurea". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 77 (23): 6351. doi:10.1021/ja01628a079.
- ↑ Effect of cytokinin-active phenylurea derivatives on shoot multiplication. T. Genkov and I. Ivanova, Bulg. J. Plant Physiol., 1995, 21(1), pages 73–83 (link to article at researchgate)
External links
 The dictionary definition of Diphenylurea at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of Diphenylurea at Wiktionary
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.